Abstract
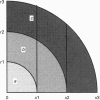
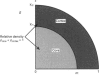
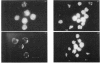
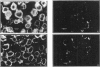
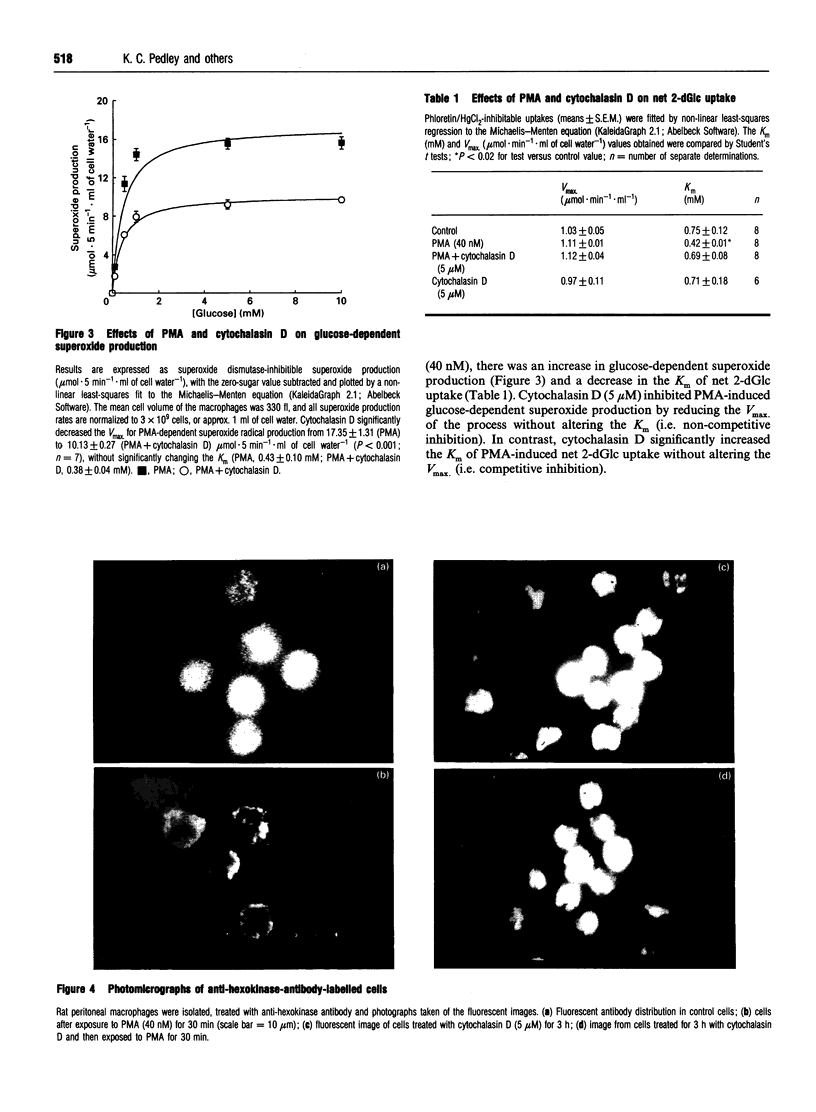
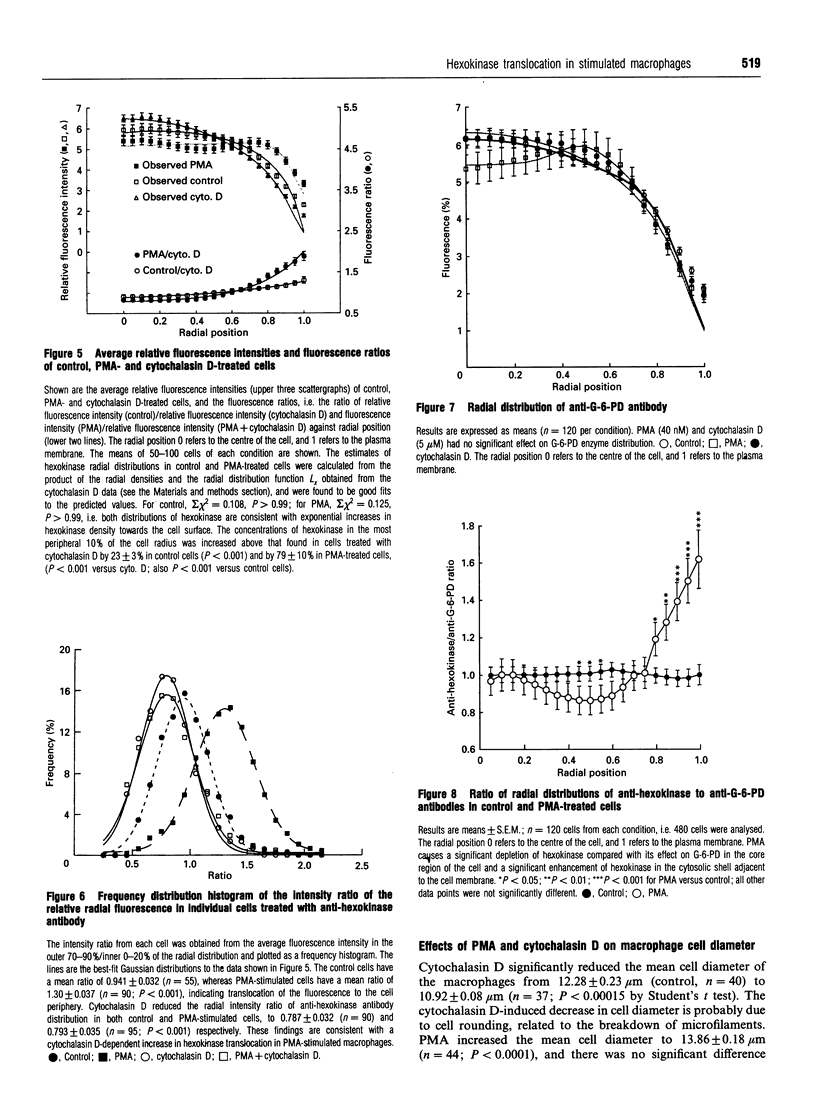
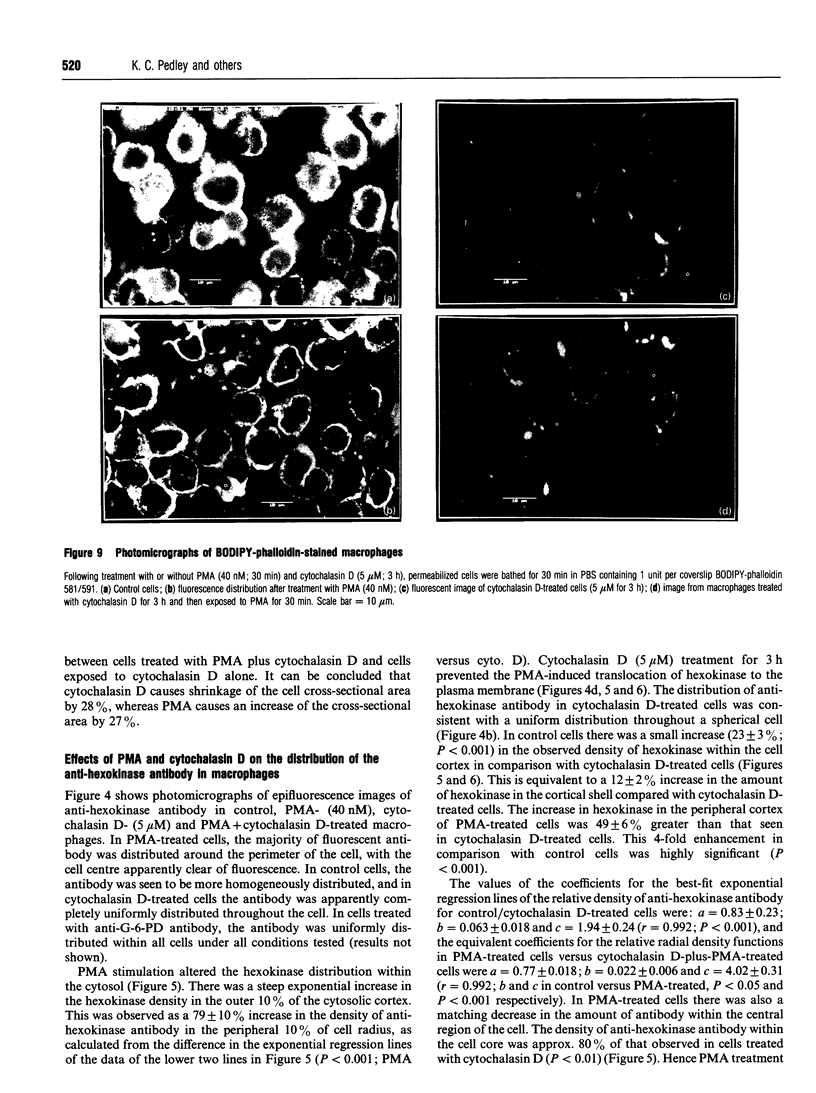
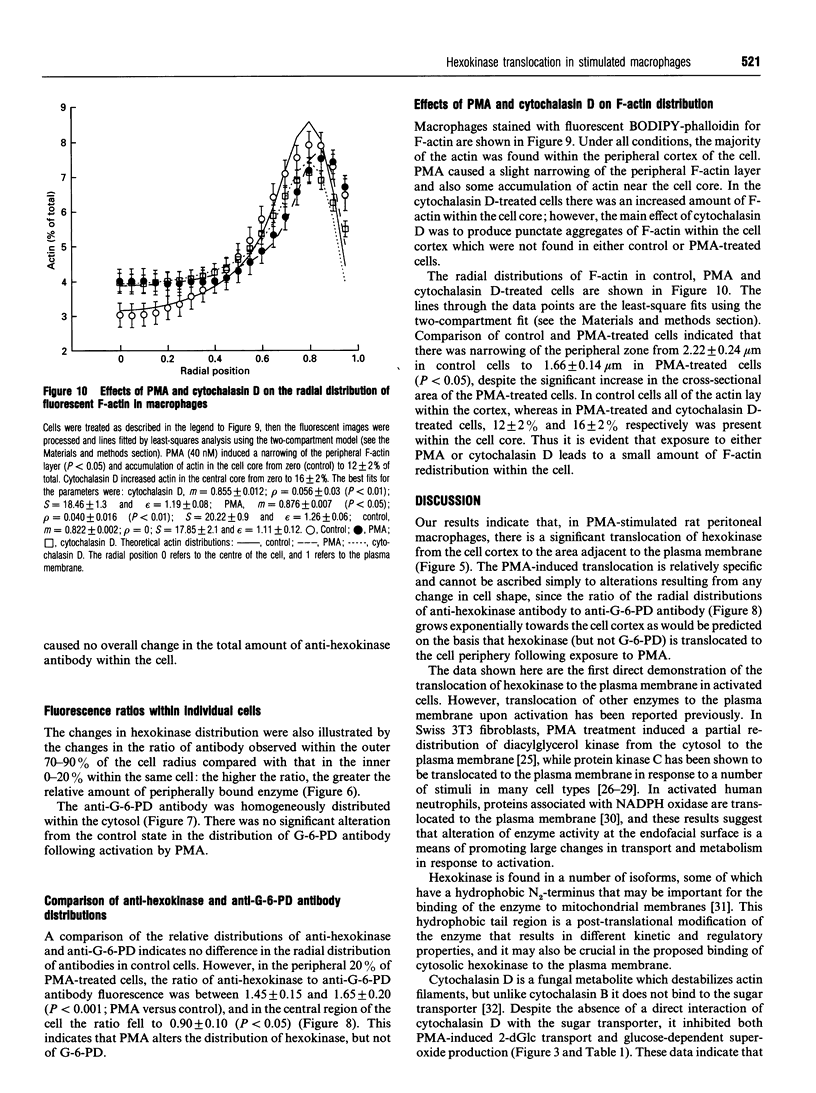
1. Fluorescence imaging of antibodies was used to show that phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) induces a 4-fold increase in the amount of hexokinase relative to the control in the cortical shell of rat peritoneal macrophage cytosol adjacent to the plasma membrane, and a corresponding depletion in the amount of hexokinase in the central core of the cytosol. However, there was no significant PMA-dependent change in the distribution of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. 2. Cytochalasin D, an inhibitor of actin microfilament polymerization, prevented the PMA-induced hexokinase translocation and also reduced the PMA-dependent increases in 2-deoxy-D-glucose transport and glucose-dependent PMA-stimulated superoxide production. 3. PMA caused a contraction of the width of the cortical F-actin zone. Cytochalasin D caused some dispersal of F-actin within the cell, increasing the density of F-actin within the central cytosolic core and causing aggregation of the F-actin within the cortex. These data are consistent with the view that PMA induces attachment of hexokinase to microfilaments within the cortical zone adjacent to the cell membrane of macrophages, and cytochalasin D prevents this attachment. This is the first direct demonstration of the translocation of hexokinase to the plasma membrane in activated cells, and supports the view that enhanced hexokinase activity in the cortical region of the cytosol is an important early component of the macrophage activation process.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apgar J. R. Regulation of the antigen-induced F-actin response in rat basophilic leukemia cells by protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(6):1157–1163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora K. K., Parry D. M., Pedersen P. L. Hexokinase receptors: preferential enzyme binding in normal cells to nonmitochondrial sites and in transformed cells to mitochondrial sites. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Feb;24(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00769530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora K. K., Pedersen P. L. Functional significance of mitochondrial bound hexokinase in tumor cell metabolism. Evidence for preferential phosphorylation of glucose by intramitochondrially generated ATP. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17422–17428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert-Foucher E., Font B., Gautheron D. C. Rabbit heart mitochondrial hexokinase: solubilization and general properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90554-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. The respiratory burst of phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):599–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI111249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante E., Morris H. P., Pedersen P. L. Energy metabolism of tumor cells. Requirement for a form of hexokinase with a propensity for mitochondrial binding. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8699–8704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Volpp B. D., Leidal K. G., Nauseef W. M. Two cytosolic components of the human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase translocate to the plasma membrane during cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI114496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey G. P., Chan C. K., Lea P., Takai A., Grinstein S. Phorbol ester-induced actin assembly in neutrophils: role of protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):695–706. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterby J. S. The analysis of metabolite channelling in multienzyme complexes and multifunctional proteins. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):605–607. doi: 10.1042/bj2640605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etoh S., Baba A., Iwata H. NMDA induces protein kinase C translocation in hippocampal slices of immature rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 May 27;126(2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90533-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Wang D. Calcium ionophore, phorbol ester, and chemotactic peptide-induced cytoskeleton reorganization in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1359–1364. doi: 10.1172/JCI112962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. M., Mayer R. J. Glucose metabolism in the rat small intestine: the effect of glucose analogues on hexokinase activity. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):125–128. doi: 10.1042/bj1320125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil R. A., Morgan K. G. Imaging of protein kinase C distribution and translocation in living vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1991 Dec;69(6):1626–1631. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.6.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki C., Peisach J., Bloom B. R. Oxygen metabolism in cloned macrophage cell lines: glucose dependence of superoxide production, metabolic and spectral analysis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knull H. R., Taylor W. F., Wells W. W. Insulin effects on brain energy metabolism and the related hexokinase distribution. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6930–6935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch R. M., Fogarty K. E., Fay F. S. Modulation of hexokinase association with mitochondria analyzed with quantitative three-dimensional confocal microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):385–395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani M., Rossi L., Bianchi M., Serafini G., Stocchi V. Role of hexokinase in the regulation of erythrocyte hexose monophosphate pathway under oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):423–428. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani M., Serafini G., Bianchi M., Casabianca A., Stocchi V. Human hexokinase type I microheterogeneity is due to different amino-terminal sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani M., Stocchi V., Serafini G., Chiarantini L., Fornaini G. Purification, properties, and evidence for two subtypes of human placenta hexokinase type I. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):388–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroney A. C., Macara I. G. Phorbol ester-induced translocation of diacylglycerol kinase from the cytosol to the membrane in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2537–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick K. L., Mick G. J. Kinetic superiority of intra- vs. extracellular pentose pathway flux: studies in porous adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 1):C476–C481. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.3.C476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowbray J., Moses V. The tentative identification in Escherichia coli of a multienzyme complex with glycolytic activity. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):25–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Márquez C., Martínez C., Boscá L. Protein kinase C mobilization in B lymphocytes. Differential isoenzyme translocation upon activation. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Stuenkel E. L., Malviya A. N. Exocytosis in neurohypophysial nerve terminals is not coupled to protein kinase C translocation. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):493–496. doi: 10.1042/bj2730493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagliaro L., Taylor D. L. 2-Deoxyglucose and cytochalasin D modulate aldolase mobility in living 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):859–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. M., Pedersen P. L. Intracellular localization and properties of particulate hexokinase in the Novikoff ascites tumor. Evidence for an outer mitochondrial membrane location. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10904–10912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rist R. J., Jones G. E., Naftalin R. J. Effects of macrophage colony-stimulating factor and phorbol myristate acetate on 2-D-deoxyglucose transport and superoxide production in rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):119–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2780119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rist R. J., Jones G. E., Naftalin R. J. Synergistic activation of 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake in rat and murine peritoneal macrophages by human macrophage colony-stimulating factor-stimulated coupling between transport and hexokinase activity and phorbol-dependent stimulation of pentose phosphate-shunt activity. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):243–249. doi: 10.1042/bj2650243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos F. J., Zimmermann A., Keller H. U. Effect of phorbol myristate acetate and the chemotactic peptide fNLPNTL on shape and movement of human neutrophils. J Cell Sci. 1987 Oct;88(Pt 3):399–406. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten D. R., Davis J. M., Meyers D. M., Durstine J. L. Altered cellular distribution of hexokinase in skeletal muscle after exercise. Int J Sports Med. 1992 Jul;13(5):436–438. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1021294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. L., Keith T. J., Knull H. R. Glycolytic enzyme interactions with tubulin and microtubules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 9;999(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yassin R., Shefcyk J., White J. R., Tao W., Volpi M., Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Effects of chemotactic factors and other agents on the amounts of actin and a 65,000-mol-wt protein associated with the cytoskeleton of rabbit and human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):182–188. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]