Abstract
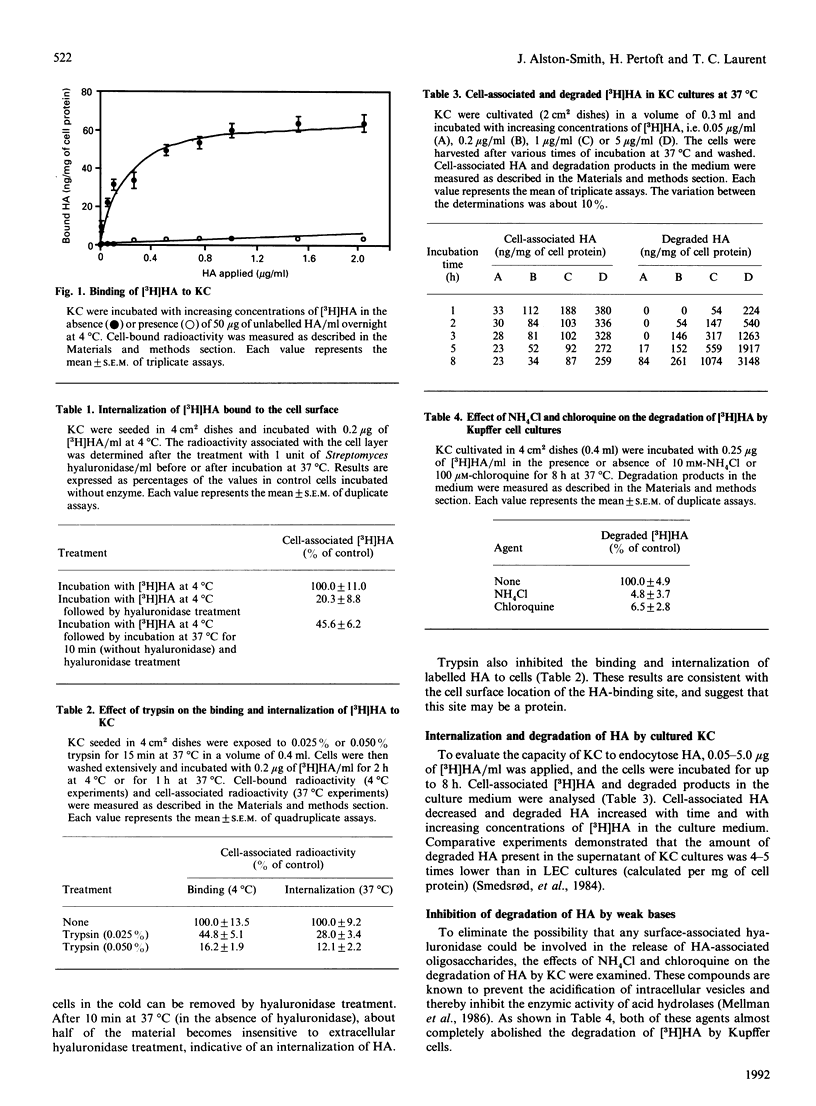
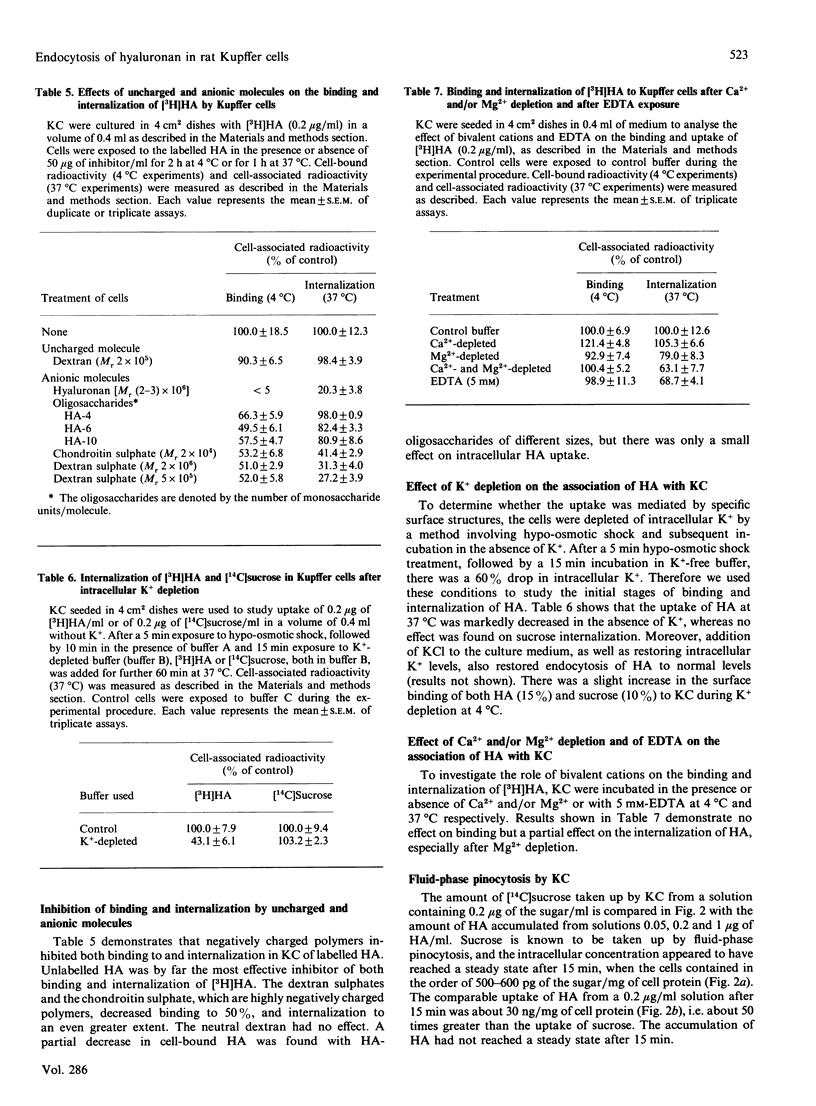
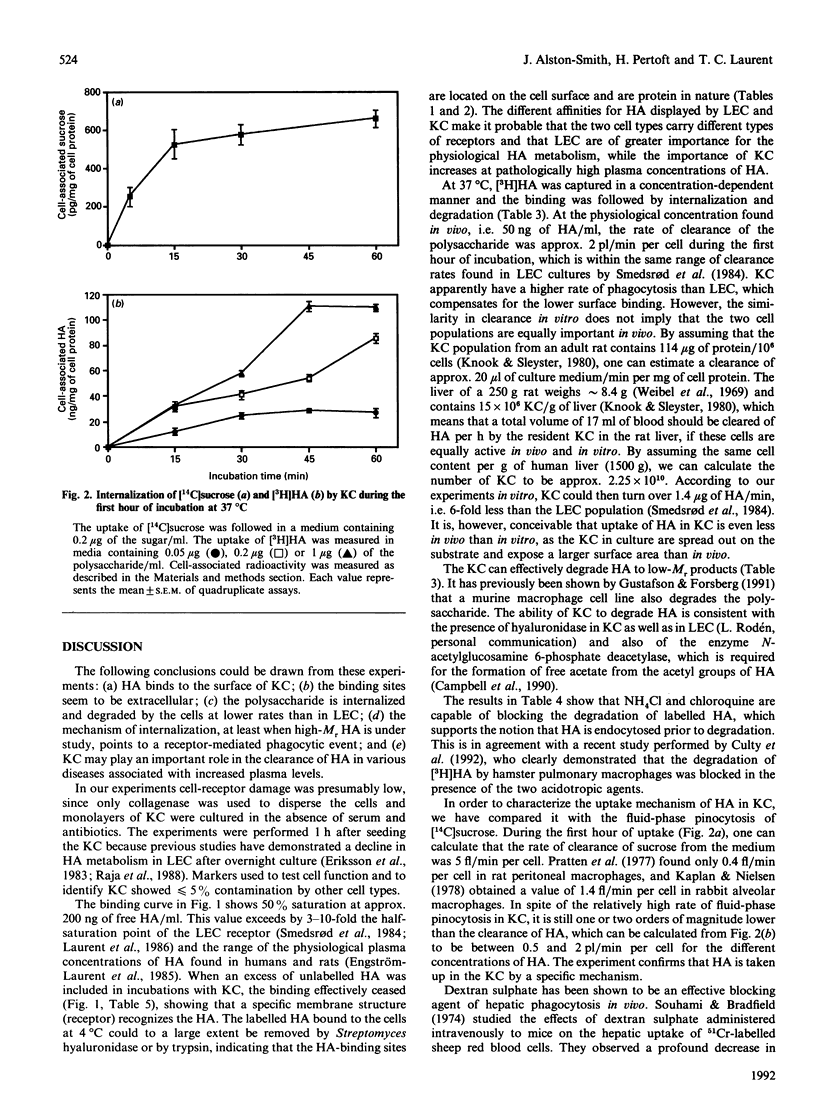
The binding, uptake and degradation of hyaluronan (HA) labelled with 3H in its acetyl group were studied in cultured rat Kupffer cells (KC). At 4 degrees C the binding increased with increasing concentrations of HA in the culture medium up to at least 1 microgram/ml, when saturation occurred. Binding could be prevented efficiently by the addition of an excess of unlabelled HA, and to a lesser extent by chondroitin sulphate and oligosaccharide fragments of HA, consisting of four sugars or more. The labelled HA bound to the cells could be removed by incubating the cells with Streptomyces hyaluronidase, or trypsin, indicating that the HA-binding sites are located on the cell surface. At 37 degrees C HA was internalized in a concentration-dependent manner, and degradation products appeared in the supernatant after 1-5 h, depending on the concentration applied. At 50 ng of free HA/ml, each KC accumulated 60 ag of the polysaccharide/min in the first 1 h, and degraded a total amount of 10 fg of HA during an 8 h period. Addition of the negatively charged polysaccharide dextran sulphate reduced binding, and to an even greater extent internalization, of HA in KC, while no effect was observed with dextran. Depletion of intracellular potassium caused a marked reduction in the rate of endocytosis of cell-membrane-associated HA into KC, without affecting binding. Addition of KCl to the culture medium returned endocytosis of [3H]HA to normal levels. There was no effect on binding and a partial effect on internalization by depletion of bivalent cations or in the presence of EDTA. The degradation of [3H]HA by KC cultures was abolished in the presence of weak bases, NH4Cl and chloroquine, supporting the idea that HA is endocytosed into lysosomes prior to degradation. The fluid-phase marker [14C]sucrose was internalized in the cells at much lower rate than was HA. Rates of binding, internalization and degradation of HA in KC point therefore to a specific endocytosis followed by an intracellular degradation to low-M(r) compounds. It was estimated that, under physiological conditions, KC only clear a minor proportion of circulating HA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggeler J., Werb Z. Initial events during phagocytosis by macrophages viewed from outside and inside the cell: membrane-particle interactions and clathrin. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):613–623. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlgren T., Jarstrand C. Hyaluronic acid enhances phagocytosis of human monocytes in vitro. J Clin Immunol. 1984 May;4(3):246–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00914973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Airhart J. A., Woodworth R. C., Low R. B. Exocytosis of pinocytosed fluid in cultured cells: kinetic evidence for rapid turnover and compartmentation. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):716–727. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P., Thompson J. N., Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C., Pertoft H., Rodén L. N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate deacetylase in hepatocytes, Kupffer cells and sinusoidal endothelial cells from rat liver. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):199–204. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culty M., Nguyen H. A., Underhill C. B. The hyaluronan receptor (CD44) participates in the uptake and degradation of hyaluronan. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. B., Laurent T. C., Smedsrød B. Preparation of biologically intact radioiodinated hyaluronan of high specific radioactivity: coupling of 125I-tyramine-cellobiose to amino groups after partial N-deacetylation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Dec;175(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das N., Basu M. K., Das M. K. Suppression of liver uptake of orally fed liposomes by injection (i.p.) of dextran sulfate 500. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jun;7(6):465–470. doi: 10.1007/BF01116502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A. Changes in hyaluronan concentration in tissues and body fluids in disease states. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:233-40; discussion 240-7, 281-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470513774.ch14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Laurent U. B., Lilja K., Laurent T. C. Concentration of sodium hyaluronate in serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Oct;45(6):497–504. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson S., Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C., Pertoft H., Smedsrød B. Endothelial cells are a site of uptake and degradation of hyaluronic acid in the liver. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Mar;144(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester J. V., Balazs E. A. Inhibition of phagocytosis by high molecular weight hyaluronate. Immunology. 1980 Jul;40(3):435–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., Alcorn D., Laurent T. C., Robinson A. D., Ryan G. B. Uptake of circulating hyaluronic acid by the rat liver. Cellular localization in situ. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(3):505–510. doi: 10.1007/BF00225415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C., Pertoft H., Baxter E. Plasma clearance, tissue distribution and metabolism of hyaluronic acid injected intravenously in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 15;200(2):415–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2000415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C. Turnover and metabolism of hyaluronan. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:41-53; discussion 53-9, 281-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. L., Roll F. J. Isolation and culture of hepatic lipocytes, Kupffer cells, and sinusoidal endothelial cells by density gradient centrifugation with Stractan. Anal Biochem. 1987 Feb 15;161(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. J., Raja R. H., Weigel P. H. Characterization of an intracellular hyaluronic acid binding site in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10425–10432. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S. J., Tarone G., Underhill C. B. Aggregation of macrophages and fibroblasts is inhibited by a monoclonal antibody to the hyaluronate receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90393-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson S., Forsberg N. Hyaluronan-binding proteins on cultured J 774 macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90218-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Nielsen M. Pinocytic activity of rabbit alveolar macrophages in vitro. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Dec;24(6):673–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knook D. L., Sleyster E. C. Isolated parenchymal, Kupffer and endothelial rat liver cells characterized by their lysosomal enzyme content. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):250–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G. Depletion of intracellular potassium arrests coated pit formation and receptor-mediated endocytosis in fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Fraser J. R., Pertoft H., Smedsrød B. Binding of hyaluronate and chondroitin sulphate to liver endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):653–658. doi: 10.1042/bj2340653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. The biology of hyaluronan. Introduction. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love S. H., Shannon B. T., Myrvik Q. N., Lynn W. S. Characterization of macrophage agglutinating factor as a hyaluronic acid-protein complex. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Mar;25(3):269–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Sandvig K., Olsnes S., van Deurs B. Effect of reduced endocytosis induced by hypotonic shock and potassium depletion on the infection of Hep 2 cells by picornaviruses. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):14–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Berg T. Extremely rapid endocytosis mediated by the mannose receptor of sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):651–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2570651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. The entry of enveloped viruses into cells by endocytosis. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGary C. T., Raja R. H., Weigel P. H. Endocytosis of hyaluronic acid by rat liver endothelial cells. Evidence for receptor recycling. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):875–884. doi: 10.1042/bj2570875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munniksma J., Noteborn M., Kooistra T., Stienstra S., Bouma J. M., Gruber M., Brouwer A., Praaning-van Dalen Dalen D., Knook D. L. Fluid endocytosis by rat liver and spleen. Experiments with 125I-labelled poly(vinylpyrrolidone) in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):613–621. doi: 10.1042/bj1920613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. R., Li M. P., Baldeschwieler J. D. Suppression of liver uptake of liposomes by dextran sulfate 500. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6518–6522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratten M. K., Williams K. E., Lloyd J. B. A quantitative study of pinocytosis and intracellular proteolysis in rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):365–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1680365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja R. H., McGary C. T., Weigel P. H. Affinity and distribution of surface and intracellular hyaluronic acid receptors in isolated rat liver endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16661–16668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Pertoft H., Eriksson S., Fraser J. R., Laurent T. C. Studies in vitro on the uptake and degradation of sodium hyaluronate in rat liver endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):617–626. doi: 10.1042/bj2230617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Pertoft H., Gustafson S., Laurent T. C. Scavenger functions of the liver endothelial cell. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):313–327. doi: 10.1042/bj2660313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Bradfield J. W. The recovery of hepatic phagocytosis after blockade of Kupffer cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1974 Aug;16(2):75–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. Quantitative studies of phagocytosis. Kinetic effects of cations and heat-labile opsonin. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):346–356. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underhill C. B. The interaction of hyaluronate with the cell surface: the hyaluronate receptor and the core protein. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;143:87-99; discussion 100-6, 281-5. doi: 10.1002/9780470513774.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underhill C. B., Toole B. P. Binding of hyaluronate to the surface of cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):475–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. Properties of fractionated chondroitin sulphate from ox nasal septa. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):477–485. doi: 10.1042/bj1220477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


