Abstract
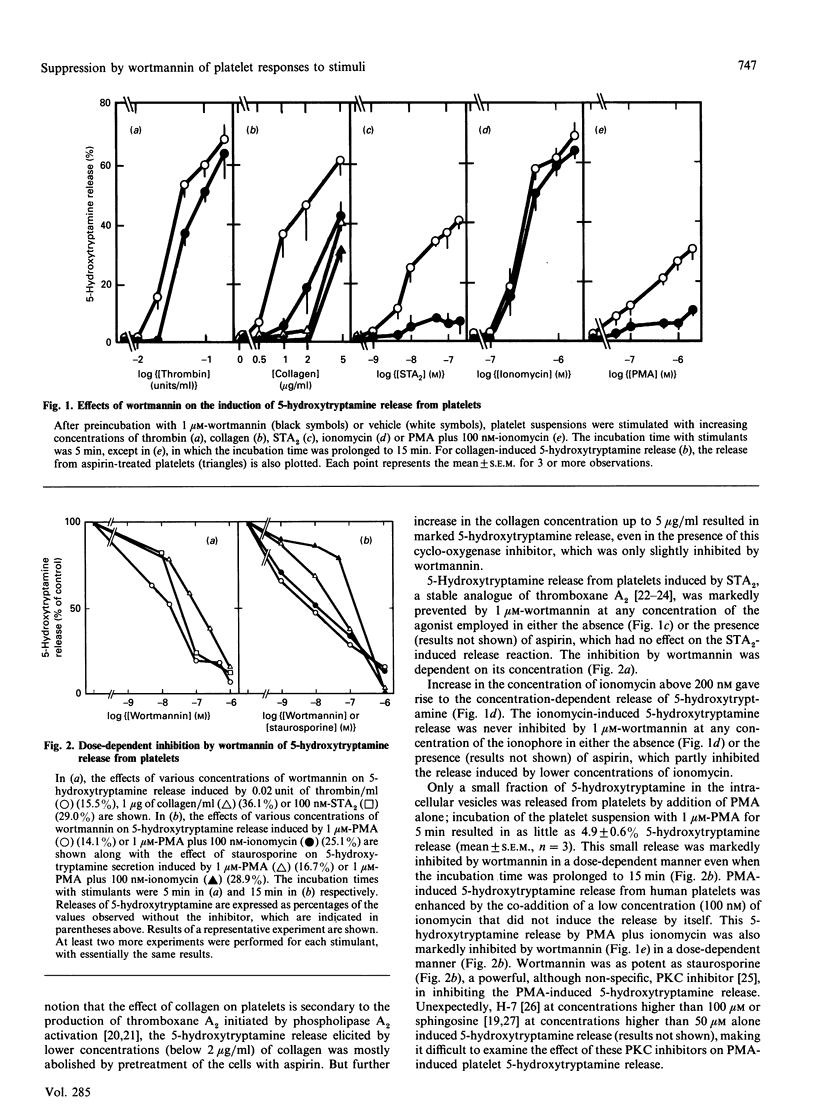
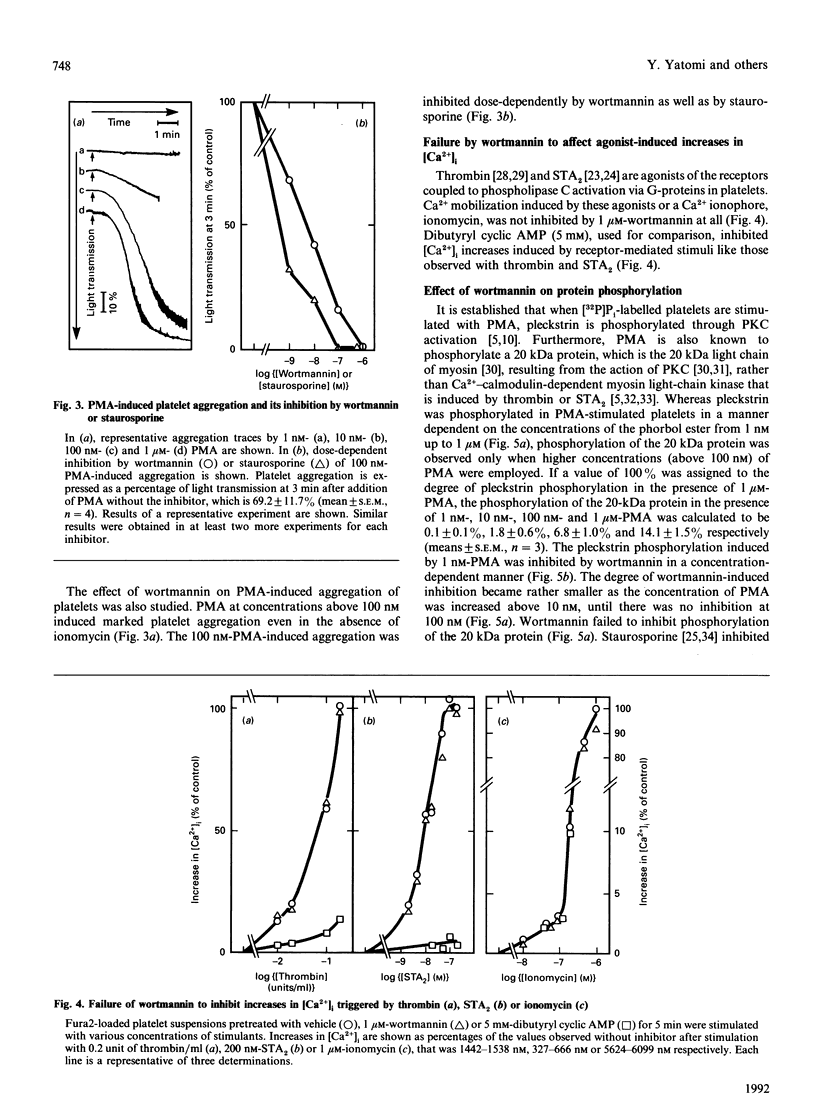
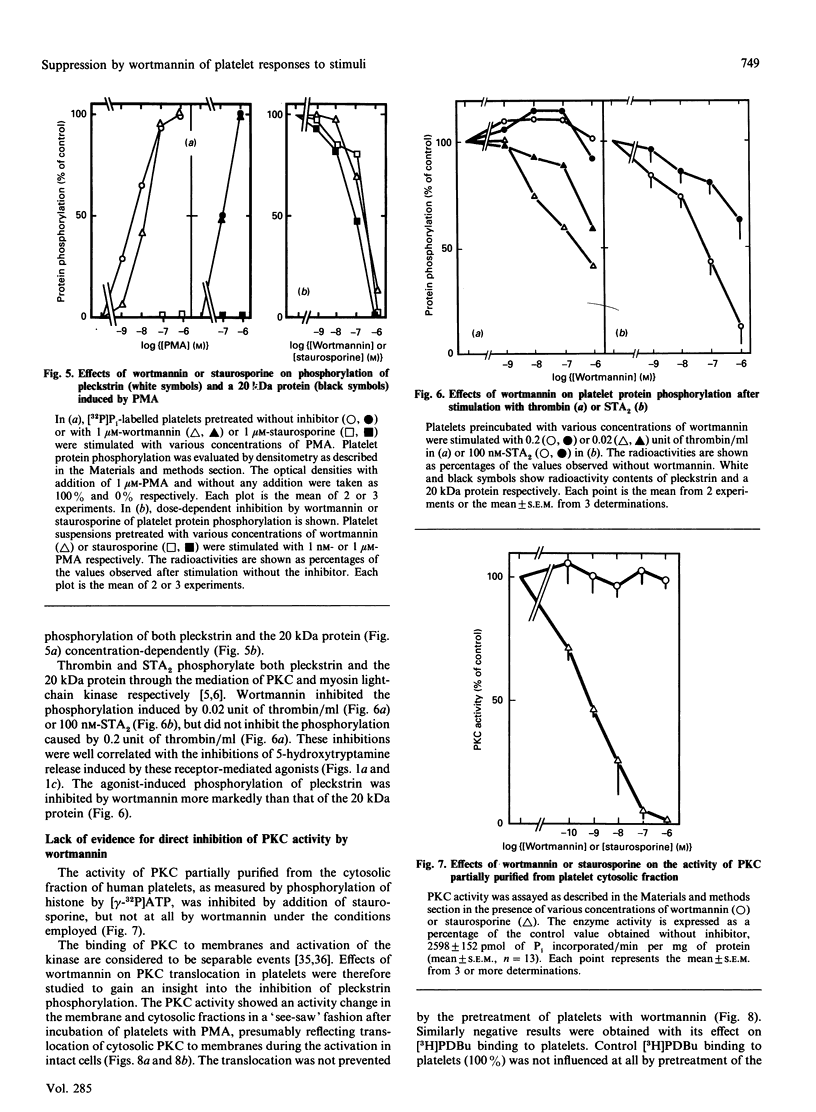
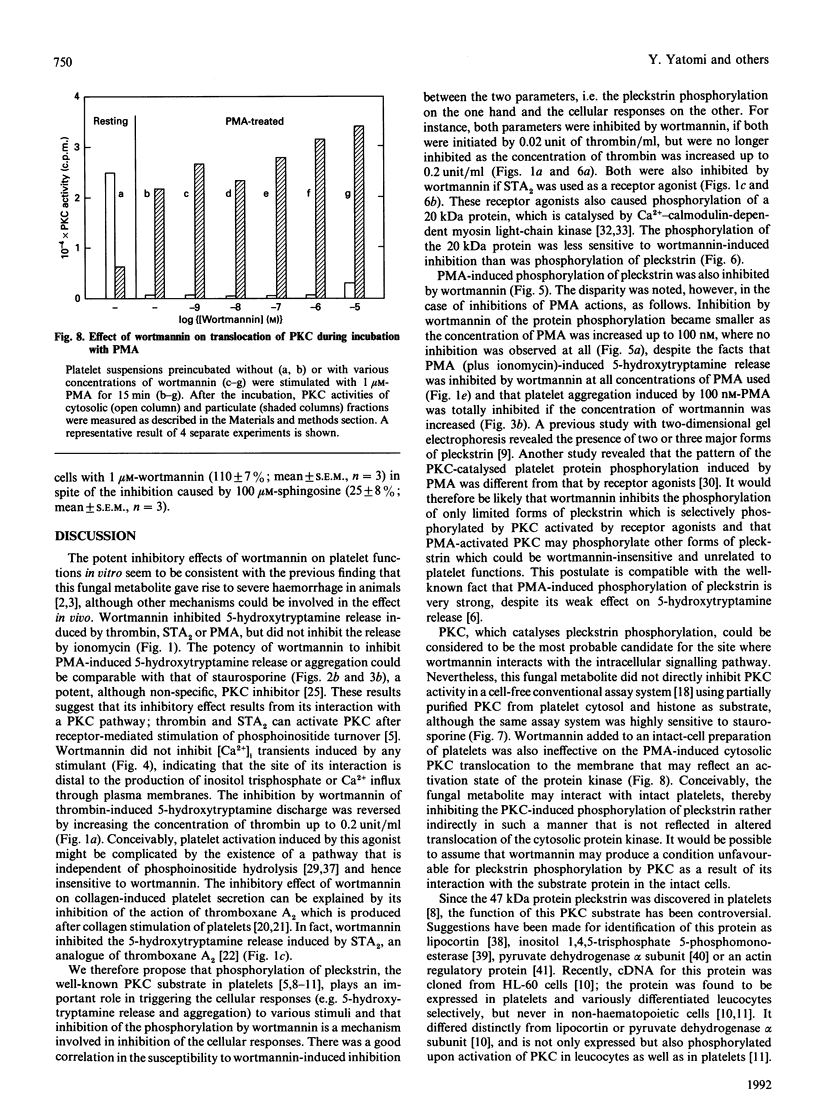
Studies were made of inhibition by wortmannin, a fungal metabolite, of human platelet responses to various stimuli. Wortmannin at concentrations as low as 1-100 nM inhibited several receptor-agonist-induced 5-hydroxytryptamine release from platelets, without affecting agonist-induced increases in the intracellular concentration of Ca2+. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), an active tumour promoter, caused 5-hydroxytryptamine release when combined with a low concentration of ionomycin, and platelet aggregation by itself; these effects of the phorbol ester were also inhibited by wortmannin as well as by staurosporine, a potent, although non-specific, protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, in a similar molar concentration range. The platelet responses to the receptor agonists or PMA were accompanied by increased incorporation of [32P]Pi into pleckstrin, a protein selectively expressed in platelets and other blood cells arising from haematopoietic stem cells, as a result of PKC activation in the intact cells. The pleckstrin phosphorylation was inhibited by wortmannin in ways mostly similar to those in which it inhibited the 5-hydroxytryptamine-release responses. Nevertheless, wortmannin failed to inhibit PKC activity measurable in a cell-free assay system which is highly susceptible to staurosporine. Nor did it inhibit the translocation of cytosolic PKC to membranes induced by addition of PMA to platelet cells. Thus wortmannin, which is not a direct inhibitor of PKC, could interfere with the kinase-dependent phosphorylation of pleckstrin, which may play an important role in the cellular responses to receptor stimulation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas H. K., Mirocha C. J., Gunther R. Mycotoxins produced by toxic Fusarium isolates obtained from agricultural and nonagricultural areas (Arctic) of Norway. Mycopathologia. 1989 Mar;105(3):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00437246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abbas H. K., Mirocha C. J. Isolation and purification of a hemorrhagic factor (wortmannin) from Fusarium oxysporum (N17B). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1268–1274. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1268-1274.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelstein R. S. Regulation of contractile proteins by phosphorylation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1863–1866. doi: 10.1172/JCI111148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balduini C. L., Bertolino G., Noris P., Sinigaglia F., Bisio A., Torti M. Interrelation of platelet aggregation, release reaction and thromboxane A2 production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):823–829. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80918-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Association of protein kinase C with phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):115–122. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Constitutive activity of membrane-inserted protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):336–343. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80719-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Rapid decrease of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12705–12708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. M., Kang E. S., Kang A. H. Identification of a 42K phosphoprotein of platelets modulated by collagen: the alpha-subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jan;252(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Rink T. J. Fluorescence and bioluminescence measurement of cytoplasmic free calcium. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):313–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2480313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Lawing W. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. Protein kinase C phosphorylates human platelet inositol trisphosphate 5'-phosphomonoesterase, increasing the phosphatase activity. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Thelen M., Baggiolini M. Two transduction sequences are necessary for neutrophil activation by receptor agonists. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16179–16184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailani D., Fisher T. C., Mills D. C., Macfarlane D. E. P47 phosphoprotein of blood platelets (pleckstrin) is a major target for phorbol ester-induced protein phosphorylation in intact platelets, granulocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes and cultured leukaemic cells: absence of P47 in non-haematopoietic cells. Br J Haematol. 1990 Feb;74(2):192–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther R., Abbas H. K., Mirocha C. J. Acute pathological effects on rats of orally administered wortmannin-containing preparations and purified wortmannin from Fusarium oxysporum. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989 Mar;27(3):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of agonist-dependent secretion and activation of human platelets implies that protein kinase C is a necessary and common event of the signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13620–13626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Hashimoto K., Im T., Tatsumi N., Okuda K., Yukioka M. Modulation of actin polymerization by 47,000-dalton protein of human platelets. Biochem Int. 1987 Apr;14(4):759–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatayama K., Kambayashi J., Kawasaki T., Morimoto K., Ohshiro T., Mori T. Interrelationship between secretion, protein phosphorylation and intracellular Ca2+ concentration in platelets stimulated by thrombin or thromboxane A2 analogue. Thromb Res. 1986 Mar 15;41(6):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90374-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Adelstein R. S. Human platelet myosin light chain kinase requires the calcium-binding protein calmodulin for activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1653–1657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashihara M., Maeda H., Shibata Y., Kume S., Ohashi T. A monoclonal anti-human platelet antibody: a new platelet aggregating substance. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):382–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Lynham J. A., Haslam R. J. Purification and characterization of the 47,000-dalton protein phosphorylated during degranulation of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11404–11414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. Serotonin secretion from human platelets may be modified by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent myosin phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14321–14323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Watanabe M., Hidaka H. N-(2-Aminoethyl)-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide, a newly synthesized protein kinase inhibitor, functions as a ligand in affinity chromatography. Purification of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent and other protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2922–2925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa N., Kikkawa U., Itoh K., Nishizuka Y. Membrane-permeable diacylglycerol, its application to platelet secretion, and regulation of platelet protein kinase C. Methods Enzymol. 1989;169:430–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)69079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Kaibuchi K., Tsuda T., Hoshijima M., Takai Y. Activation of protein kinase C by the action of 9,11-epithio-11,12-methano-thromboxane A2 (STA2), a stable analogue of thromboxane A2, in human platelets. Thromb Res. 1986 Mar 15;41(6):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Silió J., Ruggiero M. Thrombin induces serotonin secretion and aggregation independently of inositol phospholipids hydrolysis and protein phosphorylation in human platelets permeabilized with saponin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7078–7083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Dubernard V., Nurden A. T. Characteristics of collagen-induced fibrinogen binding to human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 14;812(3):802–810. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):924–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka M., Nishikawa M., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Phorbol ester-induced activation of human platelets is associated with protein kinase C phosphorylation of myosin light chains. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):490–492. doi: 10.1038/306490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate T., Jeng A. Y., Blumberg P. M. Comparison of protein kinase C functional assays to clarify mechanisms of inhibitor action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 15;37(8):1541–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Hanasaki K., Arita H. Possible involvement of cytoskeleton in collagen-stimulated activation of phospholipases in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5400–5406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touqui L., Rothhut B., Shaw A. M., Fradin A., Vargaftig B. B., Russo-Marie F. Platelet activation--a role for a 40K anti-phospholipase A2 protein indistinguishable from lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):177–180. doi: 10.1038/321177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Rachubinski R. A., Stewart M. I., Varrichio A. M., Shorr R. G., Haslam R. J., Harley C. B. Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):470–473. doi: 10.1038/333470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushikubi F., Nakajima M., Hirata M., Okuma M., Fujiwara M., Narumiya S. Purification of the thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16496–16501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


