Abstract
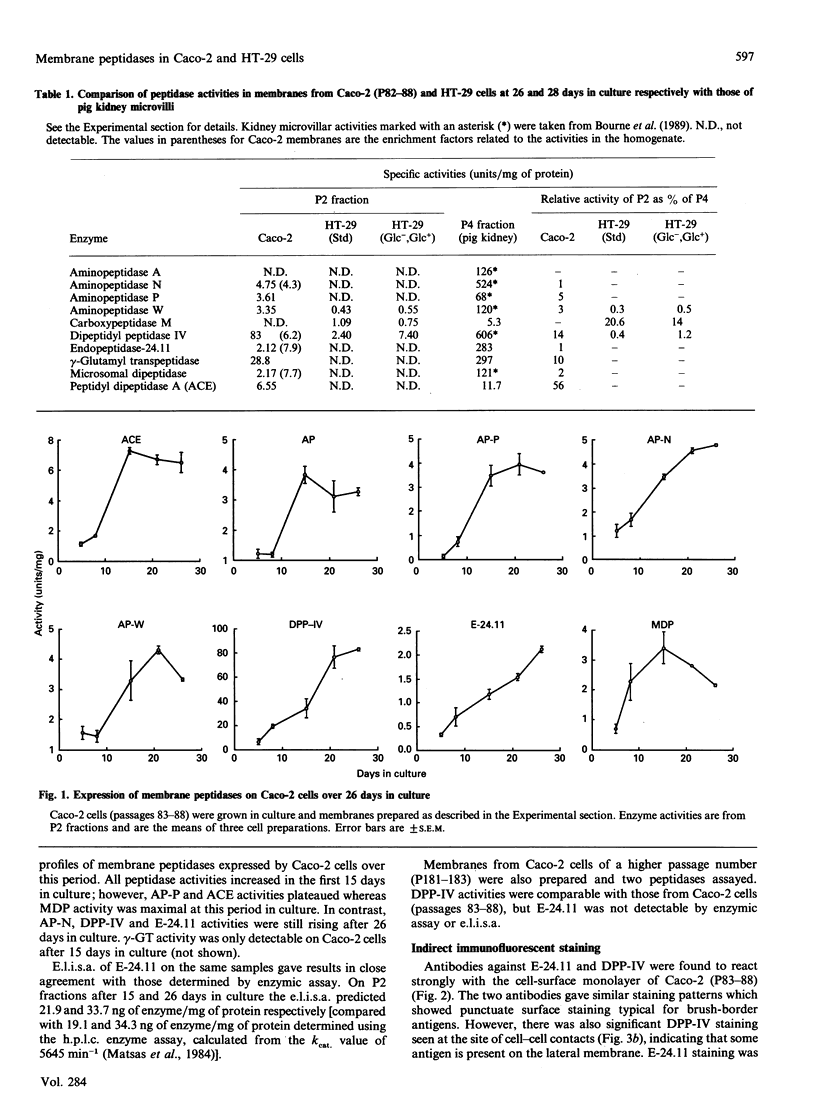
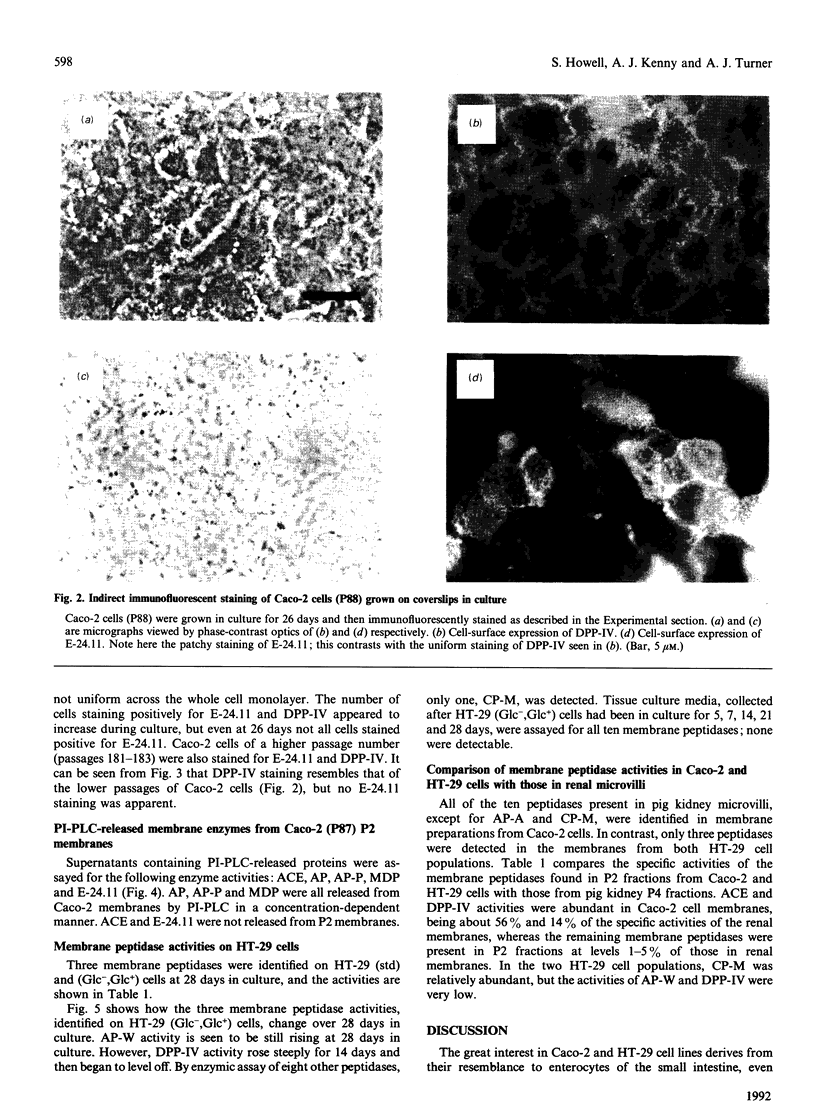
The expression of cell-surface peptidases was examined in two human colon carcinoma cell lines, Caco-2 and HT-29. Enzymic assays revealed the presence of eight cell-surface peptidases on a Caco-2 cell line (passage number 82-88), namely aminopeptidase N, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, peptidyl dipeptidase A (angiotension-converting enzyme), aminopeptidase P, aminopeptidase W, endopeptidase-24.11, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and membrane dipeptidase. The presence of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and endopeptidase-24.11 was also confirmed immunochemically. After 15 days culture, the activities of aminopeptidase P, peptidyl dipeptidase A and alkaline phosphatase activities on Caco-2 cells reached a plateau, and that of membrane dipeptidase began to decline. In contrast, aminopeptidase N, dipeptidyl peptidase IV and endopeptidase-24.11 activities were still rising after 26 days in culture. Caco-2 cells of passage number 181-183 were found to lack endopeptidase-24.11, but maintained dipeptidyl peptidase IV expression. Two populations of HT-29 cells were surveyed. Both the standard, undifferentiated population and a differentiated population expressed only three peptidases: dipeptidyl peptidase IV, aminopeptidase W and carboxypeptidase M. In the differentiated HT-29 cells the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV after 14-21 days was beginning to plateau whereas aminopeptidase W activity was still rising and that of carboxypeptidase M had begun to decline. These differences in activity profiles observed among this group of cell-surface peptidases indicate that these cell lines, especially Caco-2, are useful models to study the regulation of their expression.
Full text
PDF

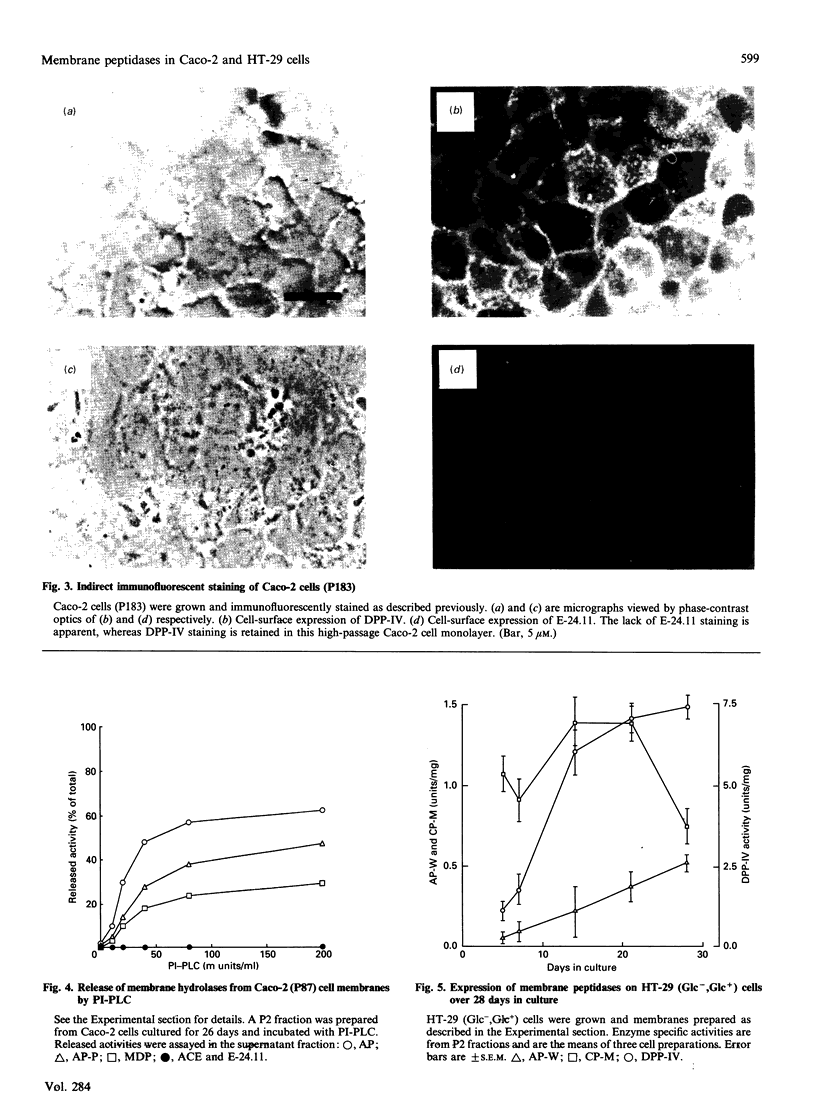


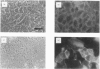
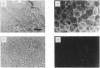
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes K., Bourne A., Cook P. A., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Membrane peptidases in the peripheral nervous system of the pig: their localization by immunohistochemistry at light and electron microscopic levels. Neuroscience. 1991;44(1):245–261. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90265-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne A., Barnes K., Taylor B. A., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Membrane peptidases in the pig choroid plexus and on other cell surfaces in contact with the cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):69–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2590069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantret I., Barbat A., Dussaulx E., Brattain M. G., Zweibaum A. Epithelial polarity, villin expression, and enterocytic differentiation of cultured human colon carcinoma cells: a survey of twenty cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1936–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic forms of endopeptidase purified from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Enzymic and molecular properties of aminopeptidase W. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2460097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Sterchi E. E., Bienz D., Fransen J. A., Marxer A. Expression and intracellular transport of microvillus membrane hydrolases in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):838–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Hryszko J., Turner A. J. Purification and characterization of pig kidney aminopeptidase P. A glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored ectoenzyme. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):509–515. doi: 10.1042/bj2670509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Aminopeptidase P is anchored by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 14;229(2):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S., Murray H., Scott C. S., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. A highly sensitive E.L.I.S.A. for endopeptidase-24.11, the common acute-lymphoblastic-leukaemia antigen (CALLA, CD-10), applicable to material of porcine and human origin. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):417–421. doi: 10.1042/bj2780417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Quaroni A., Nichols B., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Biogenetic pathways of plasma membrane proteins in Caco-2, a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1351–1361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Hauri H. P. Intracellular transport and conformational maturation of intestinal brush border hydrolases. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1916–1923. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Stieger B., Klumperman J., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Endocytosis, recycling, and lysosomal delivery of brush border hydrolases in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3503–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M. The human colon carcinoma cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2: two in vitro models for the study of intestinal differentiation. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1035–1040. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Matter K., Baur B., Bucher K., Höchli M., Hauri H. P. Dissection of the asynchronous transport of intestinal microvillar hydrolases to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1853–1861. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szasz G. A kinetic photometric method for serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Clin Chem. 1969 Feb;15(2):124–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trugnan G., Rousset M., Chantret I., Barbat A., Zweibaum A. The posttranslational processing of sucrase-isomaltase in HT-29 cells is a function of their state of enterocytic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1987 May;104(5):1199–1205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.5.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wice B. M., Trugnan G., Pinto M., Rousset M., Chevalier G., Dussaulx E., Lacroix B., Zweibaum A. The intracellular accumulation of UDP-N-acetylhexosamines is concomitant with the inability of human colon cancer cells to differentiate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Erickson R. H., Matsumoto H., Gum E., Kim Y. S. Expression of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV during enterocytic differentiation of human colon cancer (Caco-2) cells. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 1;47(6):916–921. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweibaum A., Pinto M., Chevalier G., Dussaulx E., Triadou N., Lacroix B., Haffen K., Brun J. L., Rousset M. Enterocytic differentiation of a subpopulation of the human colon tumor cell line HT-29 selected for growth in sugar-free medium and its inhibition by glucose. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]