Abstract
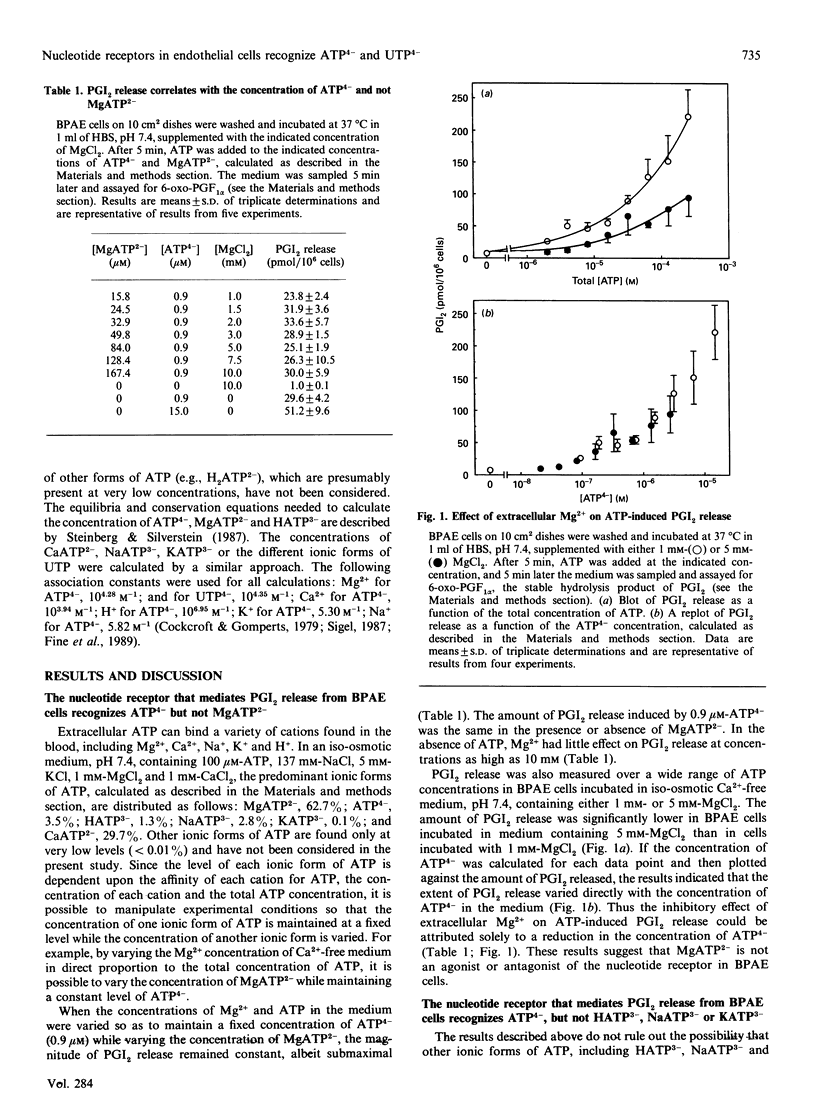
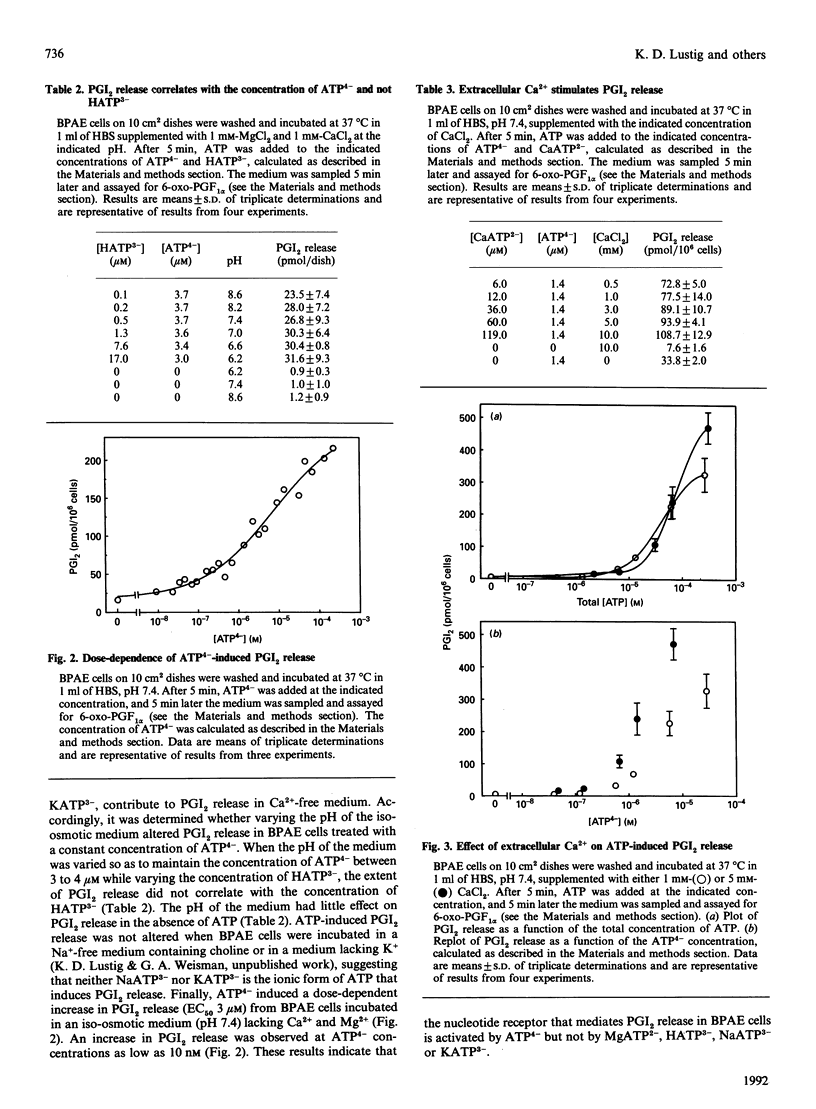
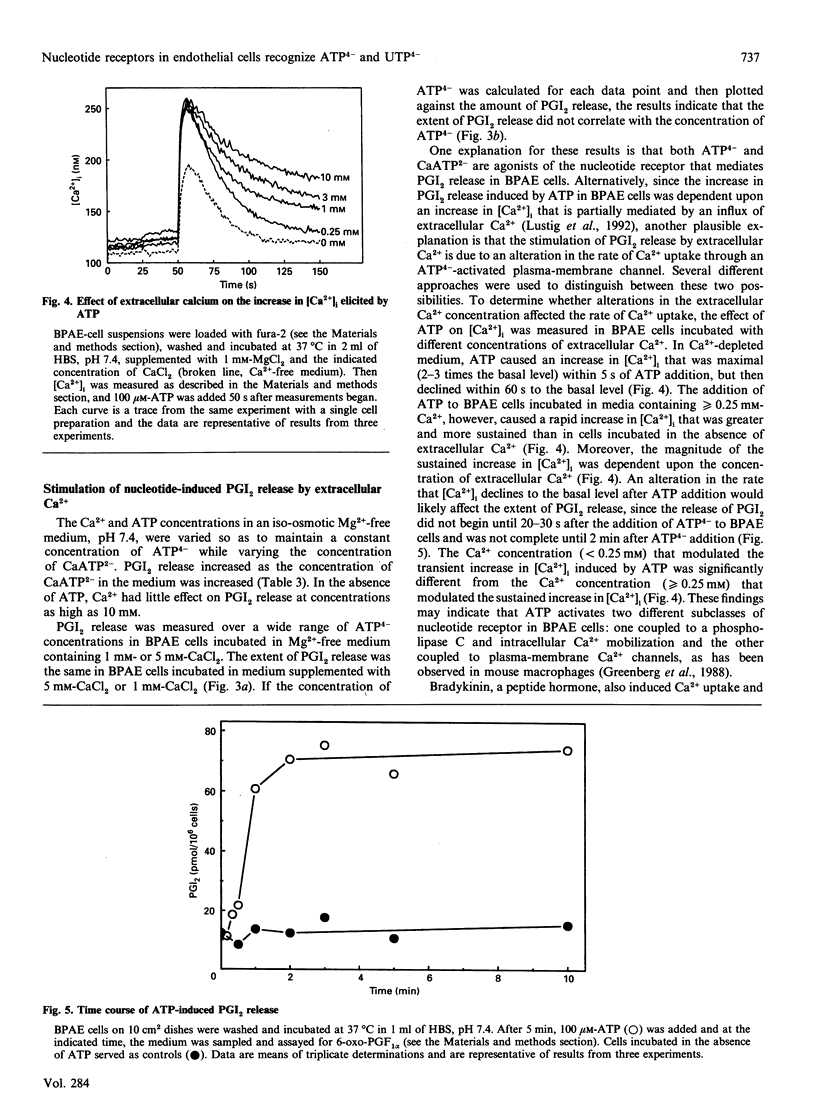
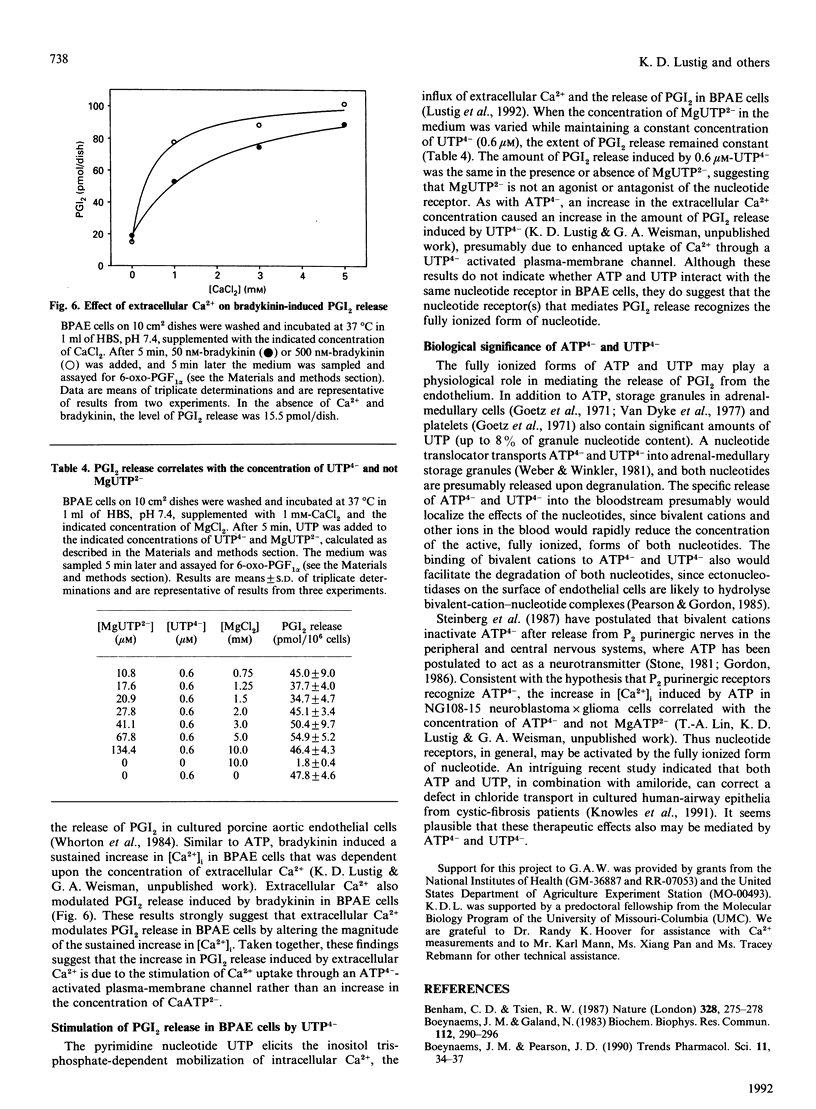
Extracellular ATP causes an increase in the concentration of cytoplasmic free calcium ([Ca2+]i) in bovine pulmonary-artery endothelial (BPAE) cells that results in the synthesis and release of prostacyclin (PGI2), a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. We show here that PGI2 release in BPAE cells correlates with the concentration of the fully ionized form of extracellular ATP (ATP4-) and not with the concentration of other ionic forms of ATP. Concentrations as low as 10 nM-ATP4- elicited an increase in PGI2 release [EC50 (concn. giving half-maximal stimulation) 3 microM] in BPAE cells incubated in an iso-osmotic medium, pH 7.4, lacking Ca2+ and Mg2+. When the pH or the Mg2+ concentration of the medium was varied so as to maintain a constant level of ATP4-, while varying the concentration of proton-ATP (HATP3-) or MgATP2- respectively, PGI2 release remained constant. An inhibitory effect of extracellular Mg2+ on PGI2 release could be attributed solely to a decrease in the concentration of ATP4-. In contrast with Mg2+, extracellular Ca2+ stimulated PGI2 release induced by ATP. Several results suggest that extracellular Ca2+ modulates PGI2 release by increasing Ca2+ uptake through an ATP(4-)-activated plasma-membrane channel. In BPAE cells incubated in Ca(2+)-free medium, ATP elicited a transient increase in [Ca2+]i that declined to the basal level within 60 s. In cells incubated in Ca(2+)-containing medium, ATP caused an increase in [Ca2+]i that had two components: a transient peak in [Ca2+]i (0-60 s) and a sustained increase in [Ca2+]i that was maintained for several minutes after ATP addition. Increasing the concentration of extracellular calcium from 0.25 mM to 10 mM had no effect on the transient rise in [Ca2+]i induced by ATP, but significantly enhanced the magnitude of the sustained increase in [Ca2+]i. Alterations in the magnitude of the sustained increase in [Ca2+]i would likely modulate PGI2 release, which was not complete until 2 min after ATP addition. Extracellular Ca2+ also stimulated PGI2 release induced by bradykinin. Bradykinin caused a sustained increase in [Ca2+]i in BPAE cells in the presence of extracellular Ca2+. Finally, the magnitude of PGI2 release induced by UTP, a more potent agonist than ATP, correlated with the concentration of extracellular fully ionized UTP (UTP4-). These findings support the hypothesis that nucleotide receptors in BPAE cells recognize the fully ionized form of ATP and UTP and are coupled to signal-transduction pathways involving the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, the influx of extracellular Ca2+ and the subsequent release of PGI2.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeynaems J. M., Galand N. Stimulation of vascular prostacyclin synthesis by extracellular ADP and ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91829-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeynaems J. M., Pearson J. D. P2 purinoceptors on vascular endothelial cells: physiological significance and transduction mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):34–37. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90039-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V., Kratzer M. A. Source and concentration of extracellular adenosine triphosphate during haemostasis in rats, rabbits and man. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:419–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Cooper C. L., Harden T. K. [32P]3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyl ATP as a photoaffinity label for a phospholipase C-coupled P2Y-purinergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13515–13520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. D., Hallam T. J., Cusack N. J., Pearson J. D. Regulation of P2y-purinoceptor-mediated prostacyclin release from human endothelial cells by cytoplasmic calcium concentration. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1181–1190. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:229–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Morris A. J., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive interaction of a radiolabeled agonist with a phospholipase C-linked P2y-purinergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6202–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist R., Diamant B. Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 May;34(5):368–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. S., Wakefield I. K., Sohnius U., van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P. A novel extracellular nucleotide receptor coupled to phosphoinositidase-C in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):80–87. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., De Young M. B. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization activated by extracellular ATP in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10653–10661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb L., Lustig K. D., Ahmed A. H., Gonzalez F. A., Weisman G. A. Covalent incorporation of 3'-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyl-ATP into a P2 purinoceptor in transformed mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7424–7431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J., Cole P., Davidson J. S. Extracellular nucleotides stimulate receptor-mediated calcium mobilization and inositol phosphate production in human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):371–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2630371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester T., Williams C. A. Release of adenosine triphosphate from isolated adult heart cells in response to hypoxia. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):371–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg E. J., Feuerstein G., Shohami E., Pollard H. B. Adenosine triphosphate stimulates inositol phospholipid metabolism and prostacyclin formation in adrenal medullary endothelial cells by means of P2-purinergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5630–5634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz U., Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Adenine-, guanine- and uridine-5'-phosphonucleotides in blood platelets and storage organelles of various species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Jul;178(1):210–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Extracellular ATP induces the release of calcium from intracellular stores without the activation of protein kinase C in Swiss 3T6 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4530–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. L., Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L. The hydrolysis of extracellular adenine nucleotides by cultured endothelial cells from pig aorta. Feed-forward inhibition of adenosine production at the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15496–15507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L., Martin W. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of the pig aorta: relationship to stimulation of 86Rb efflux from isolated endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):531–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular nucleotides mediate Ca2+ fluxes in J774 macrophages by two distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Pearson J. D. Exogenous ATP raises cytoplasmic free calcium in fura-2 loaded piglet aortic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Pearson J. D., Needham L. A. Thrombin-stimulated elevation of human endothelial-cell cytoplasmic free calcium concentration causes prostacyclin production. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):243–249. doi: 10.1042/bj2510243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A., Weisman G. A., Friedberg I. Permeabilization of transformed cells in culture by external ATP. J Membr Biol. 1985;86(3):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF01870597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Green H. Lethality of adenosine for cultured mammalian cells by interference with pyrimidine biosynthesis. J Cell Sci. 1973 Sep;13(2):429–439. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Clarke L. L., Boucher R. C. Activation by extracellular nucleotides of chloride secretion in the airway epithelia of patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 22;325(8):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108223250802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Erb L., Landis D. M., Hicks-Taylor C. S., Zhang X., Sportiello M. G., Weisman G. A. Mechanisms by which extracellular ATP and UTP stimulate the release of prostacyclin from bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 19;1134(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Busse R. Increased free calcium in endothelial cells under stimulation with adenine nucleotides. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Mar;126(3):414–420. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. C. Ca2(+)-dependent synthesis of prostaglandin I2 and mobilization of arachidonic acid from phospholipids in cultured endothelial cells permeabilized with saponin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 1;1054(2):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. P2-purinergic agonists stimulate phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylcholine in endothelial cells. Evidence for activation of phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8847–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers K. M., Holmsen H., Seachord C. L. Comparative study of platelet dense granule constituents. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):R454–R461. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.3.R454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S. Prostacyclin and arterial wall biology. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 May-Jun;2(3):193–207. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Vane J. R. Arachidonic acid metabolites and the interactions between platelets and blood-vessel walls. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 17;300(20):1142–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905173002006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Cusack N. J. Investigation of the preferred Mg(II)-adenine-nucleotide complex at the active site of ectonucleotidases in intact vascular cells using phosphorothioate analogues of ADP and ATP. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):373–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Nucleotide metabolism by endothelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:617–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Gordon J. L. Vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells in culture selectively release adenine nucleotides. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):384–386. doi: 10.1038/281384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L., Gordon J. L. Stimulation of prostaglandin production through purinoceptors on cultured porcine endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2140273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Raspe E., Demolle D., Erneux C., Boeynaems J. M. Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium in the action of adenine nucleotides on aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17461–17466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Robaye B., Lagneau C., Boeynaems J. M. Adenine nucleotides modulate phosphatidylcholine metabolism in aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Mar;142(3):449–457. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. A Specific effect of external ATP on the permeability of transformed 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 15;67(4):1581–1588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel H. Isomeric equilibria in complexes of adenosine 5'-triphosphate with divalent metal ions. Solution structures of M(ATP)2- complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Newman A. S., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8884–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular ATP4- promotes cation fluxes in the J774 mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3118–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke K., Robinson R., Urquilla P., Smith D., Taylor M., Trush M., Wilson M. An analysis of nucleotides and catecholamines in bovine medullary granules by anion exchange high pressure liquid chromatography and fluorescence. Evidence that most of the catecholamines in chromaffin granules are stored without associated ATP. Pharmacology. 1977;15(5):377–391. doi: 10.1159/000136714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Winkler H. Specificity and mechanism of nucleotide uptake by adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1981;6(11):2269–2276. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman G. A., De B. K., Friedberg I., Pritchard R. S., Heppel L. A. Cellular responses to external ATP which precede an increase in nucleotide permeability in transformed cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 May;119(2):211–219. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman G. A., Lustig K. D., Lane E., Huang N. N., Belzer I., Friedberg I. Growth inhibition of transformed mouse fibroblasts by adenine nucleotides occurs via generation of extracellular adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12367–12372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker N., Bunting S., Salmon J., Moncada S., Vane J. R., Johnson R. A., Morton D. R., Kinner J. H., Gorman R. R., McGuire J. C. The chemical structure of prostaglandin X (prostacyclin). Prostaglandins. 1976 Dec;12(6):915–928. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whorton A. R., Willis C. E., Kent R. S., Young S. L. The role of calcium in the regulation of prostacyclin synthesis by porcine aortic endothelial cells. Lipids. 1984 Jan;19(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02534603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


