Abstract
The bis-D-mannose photolabel ATB-BMPA (2-N-[4-(1-azi-2,2,2- trifluoroethyl)benzoyl]-1,3-bis-(D-mannos-4-yloxy) propyl-2-amine) has been used to radiolabel the glucose transporter present in liver plasma membranes. The labelling was inhibited by 4,6-O-ethylidene-D-glucose. Approx. 7% of the liver plasma-membrane protein that was photolabelled in a 4,6-O-ethylidene-D-glucose-inhibitable manner was specifically immunoprecipitated by either an anti-(GLUT2 C-terminal peptide) antibody or by an anti-(GLUT2 exofacial-loop peptide) antibody. After correction for non-specific labelling and precipitation, the ratio of immunoprecipitable GLUT2 to GLUT1 was approximately 5:1, suggesting that GLUT1 was not a major component of liver plasma membranes. The low levels of immunoprecipitation of the photolabelled transporter may be due to low antibody affinity for GLUT2 or may indicate that the photolabelling reagent has labelled another glucose-transporter-like protein. The hexose-transport inhibitors phloretin, cytochalasin B and 4,6-O-ethylidene-D-glucose all inhibited the photolabelling by ATB-BMPA of immunoprecipitable GLUT2. D-Glucose inhibited approx. 57% of the ATB-BMPA labelling of GLUT2. D-Fructose also inhibited the GLUT2 labelling confirming that it is a substrate for GLUT2 [Gould, Thomas, Jess & Bell (1991) Biochemistry 30, 5139-5145]. From photolabel displacement by a range of concentrations of non-labelled ATB-BMPA, the affinity constant (Kd) of ATB-BMPA was found to be 250 +/- 78 microM, whereas the Bmax. (total number of binding sites) value was 2.1 +/- 0.29 pmol of GLUT2/mg of membrane protein. Since GLUT1, GLUT4 and GLUT2 have approximately equal affinities for the external ligand ATB-BMPA, but have widely varying affinities for equilibrated and transported substrates, it is suggested that the isoforms may differ in their ability to bind hexoses at the internal site.
Full text
PDF


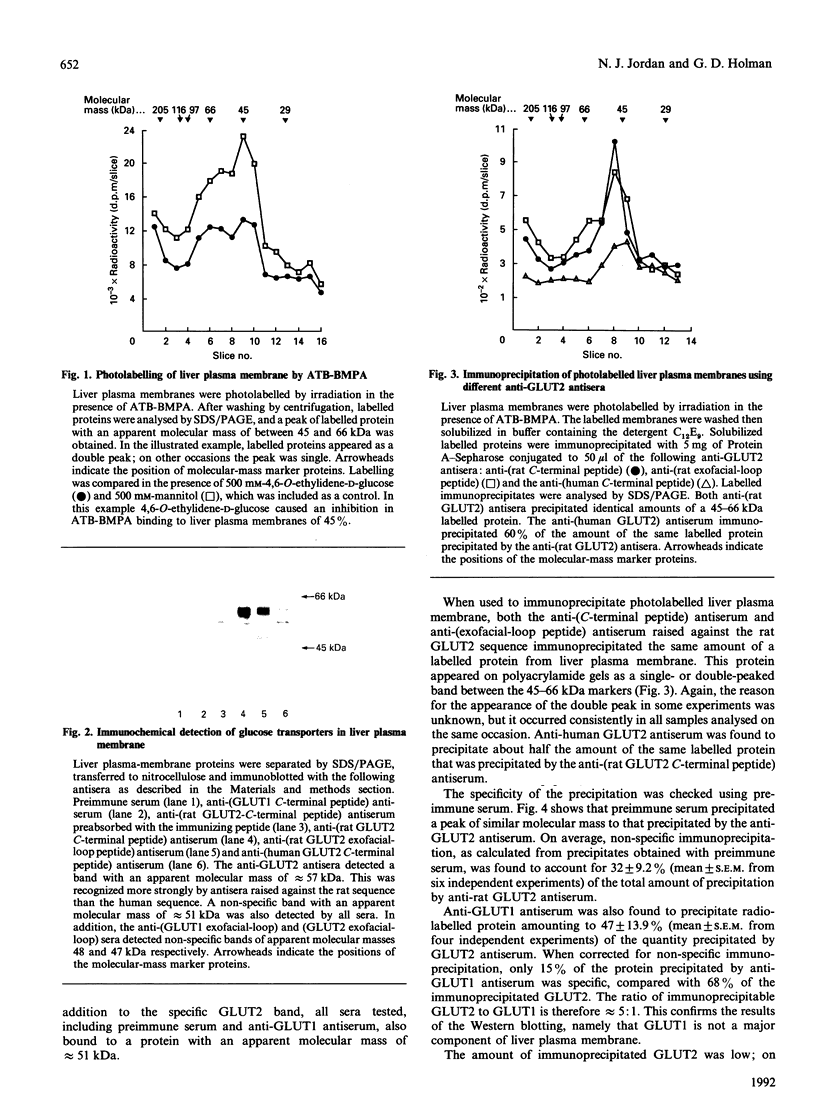
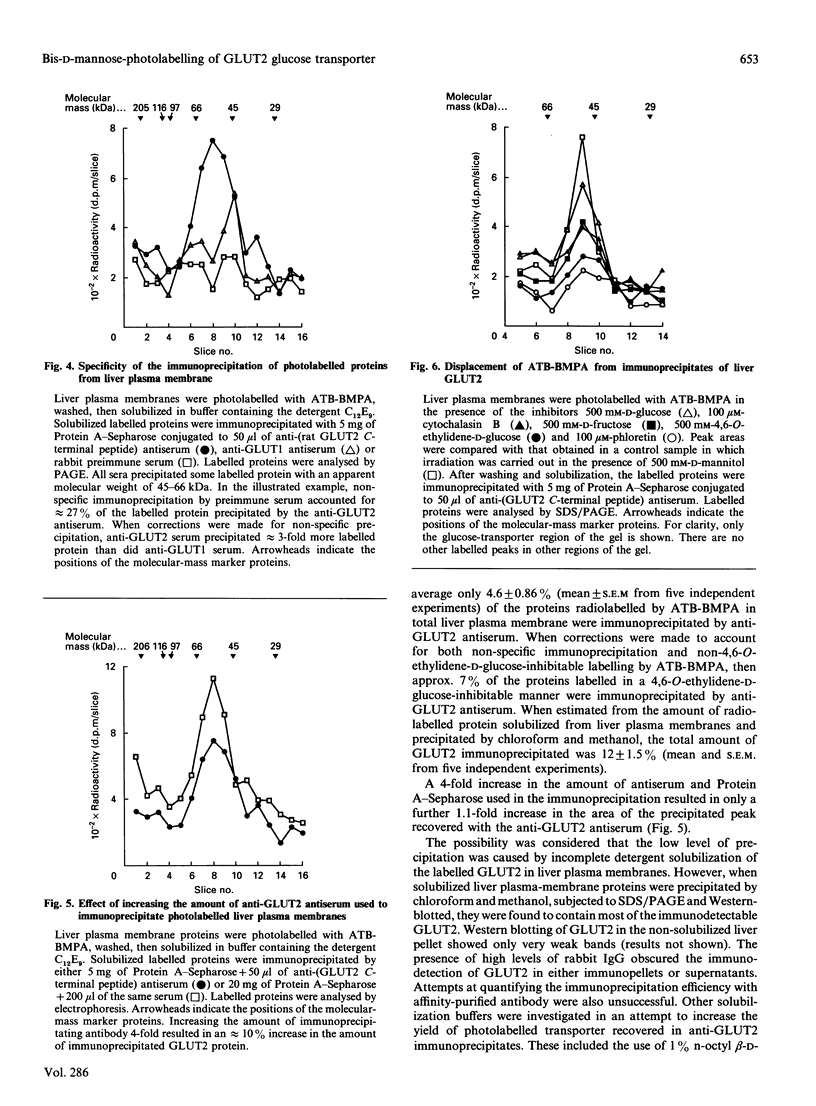
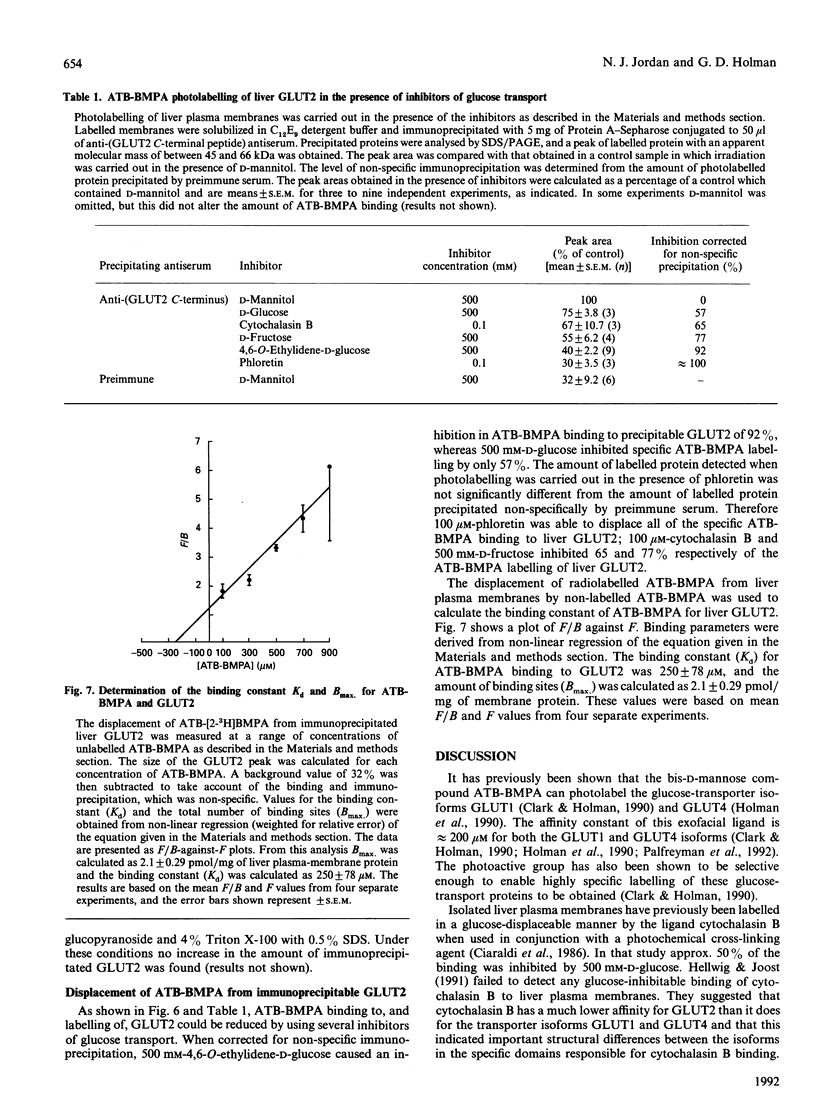


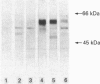
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. D., Pilch P. F. Unique cytochalasin B binding characteristics of the hepatic glucose carrier. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2222–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basketter D. A., Widdas W. F. Asymmetry of the hexose transfer system in human erythrocytes. Comparison of the effects of cytochalasin B, phloretin and maltose as competitive inhibitors. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:389–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Lienhard G. E. Labeling of glucose transporters at the cell surface in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evidence for both translocation and a second mechanism in the insulin stimulation of transport. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12171–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaraldi T. P., Horuk R., Matthaei S. Biochemical and functional characterization of the rat liver glucose-transport system. Comparisons with the adipocyte glucose-transport system. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):115–123. doi: 10.1042/bj2400115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. E., Holman G. D. Exofacial photolabelling of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter with an azitrifluoroethylbenzoyl-substituted bismannose. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj2690615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. E., Holman G. D., Kozka I. J. Determination of the rates of appearance and loss of glucose transporters at the cell surface of rat adipose cells. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):235–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2780235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik J. D., Elliott K. R. Kinetics of 3-O-methyl-D-glucose transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):503–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1820503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Meeran K., Cairns M. T., Baldwin S. A. Peptide-specific antibodies as probes of the orientation of the glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9347–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devés R., Krupka R. M. Cytochalasin B and the kinetics of inhibition of biological transport: a case of asymmetric binding to the glucose carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 4;510(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott K. R., Craik J. D. Sugar transport across the hepatocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Soc Trans. 1982 Feb;10(1):12–13. doi: 10.1042/bst0100012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Bell G. I. Facilitative glucose transporters: an expanding family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jan;15(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90125-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Thomas H. M., Jess T. J., Bell G. I. Expression of human glucose transporters in Xenopus oocytes: kinetic characterization and substrate specificities of the erythrocyte, liver, and brain isoforms. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5139–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Pilkis S. The genes of hepatic glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10173–10176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellwig B., Joost H. G. Differentiation of erythrocyte-(GLUT1), liver-(GLUT2), and adipocyte-type (GLUT4) glucose transporters by binding of the inhibitory ligands cytochalasin B, forskolin, dipyridamole, and isobutylmethylxanthine. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Rees W. D. Photolabelling of the hexose transporter at external and internal sites: fragmentation patterns and evidence for a conformational change. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Mar 12;897(3):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D. Side-specific photolabelling of the hexose transporter. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Jun;17(3):438–440. doi: 10.1042/bst0170438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Crider B. P., McCorkle K., Alford M., Unger R. H. Inhibition of glucose transport into rat islet cells by immunoglobulins from patients with new-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 8;322(10):653–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003083221003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Ogawa A., Chen L., Orci L., Newgard C. B., Alam T., Unger R. H. Underexpression of beta cell high Km glucose transporters in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.2237405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatsuna T., Baekkeskov S., Lernmark A., Ludvigsson J. Immunoglobulin from insulin-dependent diabetic children inhibits glucose-induced insulin release. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):520–524. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Kanatsuna T., Kajiyama S., Nakamura N., Nakamura Y., Kano Y., Nakano K., Kondo M., Ludvigsson J. Islet cell surface antibodies preferentially inhibit glucose-stimulated insulin release in vitro. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1990 Apr;9(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(90)90003-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. Family of glucose-transporter genes. Implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):6–11. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno Y., Gliemann J. Transport of glucose and fructose in rat hepatocytes at 37 degrees C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 17;862(2):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H., Ravazzola M., Ogawa A., Komiya I., Baetens D., Lodish H. F., Thorens B. Reduced beta-cell glucose transporter in new onset diabetic BB rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1615–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI114883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman R. W., Clark A. E., Denton R. M., Holman G. D., Kozka I. J. Kinetic resolution of the separate GLUT1 and GLUT4 glucose transport activities in 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem J. 1992 May 15;284(Pt 1):275–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2840275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpić V., Green K. C., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Vasopressin-, angiotensin II-, and alpha 1-adrenergic-induced inhibition of Ca2+ transport by rat liver plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1382–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Cheng Z. Q., Brown D., Lodish H. F. Liver glucose transporter: a basolateral protein in hepatocytes and intestine and kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C279–C285. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Differential localization of two glucose transporter isoforms in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C286–C294. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga M., Komiya I., Johnson J. H., Inman L., Alam T., Moltz J., Crider B., Stefan Y., Baetens D., McCorkle K. Loss of insulin response to glucose but not arginine during the development of autoimmune diabetes in BB/W rats: relationships to islet volume and glucose transport rate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9749–9753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H. Diabetic hyperglycemia: link to impaired glucose transport in pancreatic beta cells. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1200–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.2006409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]