Abstract
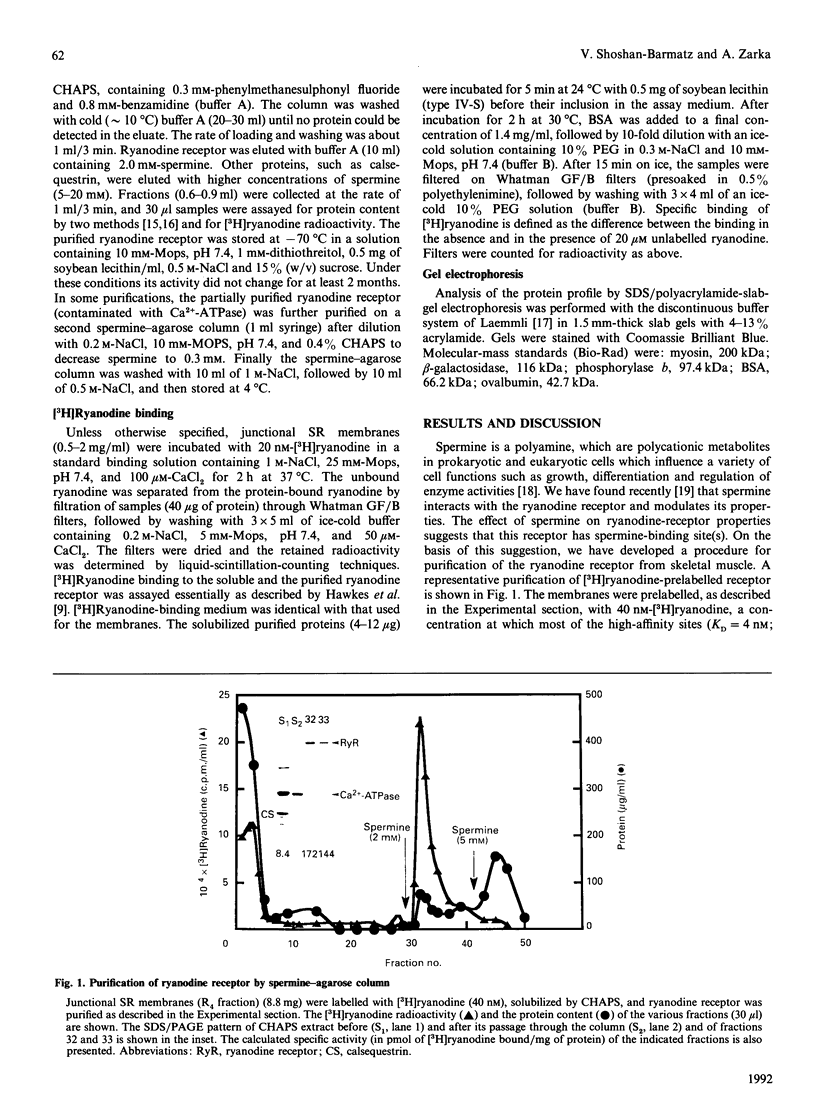
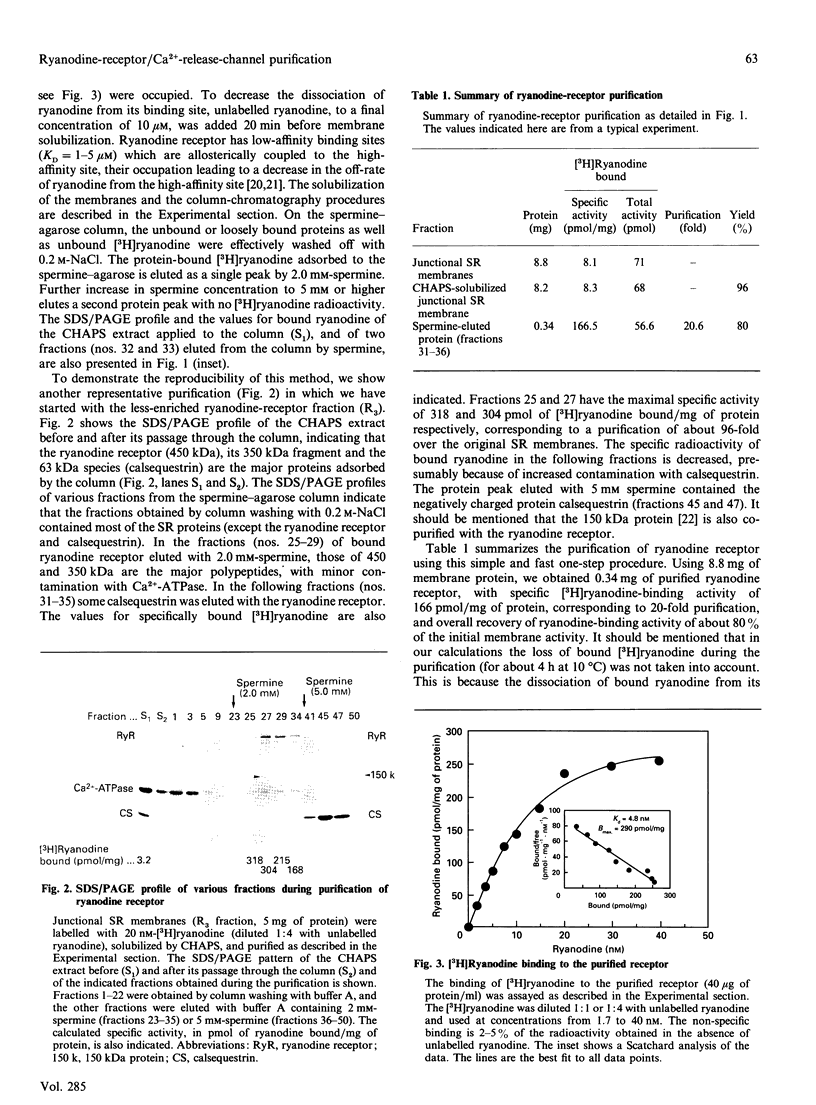
In this paper we describe a simple, fast, one-step method for the purification of the skeletal-muscle ryanodine receptor. The ryanodine receptor from CHAPS-solubilized junctional sarcoplasmic-reticulum membranes was adsorbed to a spermine-agarose column and eluted by 2 mM-spermine. The purified receptor, consisting predominantly of a 450 kDa polypeptide on SDS/PAGE, binds [3H]ryanodine with a specific activity of approximately 300 pmol/mg of protein and with a high affinity (KD = 4.7 +/- 2 nM). The purified receptor appears to retain the pharmacological properties of the receptor in the original membranes. The purification resulted in over 80% recovery of the initial ryanodine-binding sites and about 30-96-fold purification. This simple and fast method is highly reproducible and suitable for purification of small as well as large quantities of ryanodine receptor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell K. P., Knudson C. M., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Sutko J. L., Kahl S. D., Raab C. R., Madson L. Identification and characterization of the high affinity [3H]ryanodine receptor of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6460–6463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes M. J., Díaz-Muñoz M., Hamilton S. L. A procedure for purification of the ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. Membr Biochem. 1989;8(3):133–145. doi: 10.3109/09687688909025827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hymel L., Inui M., Fleischer S., Schindler H. Purified ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum forms Ca2+-activated oligomeric Ca2+ channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):441–445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Takasago T., Shigekawa M. Cardiac ryanodine receptor is absent in type I slow skeletal muscle fibers: immunochemical and ryanodine binding studies. J Biochem. 1989 Aug;106(2):342–348. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation of the ryanodine receptor from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and identity with the feet structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15637–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Anderson K., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Evidence for a Ca2+ channel within the ryanodine receptor complex from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Meissner G. The muscle ryanodine receptor and its intrinsic Ca2+ channel activity. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Apr;21(2):227–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00812070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Misra M., Xu L., Smith H. A., Meissner G. The ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for a cooperatively coupled, negatively charged homotetramer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16776–16785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew S. G., Wolleben C., Siegl P., Inui M., Fleischer S. Positive cooperativity of ryanodine binding to the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum from heart and skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1686–1691. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr I., Gechtman Z., Shoshan-Barmatz V. Characterization of Ca(2+)-dependent endogenous phosphorylation of 160,000- and 150,000-Dalton proteins of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1991 May 15;276(Pt 1):89–96. doi: 10.1042/bj2760089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Seiler S., Chu A., Fleischer S. Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):875–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuber F. Influence of polyamines on membrane functions. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2600001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P. The messenger across the gap. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):298–299. doi: 10.1038/316298b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]