Abstract
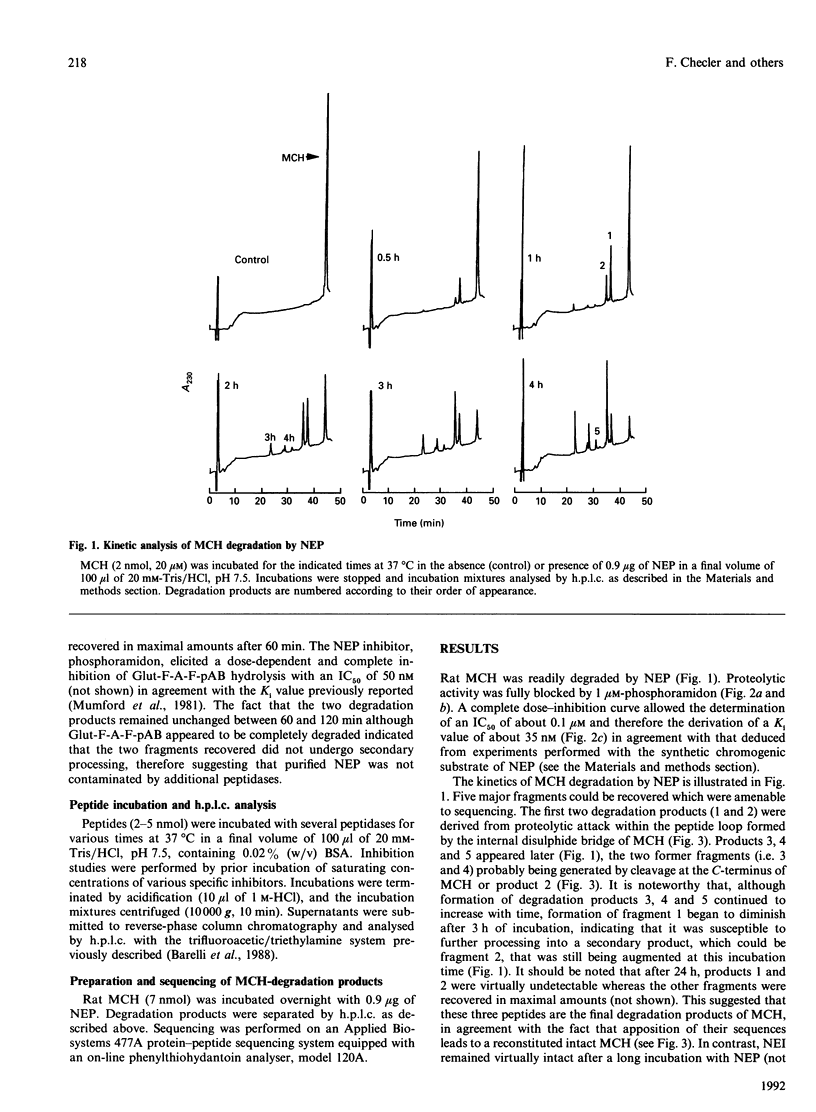
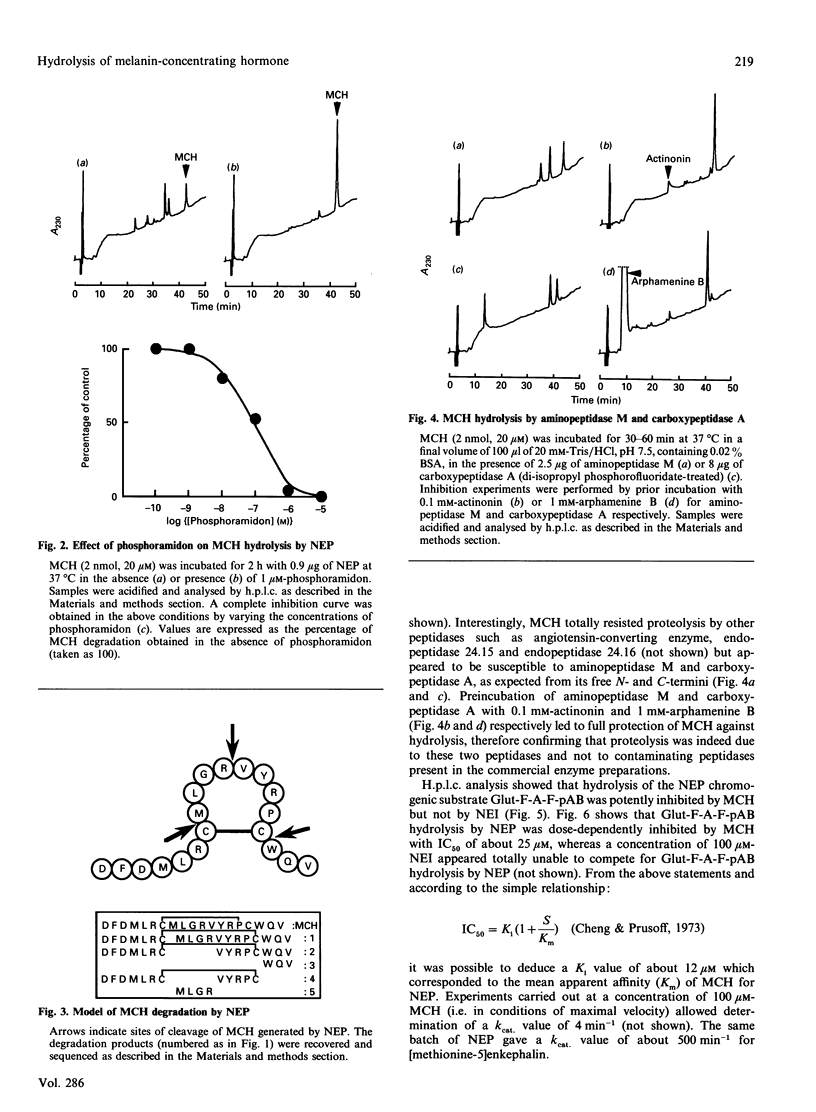
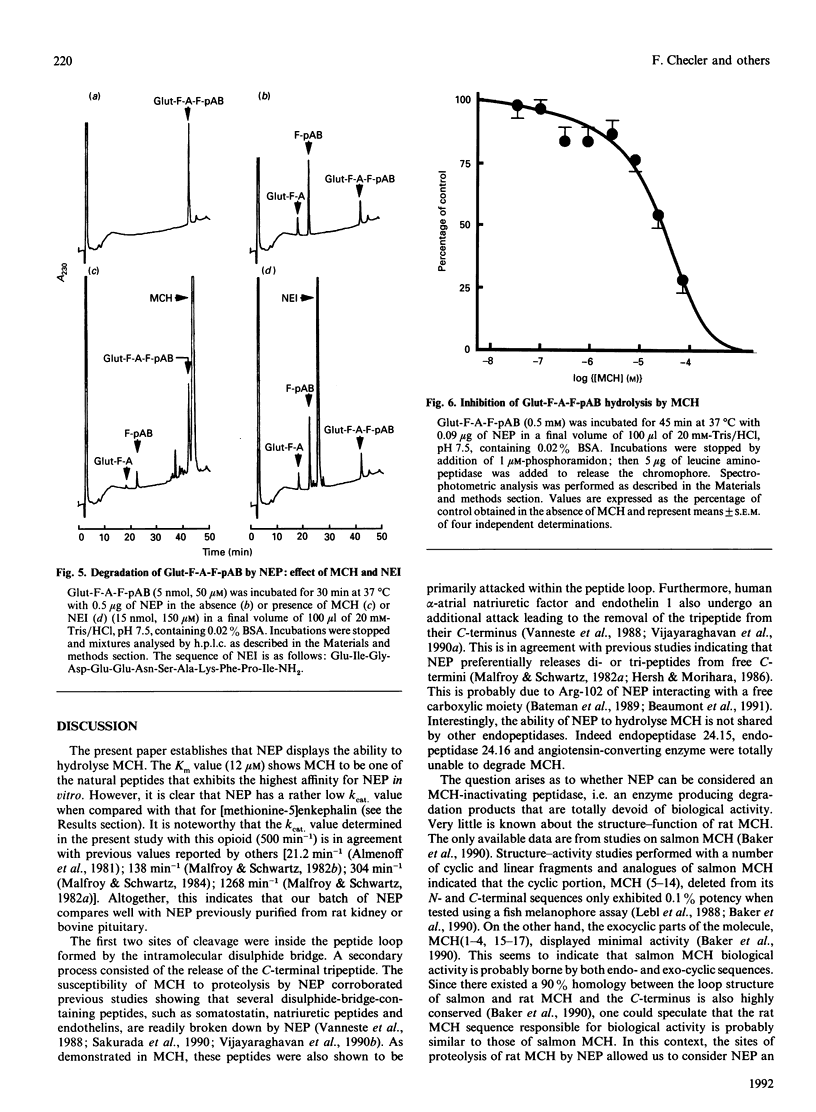
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) is a cyclic peptide which behaves as an antagonist of the pituitary melanotropic hormone alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in fishes. Cloning of the rat MCH cDNA precursor recently revealed the presence of an additional putative peptide named NEI. The present work examined the susceptibility of these novel peptides to hydrolysis by various purified exo- and endo-peptidases including endopeptidases 24.11 (NEP), 24.15, 24.16, angiotensin-converting enzyme, leucine aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase A. NEP attacked MCH at three sites of the molecule with an apparent affinity of about 12 microM and a kcat. of 4 min-1. The first site of cleavage was at Cys-7-Met-8, i.e. within the peptide loop formed by the internal disulphide bridge. NEP could therefore be considered as an MCH-inactivating peptidase since the degradation products generated are probably devoid of biological activity. In contrast, NEI neither inhibited the degradation of the NEP chromogenic substrate glutaryl-Phe-Ala-Phe-p-aminobenzoate nor was susceptible to proteolysis by NEP. Unlike NEP, angiotensin-converting enzyme, endopeptidase 24.15 and endopeptidase 24.16 appeared totally unable to cleave MCH, whereas the peptide was readily degraded by aminopeptidase M and carboxypeptidase A.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almenoff J., Wilk S., Orlowski M. Membrane bound pituitary metalloendopeptidase: apparent identity to enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. I., Bird D. J., Buckingham J. C. Effects of chronic administration of melanin-concentrating hormone on corticotrophin, melanotrophin, and pigmentation in the trout. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1986 Jul;63(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(86)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. I., Kinsman R. G., Moss C. A., White P. D., Paul P. K., Brown D. W., Campbell M. M., Osguthorpe D. J. Structure-activity studies with fragments and analogous of salmonid melanin-concentrating hormone. Peptides. 1990 Nov-Dec;11(6):1103–1108. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90137-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman R. C., Jr, Jackson D., Slaughter C. A., Unnithan S., Chai Y. G., Moomaw C., Hersh L. B. Identification of the active-site arginine in rat neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) as arginine 102 and analysis of a glutamine 102 mutant. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6151–6157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont A., Le Moual H., Boileau G., Crine P., Roques B. P. Evidence that both arginine 102 and arginine 747 are involved in substrate binding to neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11). J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):214–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne A., Barnes K., Taylor B. A., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Membrane peptidases in the pig choroid plexus and on other cell surfaces in contact with the cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):69–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2590069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresson J. L., Clavequin M. C., Fellmann D., Bugnon C. Données ontogénétiques sur la population d'interneurones peptidergiques à immunoréactivité de type GRF 37 de l'hypothalamus postéro-latéral humain. Etudes immunocytochimiques à l'aide d'un IS anti-GRF 37 et d'un IS anti-MCH (melanin-concentrating hormone). C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1987;181(4):376–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Purification and characterization of a novel neurotensin-degrading peptidase from rat brain synaptic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11274–11281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilham I. D., Baker B. I. Evidence for the participation of a melanin-concentrating hormone in physiological colour change in the eel. J Endocrinol. 1984 Aug;102(2):237–243. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1020237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Morihara K. Comparison of the subsite specificity of the mammalian neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) to the bacterial neutral endopeptidase thermolysin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6433–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi H., Kawazoe I., Tsubokawa M., Kishida M., Baker B. I. Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone in chum salmon pituitaries. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):321–323. doi: 10.1038/305321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebl M., Hruby V. J., Castrucci A. M., Visconti M. A., Hadley M. E. Melanin concentrating hormone analogues: contraction of the cyclic structure. 1. Agonist activity. J Med Chem. 1988 May;31(5):949–954. doi: 10.1021/jm00400a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C. Enkephalinase from rat kidney. Purification, characterization, and study of substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14365–14370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C. Properties of "enkephalinase" from rat kidney: comparison of dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase and endopeptidase activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schwartz J. C. Purification and substrate specificity of rat kidney "enkephalinase". Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1745–1748. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumford R. A., Pierzchala P. A., Strauss A. W., Zimmerman M. Purification of a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from porcine kidney that degrades peptide hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6623–6627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahon J. L., Presse F., Bittencourt J. C., Sawchenko P. E., Vale W. The rat melanin-concentrating hormone messenger ribonucleic acid encodes multiple putative neuropeptides coexpressed in the dorsolateral hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2056–2065. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozsgay M., Michaud C., Liebman M., Orlowski M. Substrate and inhibitor studies of thermolysin-like neutral metalloendopeptidase from kidney membrane fractions. Comparison with bacterial thermolysin. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1292–1299. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada C., Yokosawa H., Ishii S. The degradation of somatostatin by synaptic membrane of rat hippocampus is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90084-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M., Zamir N. Immunohistochemical localization of a melanin concentrating hormone-like peptide in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Dec;15(6):635–649. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Isolation and characterization of the intestinal peptide porcine PHI (PHI-27), a new member of the glucagon--secretin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6603–6607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanneste Y., Michel A., Dimaline R., Najdovski T., Deschodt-Lanckman M. Hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in vitro by human kidney membranes and purified endopeptidase-24.11. Evidence for a novel cleavage site. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):531–537. doi: 10.1042/bj2540531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. M., Fischer W. H., Hoeger C., Rivier J., Vale W. Characterization of melanin-concentrating hormone from rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1660–1665. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan J., Kim Y. A., Jackson D., Orlowski M., Hersh L. B. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to identify valine-573 in the S'1 binding site of rat neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase). Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 4;29(35):8052–8056. doi: 10.1021/bi00487a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan J., Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hersh L. B. The hydrolysis of endothelins by neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase). J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14150–14155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. C., Hruby V. J., Castrucci A. M., Sherbrooke W. C., Hadley M. E. Synthesis of a cyclic melanotropic peptide exhibiting both melanin-concentrating and -dispersing activities. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1111–1113. doi: 10.1126/science.6609433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes B. C., Hruby V. J., Sherbrooke W. C., Castrucci A. M., Hadley M. E. Synthesis and biological actions of melanin concentrating hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):613–619. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac J. M., Charnay Y., Soleilhic J. M., Sales N., Roques B. P. Enkephalin-degrading enzymes and angiotensin-converting enzyme in human and rat meninges. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80768-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


