Abstract
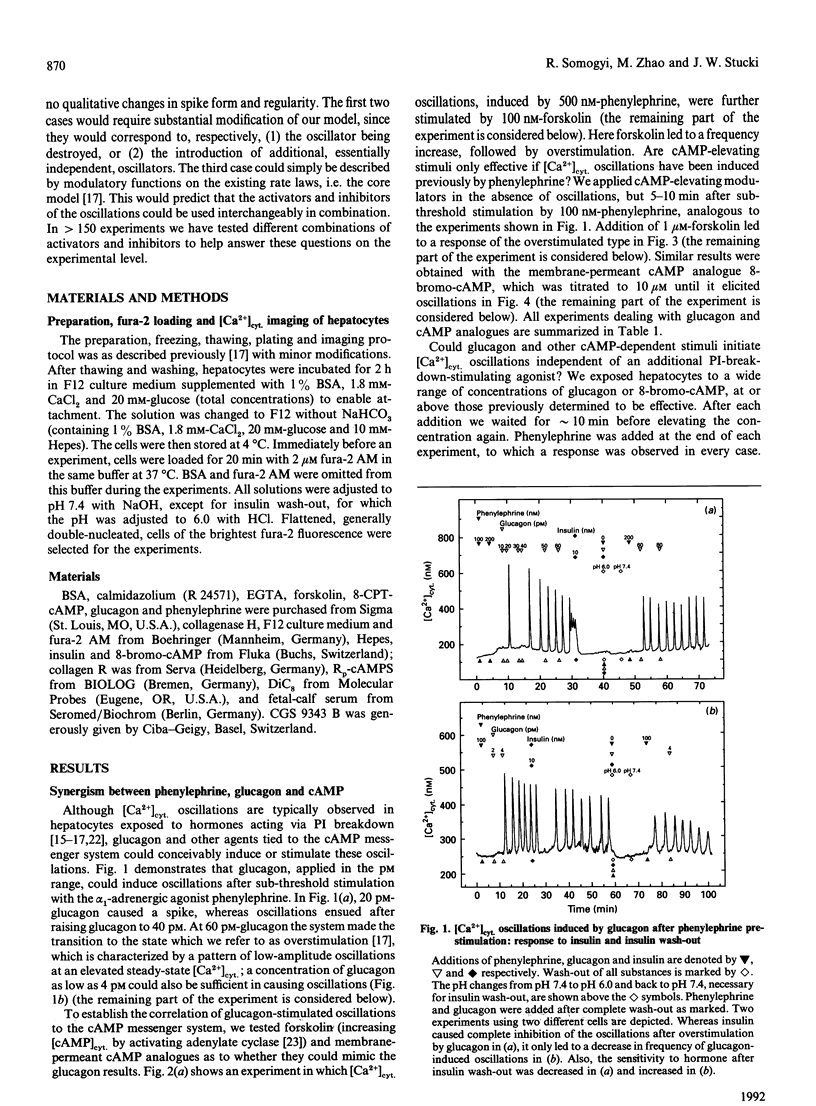
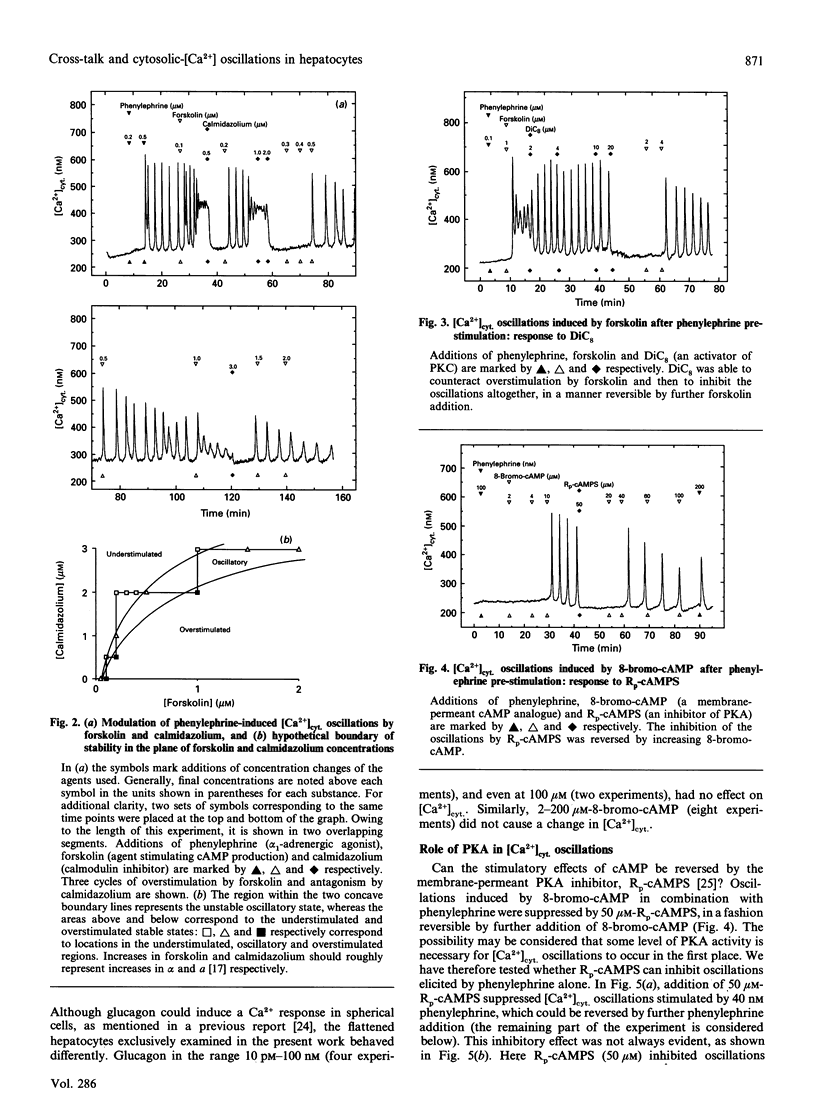
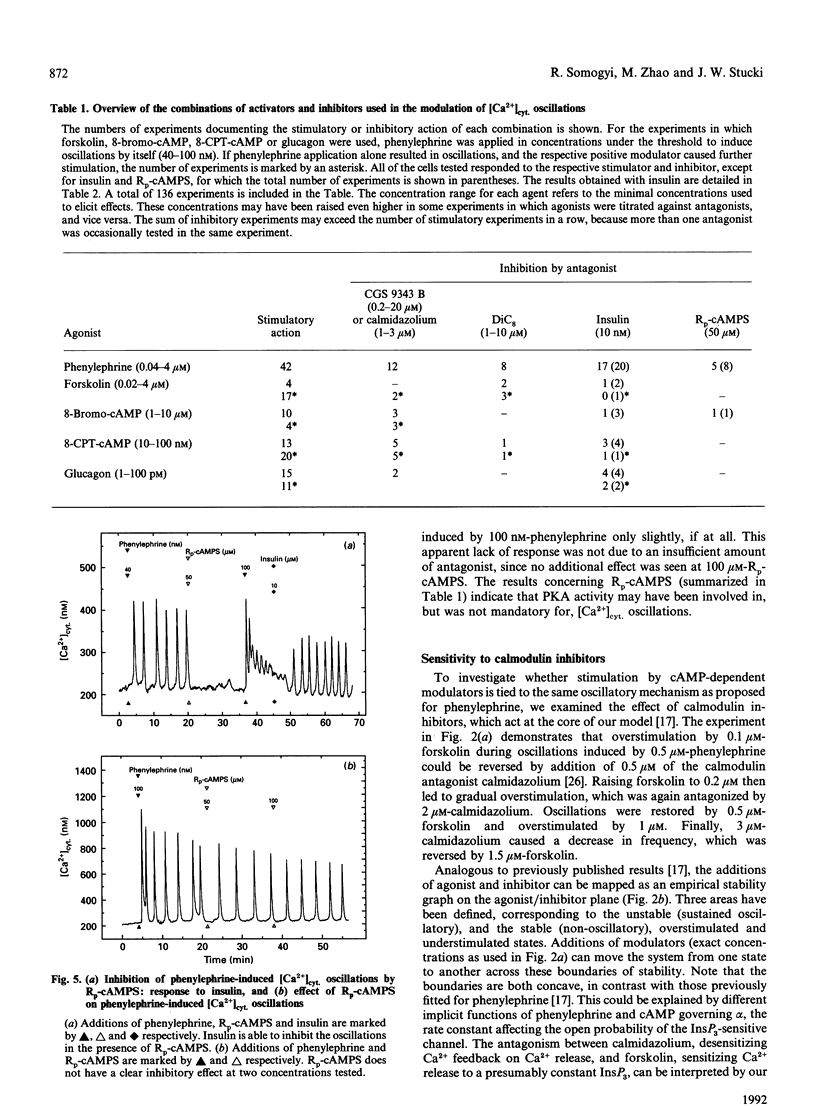
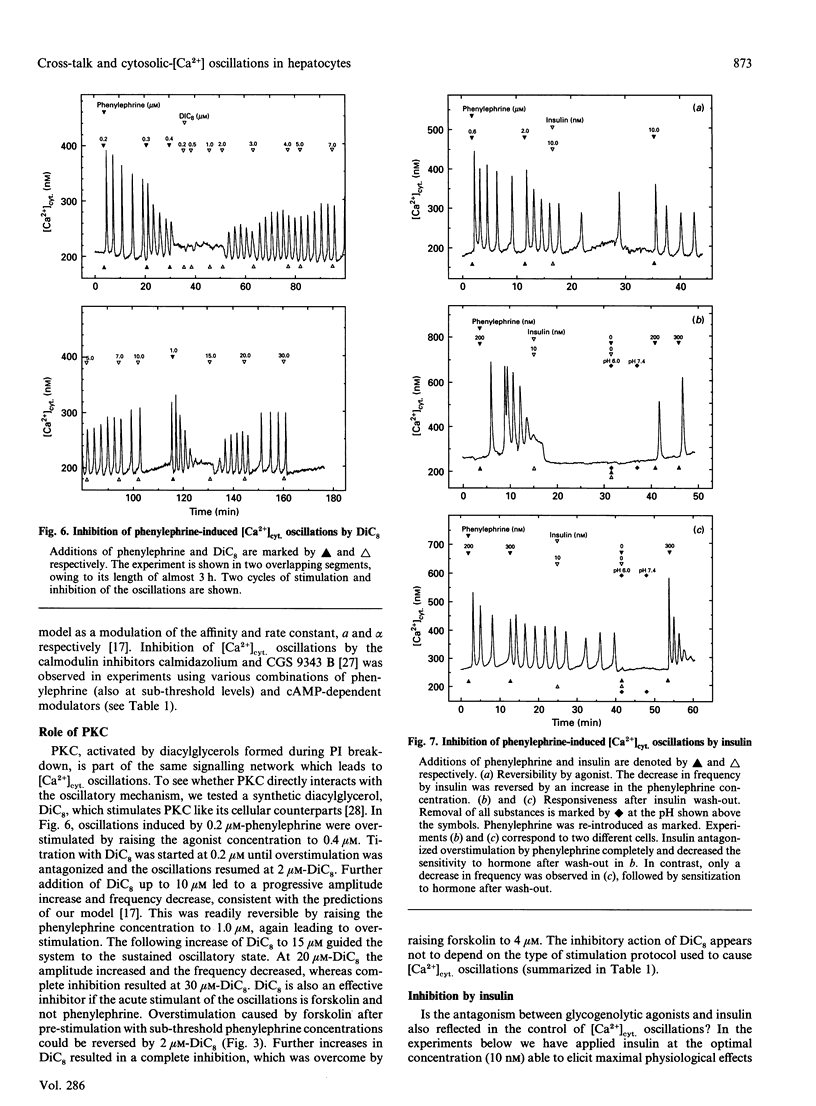
Hepatocytes respond to stimulation by glycogenolytic agonists acting via phosphoinositide (PI) breakdown through oscillations of the free cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ ([Ca2+]cyt.). Since the second-messenger repertoire of hepatocytes includes many other factors besides Ca2+, we investigated to what degree the regulation of [Ca2+]cyt. oscillations is integrated into these other signalling systems. [Ca2+]cyt. was recorded in single rat hepatocytes by using the Ca(2+)-indicator fura-2. Parallel stimulation with phenylephrine (an alpha 1-adrenergic agonist of PI breakdown) and glucagon resulted in a synergistic stimulation of [Ca2+]cyt. oscillations. Direct activation of the cyclic-AMP-dependent pathway with several stimuli (forskolin, 8-bromo cyclic AMP, 8-CPT cyclic AMP) mimicked the response to glucagon. In contrast, [Ca2+]cyt. oscillations induced by various combinations of these agonists could be antagonized by the glycogenic hormone insulin. As one of the options in the insulin-signalling network, we tested a diacylglycerol activator of protein kinase C, DiC8. It also acted as an inhibitor of [Ca2+]cyt. oscillations. We investigated how these observations could be reconciled with our previously introduced model of [Ca2+]cyt. oscillations in hepatocytes [Somogyi and Stucki (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 11068-11077]. First of all, the effect of calmodulin inhibitors (calmidazolium and CGS 9343 B), acting at the core of our model on the feedback of Ca2+ on Ins(1,4,5)P3-induced Ca2+ release, was not altered by the new modulators. In addition, all agonists and antagonists could be used interchangeably in combination and introduced no significant change in the oscillatory pattern or spike shape. Since the response was solely limited to frequency modulation, over- or understimulation of the oscillatory system, there is no need to create a new oscillator or to introduce further reaction steps into the core of the model. We conclude that the regulation of [Ca2+]cyt. via the explored second-messenger pathways can be embedded into the oscillatory system as modulation of rate constants already present in this model.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):325–343. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F., Bouscarel B., Slaton J., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Epidermal growth factor mimics insulin effects in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):523–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2390523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botelho L. H., Rothermel J. D., Coombs R. V., Jastorff B. cAMP analog antagonists of cAMP action. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:159–172. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Bird G. S., Obie J. F., Putney J. W., Jr The mechanism for synergism between phospholipase C- and adenylylcyclase-linked hormones in liver. Cyclic AMP-dependent kinase augments inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ mobilization without increasing the cellular levels of inositol polyphosphates. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4772–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Berthon B., Binet A., Claret M. Glucagon and vasopressin interactions on Ca2+ movements in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):675–683. doi: 10.1042/bj2370675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. A., Botelho L. H., Sisk R. B., Garrison J. C. A study of the mechanism of glucagon-induced protein phosphorylation in isolated rat hepatocytes using (Sp)-cAMPS and (Rp)-cAMPS, the stimulatory and inhibitory diastereomers of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphorothioate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4324–4332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Hernandez H., Kuo J. Y., Farese R. V. Insulin increases the synthesis of phospholipid and diacylglycerol and protein kinase C activity in rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 1;276(2):486–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90749-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehaye J. P., Hughes B. P., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Insulin inhibition of alpha-adrenergic actions in liver. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):949–956. doi: 10.1042/bj1940949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V. Phospholipid signaling systems in insulin action. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong B. R., Loomis C. R., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Specificity and mechanism of protein kinase C activation by sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan A., Prentki M., Knowles B. B. EGF receptor down-regulation attenuates ligand-induced second messenger formation. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Mar;187(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90127-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harootunian A. T., Kao J. P., Paranjape S., Tsien R. Y. Generation of calcium oscillations in fibroblasts by positive feedback between calcium and IP3. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1986413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. D., Campos-Gonzalez R., Kindmark H., Boynton A. L. Inhibition of inositol trisphosphate-stimulated calcium mobilization by calmodulin antagonists in rat liver epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16479–16484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B., Jotterand D., Nouspikel T., Asfari M., Pilot P. R. Transcriptional induction of glucokinase gene by insulin in cultured liver cells and its repression by the glucagon-cAMP system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21824–21829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. Calcium oscillations in electrically non-excitable cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi T., Blank L. M., Harootunian A. T., Smith M. T., Tsien R. Y. Ca2+ oscillations induced by hormonal stimulation of individual fura-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12859–12866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J. Insulin-signaling mechanisms. Lessons from the old testament of glycogen metabolism and the new testament of molecular biology. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):262–275. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Marty A. Protein kinase C activators inhibit the inositol trisphosphate-mediated muscarinic current responses in rat lacrimal cells. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:239–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchoff C. D., Huang L., Gillespie N., Palasi C. V., Schwartz C. F., Cheng K., Hewlett E. L., Larner J. A putative mediator of insulin action which inhibits adenylate cyclase and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase: partial purification from rat liver: site and kinetic mechanism of action. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1327–1337. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Potentiation of alpha 1-adrenergic responses in rat liver by a cAMP-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin O., Fehlmann M., Freychet P. Binding and action of insulin and glucagon in monolayer cultures and fresh suspensions of rat hepatocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Mar;25(3):339–352. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J. A., Ansell J., Stone G. A., Wennogle L. P., Wasley J. W. CGS 9343B, a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of calmodulin activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 May;31(5):535–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Guanosine 5'-O-(thiotriphosphate)-dependent inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes is inhibited by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1638–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Mauger J. P., Claret M. Effect of cyclic AMP-dependent hormones and Ca2+-mobilizing hormones on the Ca2+ influx and polyphosphoinositide metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):663–669. doi: 10.1042/bj2350663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reber B. F., Somogyi R., Stucki J. W. Hormone-induced intracellular calcium oscillations and mitochondrial energy supply in single hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 25;1018(2-3):190–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90246-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Sass E. J., Thomas A. P. Characterization of cytosolic calcium oscillations induced by phenylephrine and vasopressin in single fura-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17131–17141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. J. Recent progress in our understanding of the mechanism of action of insulin. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(9):897–908. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R. Insulin generates an enzyme modulator from hepatic plasma membranes: regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):967–972. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Bueno A., Dixon C. J., Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Inhibitors of protein kinase C prolong the falling phase of each free-calcium transient in a hormone-stimulated hepatocyte. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 15;268(3):627–632. doi: 10.1042/bj2680627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Cripe T. P., Koch S. R., Andreone T. L., Petersen D. D., Beale E. G., Granner D. K. Multihormonal regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene transcription. The dominant role of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15242–15251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöfl C., Sanchez-Bueno A., Brabant G., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Frequency and amplitude enhancement of calcium transients by cyclic AMP in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):799–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2730799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Uhing R. J., Snyderman R. Nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated activation of phospholipase C in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes is disrupted by phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6121–6127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi R., Stucki J. W. Hormone-induced calcium oscillations in liver cells can be explained by a simple one pool model. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11068–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. M., Hansford R. G. 4 beta-Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate attenuates the glucagon-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):737–743. doi: 10.1042/bj2380737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Danoff S. K., Theibert A., Joseph S. K., Steiner J., Snyder S. H. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of a brain inositol trisphosphate receptor decreases its release of calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8747–8750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Martin-Requero A., Williamson J. R. Interactions between insulin and alpha 1-adrenergic agents in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5963–5973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Williamson J. R. Effects of insulin on phenylephrine-induced activation of phosphorylase and phosphatidylinositol turnover in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1411–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Calcium channels, stores, and oscillations. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:715–760. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Fluorescence measurement and photochemical manipulation of cytosolic free calcium. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Phorbol-ester-induced alterations of free calcium ion transients in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):619–623. doi: 10.1042/bj2460619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


