Abstract
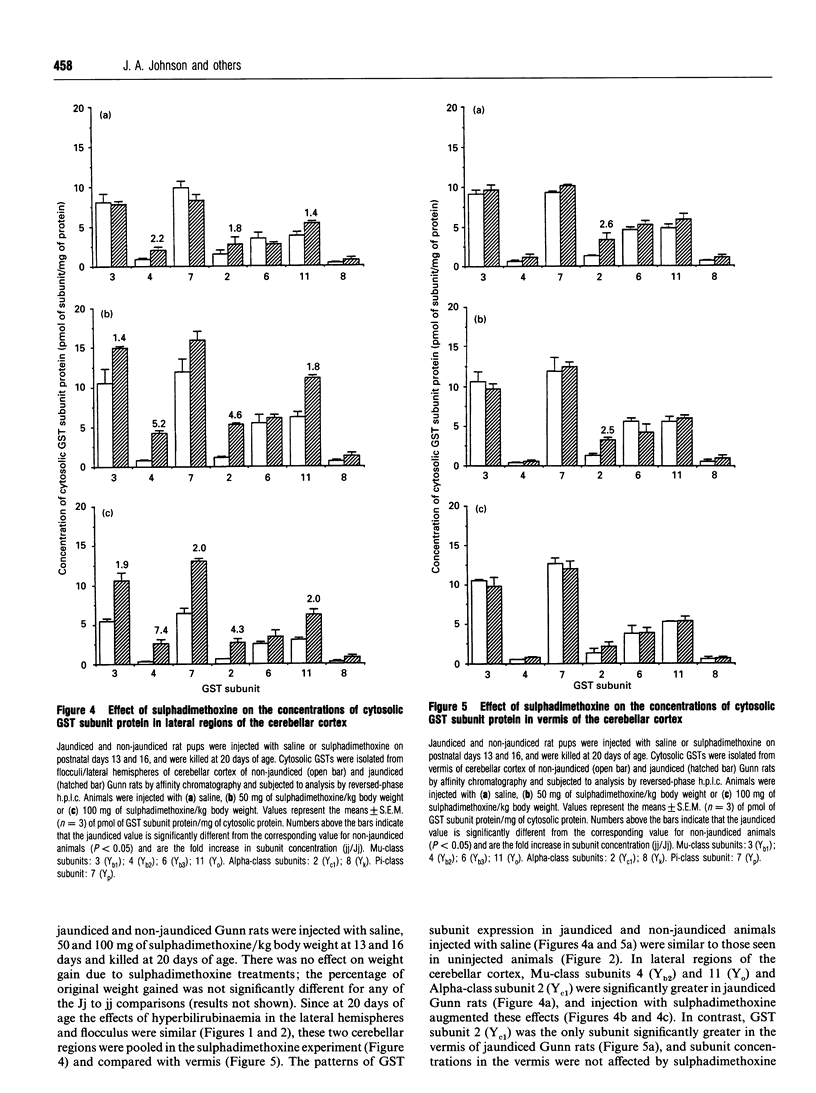
The glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are a family of isoenzymes involved in the detoxication of a variety of electrophilic xenobiotics. The present investigation demonstrates that GST activity and the concentration of cytosolic GSTs in cerebellar cortex of Gunn rats were increased in hyperbilirubinaemic animals compared with non-jaundiced controls. Age-dependent and region-specific increases in GST isoenzymes were seen in three regions of the cerebellar cortex of jaundiced Gunn rats, whereas GST concentrations were not altered in the brainstem, thalamus/hypothalamus, cortex or liver. Cytosolic GST activity was increased 1.3-fold in the flocculus and lateral hemispheres of 20-day-old and 1.7-fold in the flocculus, lateral hemispheres and vermis of 60-day-old jaundiced (jj; homozygous) Gunn rats compared with non-jaundiced (Jj; heterozygous) Gunn rats. H.p.l.c. was used to determine the GST subunit protein concentrations in cytosolic fractions isolated from liver and brain regions of jaundiced and non-jaundiced animals. In all regions of the cerebellum from 20-day-old animals, the levels of Alpha-class GST subunits 2 (Yc1; 3.0-fold) and 8 (Yk; 2.0-fold) were increased in jaundiced rats. In 60-day-old animals, the concentrations of Alpha-class GST subunits 2 (Yc1; 5.0-fold) and 8 (Yk; 3.0-fold), Mu-class subunit 11 (Yo; 2.5-fold) and Pi-class subunit 7 (Yp; 2.0-fold) were increased in all regions of cerebellar cortex of jaundiced animals. In cerebellum of 10-, 20- and 60-day-old non-jaundiced and jaundiced Gunn rats, the flocculus had the highest concentration of Mu-class GST subunit 4 (Yb2) and vermis the lowest; hyperbilirubinaemia increased the concentration of subunit 4 (Yb2; 3- to 5-fold) in the flocculus and lateral hemispheres, but not the vermis, of 20- and 60-day-old rats. Intraperitoneal injection of sulphadimethoxine, a long-acting sulphonamide which displaces bilirubin from its albumin-binding sites and increases the bilirubin levels in tissues, further increased the already elevated concentrations of GST subunits in the lateral regions of cerebellar cortex of hyperbilirubinaemic rats. For example, the concentration of subunit 4 (Yb2) was increased 2.2-fold (compared with non-jaundiced controls) in Gunn rats injected with saline and 7.4-fold in rats injected with 100 mg of sulphadimethoxine/kg body weight. In contrast, GSTs in the vermis of jaundiced animals were not affected by sulphadimethoxine injection. Sulphadimethoxine had no effect on GST concentrations in lateral regions and vermis of heterozygous (Jj) Gunn rats.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
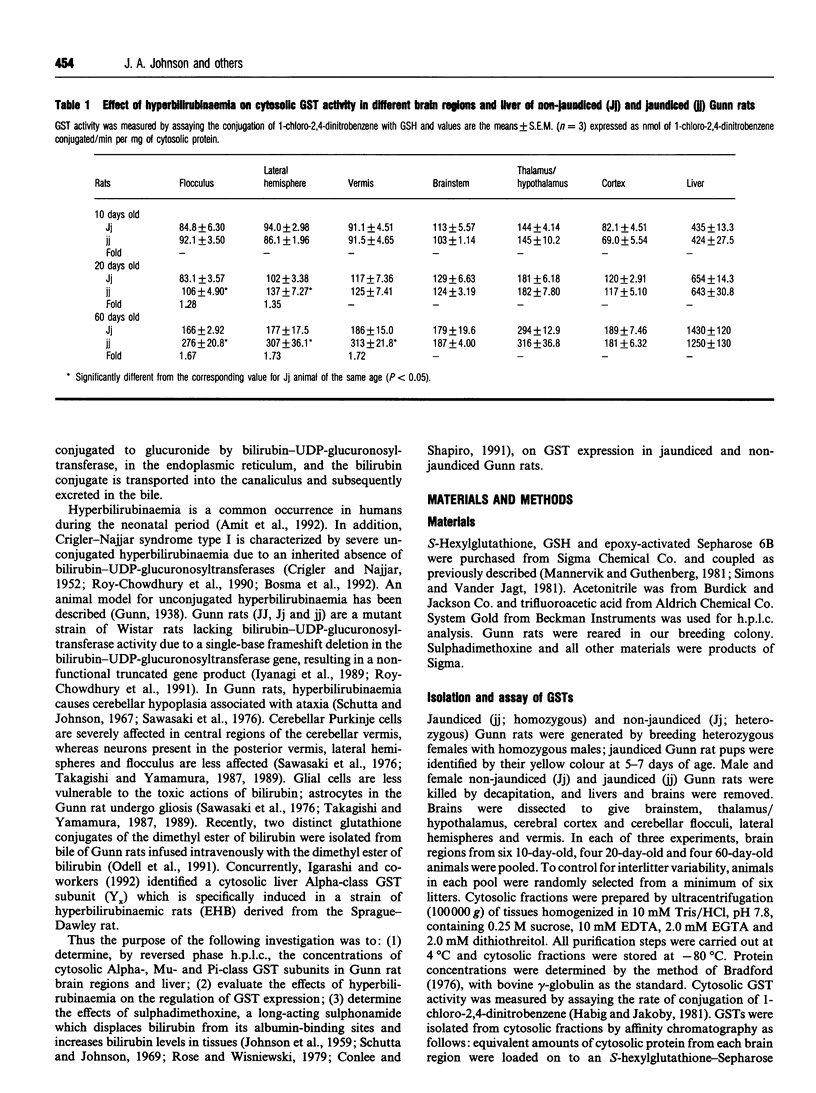
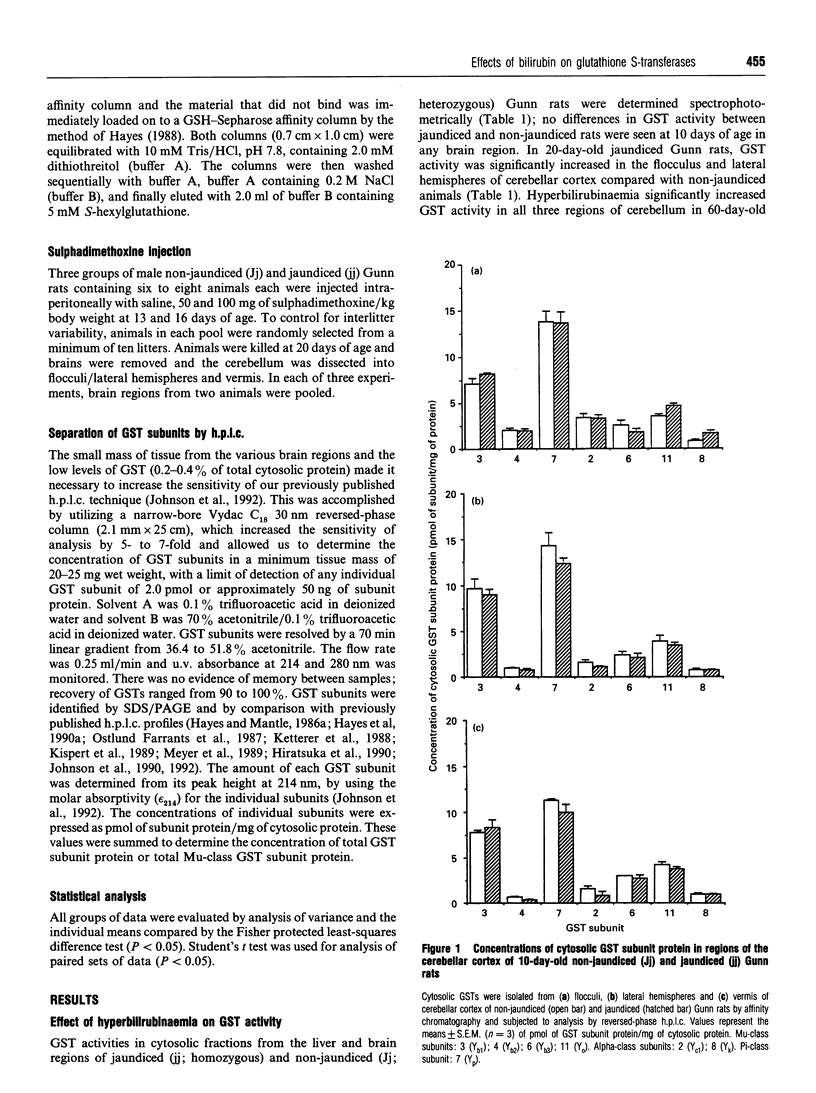
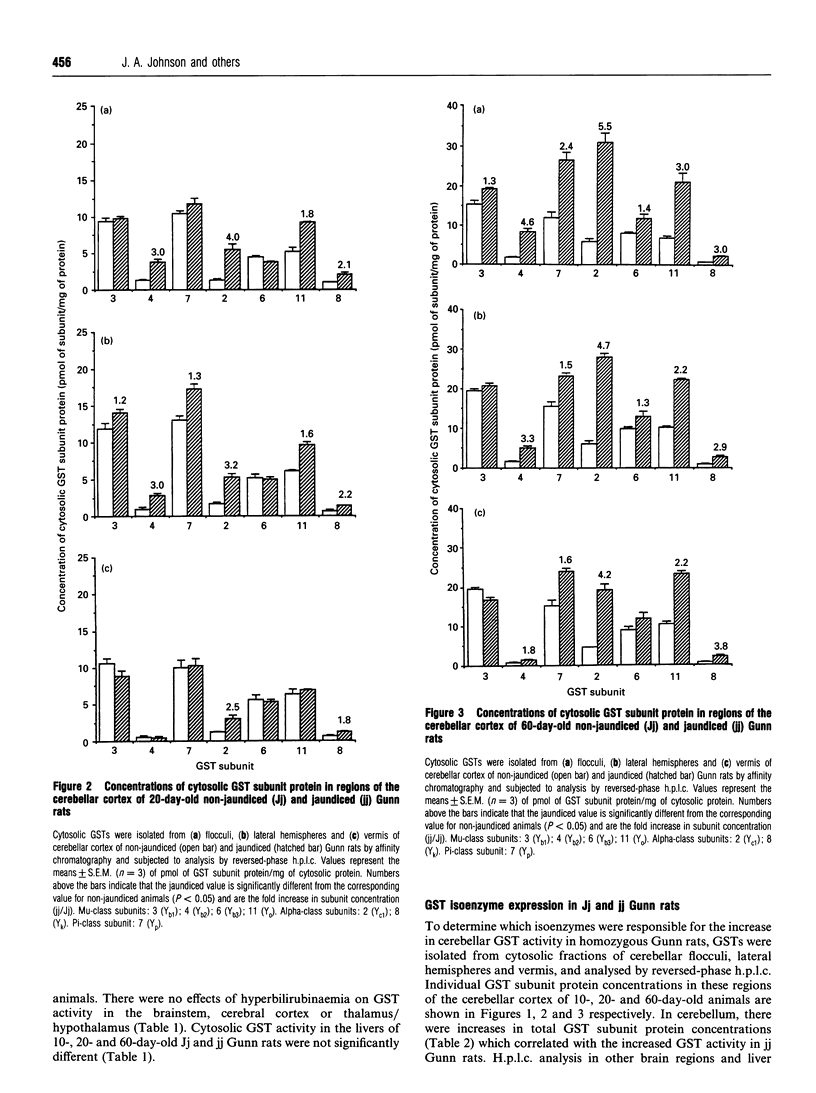



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovitz M., Homma H., Ishigaki S., Tansey F., Cammer W., Listowsky I. Characterization and localization of glutathione-S-transferases in rat brain and binding of hormones, neurotransmitters, and drugs. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):50–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amit Y., Poznansky M. J., Schiff D. Neonatal jaundice and bilirubin encephalopathy: a clinical and experimental reappraisal. Isr J Med Sci. 1992 Feb;28(2):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anandatheerthavarada H. K., Shankar S. K., Ravindranath V. Rat brain cytochromes P-450: catalytic, immunochemical properties and inducibility of multiple forms. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 17;536(1-2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90047-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Hunkeler M. J., York J. L. Mouse hepatic glutathione transferase isoenzymes and their differential induction by anticarcinogens. Specificities of butylated hydroxyanisole and bisethylxanthogen as inducers of glutathione transferases in male and female CD-1 mice. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):1023–1029. doi: 10.1042/bj2611023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanckaert N., Fevery J., Heirwegh K. P., Compernolle F. Characterization of the major diazo-positive pigments in bile of homozygous Gunn rats. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):237–249. doi: 10.1042/bj1640237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthius D. J., West J. R. Permanent neuronal deficits in rats exposed to alcohol during the brain growth spurt. Teratology. 1991 Aug;44(2):147–163. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420440203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma P. J., Chowdhury N. R., Goldhoorn B. G., Hofker M. H., Oude Elferink R. P., Jansen P. L., Chowdhury J. R. Sequence of exons and the flanking regions of human bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene complex and identification of a genetic mutation in a patient with Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I. Hepatology. 1992 May;15(5):941–947. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIGLER J. F., Jr, NAJJAR V. A. Congenital familial nonhemolytic jaundice with kernicterus. Pediatrics. 1952 Aug;10(2):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammer W., Tansey F., Abramovitz M., Ishigaki S., Listowsky I. Differential localization of glutathione-S-transferase Yp and Yb subunits in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1989 Mar;52(3):876–883. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb02536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase D. G., Pikó L. Expression of A- and C-type particles in early mouse embryos. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Dec;51(6):1971–1975. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.6.1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. T., Rettig W. J., Yenamandra A. K., Kozak C. A., Chaganti R. S., Posner J. B., Old L. J. Cerebellar degeneration-related antigen: a highly conserved neuroectodermal marker mapped to chromosomes X in human and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3077–3081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlee J. W., Shapiro S. M. Morphological changes in the cochlear nucleus and nucleus of the trapezoid body in Gunn rat pups. Hear Res. 1991 Dec;57(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(91)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courchesne E., Yeung-Courchesne R., Press G. A., Hesselink J. R., Jernigan T. L. Hypoplasia of cerebellar vermal lobules VI and VII in autism. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 26;318(21):1349–1354. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805263182102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. H., Batist G., Tulpule A., Sinha B. K., Myers C. E. Similar biochemical changes associated with multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells and carcinogen-induced resistance to xenobiotics in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9328–9332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Simplicio P., Jensson H., Mannervik B. Effects of inducers of drug metabolism on basic hepatic forms of mouse glutathione transferase. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj2630679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding G. J., Ding V. D., Rodkey J. A., Bennett C. D., Lu A. Y., Pickett C. B. Rat liver glutathione S-transferases. DNA sequence analysis of a Yb2 cDNA clone and regulation of the Yb1 and Yb2 mRNAs by phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7952–7957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath G., Bijlani V., Deo M. G. Undernutrition and the developing cerebellar cortex in the rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1976 Mar;35(2):125–135. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197603000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Jakoby W. B. Assays for differentiation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:398–405. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habig W. H., Pabst M. J., Fleischner G., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M., Jakoby W. B. The identity of glutathione S-transferase B with ligandin, a major binding protein of liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. M., Meyer D. J., Coles B., Ketterer B. A novel glutathione transferase (13-13) isolated from the matrix of rat liver mitochondria having structural similarity to class theta enzymes. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):137–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2780137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Judah D. J., McLellan L. I., Kerr L. A., Peacock S. D., Neal G. E. Ethoxyquin-induced resistance to aflatoxin B1 in the rat is associated with the expression of a novel alpha-class glutathione S-transferase subunit, Yc2, which possesses high catalytic activity for aflatoxin B1-8,9-epoxide. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):385–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2790385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Kerr L. A., Harrison D. J., Cronshaw A. D., Ross A. G., Neal G. E. Preferential over-expression of the class alpha rat Ya2 glutathione S-transferase subunit in livers bearing aflatoxin-induced pre-neoplastic nodules. Comparison of the primary structures of Ya1 and Ya2 with cloned class alpha glutathione S-transferase cDNA sequences. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):295–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2680295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Mantle T. J. Anomalous electrophoretic behaviour of the glutathione S-transferase Ya and Yk subunits isolated from man and rodents. A potential pitfall for nomenclature. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):731–740. doi: 10.1042/bj2370731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D. Selective elution of rodent glutathione S-transferases and glyoxalase I from the S-hexyglutathione-Sepharose affinity matrix. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):913–922. doi: 10.1042/bj2550913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka A., Sebata N., Kawashima K., Okuda H., Ogura K., Watabe T., Satoh K., Hatayama I., Tsuchida S., Ishikawa T. A new class of rat glutathione S-transferase Yrs-Yrs inactivating reactive sulfate esters as metabolites of carcinogenic arylmethanols. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11973–11981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi T., Tsuchiya T., Shikata Y., Sagami F., Tagaya O., Horie T., Satoh T. Developmental aspects of a unique glutathione S-transferase subunit Yx in the liver cytosol from rats with hereditary hyperbilirubinuria. Comparison with rat fetal liver transferase subunit Yfetus. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):307–311. doi: 10.1042/bj2830307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyanagi T., Watanabe T., Uchiyama Y. The 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible UDP-glucuronosyltransferase deficiency in the hyperbilirubinemic rat (Gunn rat) is caused by a -1 frameshift mutation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21302–21307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON L., SARMIENTO F., BLANC W. A., DAY R. Kernicterus in rats with an inherited deficiency of glucuronyl transferase. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):591–608. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010593009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Finn K. A., Siegel F. L. Tissue distribution of enzymic methylation of glutathione S-transferase and its effects on catalytic activity. Methylation of glutathione S-transferase 11-11 inhibits conjugating activity towards 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):279–289. doi: 10.1042/bj2820279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Neal T. L., Collins J. H., Siegel F. L. Characterization of methylation of rat liver cytosolic glutathione S-transferases by using reverse-phase h.p.l.c. and chromatofocusing. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):483–489. doi: 10.1042/bj2700483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitulnik J., Hardwick J. P., Ostrow J. D., Webster C. C., Park S. S., Gelboin H. V. Increase in a specific cytochrome P-450 isoenzyme in the liver of congenitally jaundiced Gunn rats. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2420297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitulnik J., Ostrow J. D. Stimulation of bilirubin catabolism in jaundiced Gunn rats by an induced of microsomal mixed-function monooxygenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kispert A., Meyer D. J., Lalor E., Coles B., Ketterer B. Purification and characterization of a labile rat glutathione transferase of the Mu class. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):789–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2600789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S. E., Anderson J. W., Scott G. Observations on the ultrastructure of the developing cerebellum of the Macaca mulatta. J Comp Neurol. 1967 May;130(1):1–23. doi: 10.1002/cne.901300102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S. E., Rutledge J. J., Sunderland E., Siegel F., Carlson I., Smollens J., Juhl U., Young B. Impeded cerebellar development and reduced serum thyroxine levels associated with fetal alcohol intoxication. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 16;177(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90785-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornguth S., Knobeloch L., Viseskul C., Gilbert E., Opitz J. Defect of cerebellar Purkinje cell histogenesis associated with type I and type II renal cystic disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Sep 26;40(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00688568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert S. R., Kriss A., Gresty M., Benton S., Taylor D. Joubert syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 May;107(5):709–713. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070010727035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E., Okuno S., Kariya K. Propylthiouracil inducible glutathione transferases. Selective induction of ligandin (glutathione transferase 1-1). Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 1;35(11):1835–1839. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Clos J. Biochemical, immunocytochemical and morphological evidence for an interaction between thyroid hormone and nerve growth factor in the developing cerebellum of normal and hypothyroid rats. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(6):382–396. doi: 10.1159/000112189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listowsky I., Abramovitz M., Homma H., Niitsu Y. Intracellular binding and transport of hormones and xenobiotics by glutathione-S-transferases. Drug Metab Rev. 1988;19(3-4):305–318. doi: 10.3109/03602538808994138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Alin P., Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Tahir M. K., Warholm M., Jörnvall H. Identification of three classes of cytosolic glutathione transferase common to several mammalian species: correlation between structural data and enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7202–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Danielson U. H. Glutathione transferases--structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(3):283–337. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Guthenberg C. Glutathione transferase (human placenta). Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:231–235. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Padilla M. Abnormal Purkinje cell morphogenesis in human renal agenesis. A Golgi study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Jul;48(4):448–461. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198907000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell P., Berry M. The effects of undernutrition on Purkinje cell dendritic growth in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 1;177(1):159–171. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Coles B., Pemble S. E., Gilmore K. S., Fraser G. M., Ketterer B. Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2740409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Lalor E., Coles B., Kispert A., Alin P., Mannervik B., Ketterer B. Single-step purification and h.p.l.c. analysis of glutathione transferase 8-8 in rat tissues. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):785–788. doi: 10.1042/bj2600785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscow J. A., Fairchild C. R., Madden M. J., Ransom D. T., Wieand H. S., O'Brien E. E., Poplack D. G., Cossman J., Myers C. E., Cowan K. H. Expression of anionic glutathione-S-transferase and P-glycoprotein genes in human tissues and tumors. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1422–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville H. E., Chase H. P. Undernutrition and cerebellar development. Exp Neurol. 1971 Dec;33(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(71)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson J. L., Altman J. The effects of early hypo- and hyperthyroidism on the development of rat cerebellar cortex. I. Cell proliferation and differentiation. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell G. B., Mogilevsky W. S., Smith P. B., Fenselau C. Identification of glutathione conjugates of the dimethyl ester of bilirubin in the bile of Gunn rats. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;40(4):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund Farrants A. K., Meyer D. J., Coles B., Southan C., Aitken A., Johnson P. J., Ketterer B. The separation of glutathione transferase subunits by using reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):423–428. doi: 10.1042/bj2450423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. J., Balázs R., Johnson A. L. Effect of undernutrition on cell formation in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):1151–1165. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philbert M. A., Beiswanger C. M., Waters D. K., Reuhl K. R., Lowndes H. E. Cellular and regional distribution of reduced glutathione in the nervous system of the rat: histochemical localization by mercury orange and o-phthaldialdehyde-induced histofluorescence. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;107(2):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(91)90204-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Telakowski-Hopkins C. A., Ding G. J., Argenbright L., Lu A. Y. Rat liver glutathione S-transferases. Complete nucleotide sequence of a glutathione S-transferase mRNA and the regulation of the Ya, Yb, and Yc mRNAs by 3-methylcholanthrene and phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5182–5188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss A. L., Patel S., Kumar A. J., Freund L. Preliminary communication: neuroanatomical variations of the posterior fossa in men with the fragile X (Martin-Bell) syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Oct;31(2):407–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320310220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel C. J., Muraszko K. M., Youle R. J. Diphtheria toxin mutant selectively kills cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. L., Wisniewski H. Acute bilirubin encephalopathy induced with sulfadimethoxine in Gunn rats. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1979 Mar;38(2):152–164. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197903000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Chowdhury J., Huang T. J., Kesari K., Lederstein M., Arias I. M., Roy-Chowdhury N. Molecular basis for the lack of bilirubin-specific and 3-methylcholanthrene-inducible UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activities in Gunn rats. The two isoforms are encoded by distinct mRNA species that share an identical single base deletion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18294–18298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., King R. G., Paulson K. E., Pickett C. B. Regulation of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene expression: identification of a unique xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Morton M. R., Pickett C. B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11632–11639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R., HAMMAKER L. METABOLISM AND DISPOSITION OF C14-BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL NONHEMOLYTIC JAUNDICE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1720–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI104858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Kitahara A., Soma Y., Inaba Y., Hatayama I., Sato K. Purification, induction, and distribution of placental glutathione transferase: a new marker enzyme for preneoplastic cells in the rat chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3964–3968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawasaki Y., Yamada N., Nakajima H. Developmental features of cerebellar hypoplasia and brain bilirubin levels in a mutant (Gunn) rat with hereditary hyperbilirubinaemia. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutta H. S., Johnson L. Bilirubin encephalopathy in the Gunn rat: a fine structure study of the cerebellar cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jul;26(3):377–396. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196707000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutta H. S., Johnson L. Clinical signs and morphologic abnormalities in Gunn rats treated with sulfadimethoxine. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1070–1079. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva J. E., Rudas P. Effects of congenital hypothyroidism on microtubule-associated protein-2 expression in the cerebellum of the rat. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):1276–1282. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A., Persson L. The effect of pre- and postnatal undernutrition on the development of the rat cerebellar cortex. I. Morphological observations. Neurobiology. 1975 Mar;5(1):23–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons P. C., Vander Jagt D. L. Purification of glutathione S-transferases by glutathione-affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1981;77:235–237. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobie P. E., Hansen C. T., Hailey J. R., Levine R. L. A difference in mortality between two strains of jaundiced rats. Pediatrics. 1991 Jan;87(1):88–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker R., Yamamoto Y., McDonagh A. F., Glazer A. N., Ames B. N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1043–1046. doi: 10.1126/science.3029864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagishi Y., Yamamura H. Purkinje cell abnormalities and synaptogenesis in genetically jaundiced rats (Gunn rats). Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):116–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90894-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagishi Y., Yamamura H. The critical period of Purkinje cell degeneration and cerebellar hypoplasia due to bilirubin. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(1):41–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00686791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansey F. A., Cammer W. A pi form of glutathione-S-transferase is a myelin- and oligodendrocyte-associated enzyme in mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1991 Jul;57(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansey F. A., Cammer W. Depletion of glutathione interferes with induction of glycerolphosphate dehydrogenase in the brains of young rats. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 8;564(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91348-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida S., Sato K. Rat spleen glutathione transferases. A new acidic form belonging to the Alpha class. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):461–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2660461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. P., Weiss M. J., Li N. Q., Reddy C. C. Tissue-specific expression of the rat glutathione S-transferases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4659–4662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos R. M., Van Bladeren P. J. Glutathione S-transferases in relation to their role in the biotransformation of xenobiotics. Chem Biol Interact. 1990;75(3):241–265. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(90)90069-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warkany J., Passarge E., Smith L. B. Congenital malformations in autosomal trisomy syndromes. Am J Dis Child. 1966 Dec;112(6):502–517. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1966.02090150046002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. C., Lee J. C., Bakay L. The ultrastructure of the rat central nervous system in chronic undernutrition. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;30(3):197–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00688921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagon I. S., McLaughlin P. J. Perinatal methadone exposure and brain development: a biochemical study. J Neurochem. 1978 Jul;31(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



