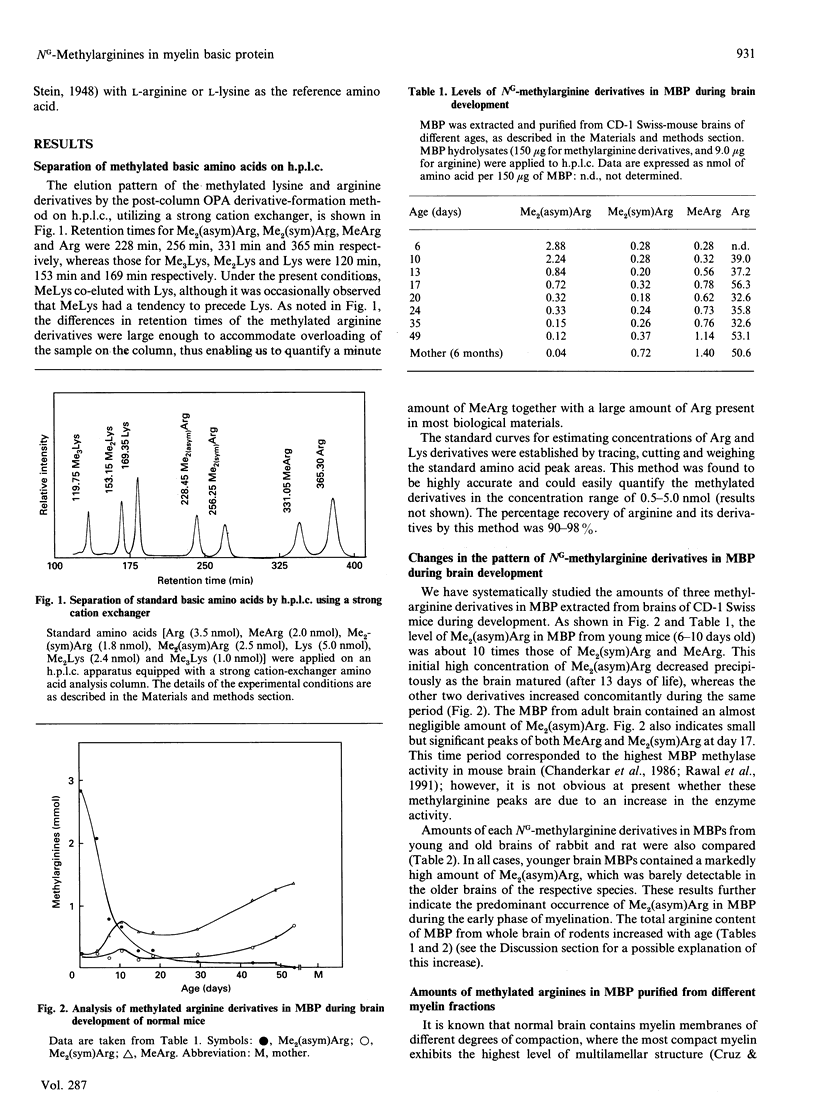
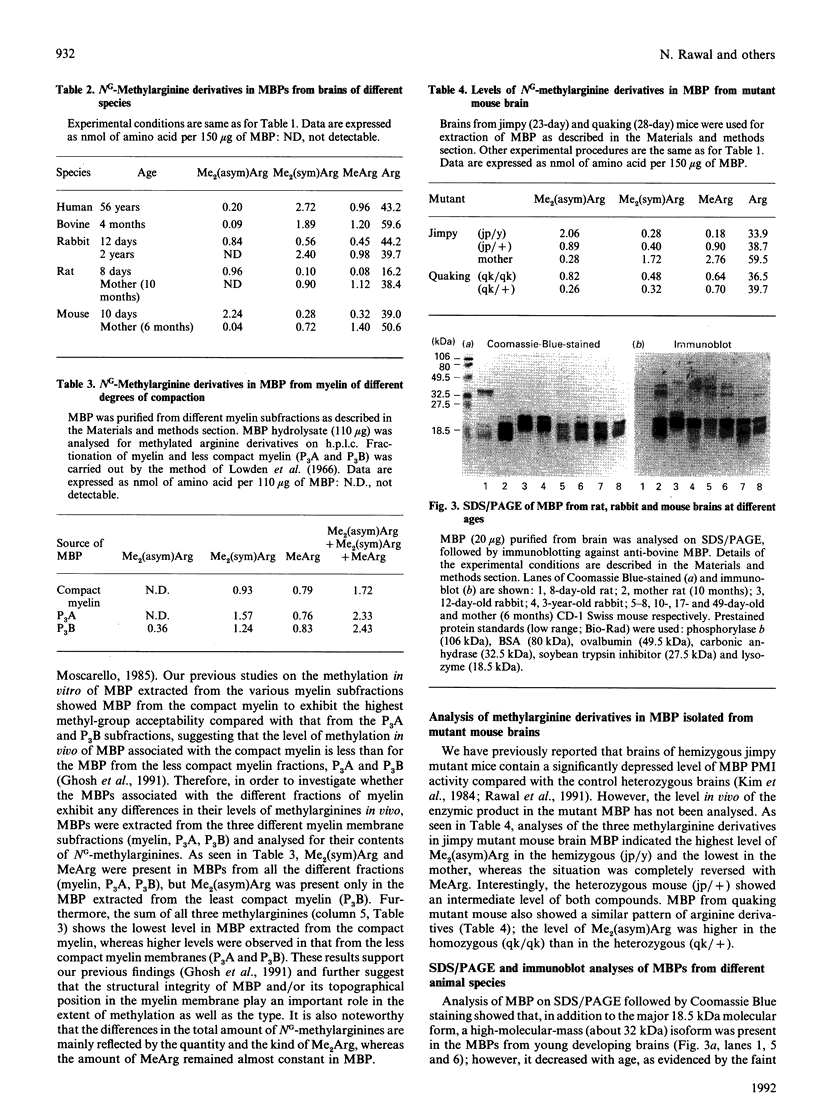
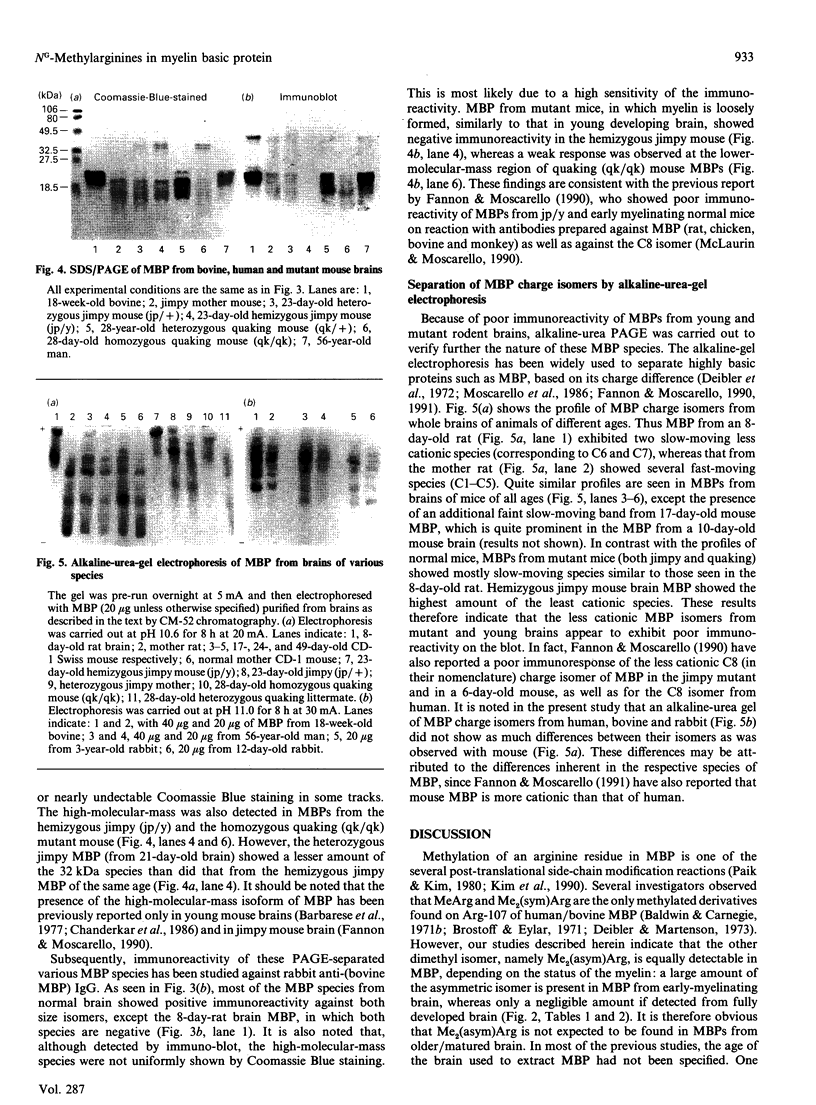
Abstract
The amounts of NG-methylarginine derivatives in myelin basic protein (MBP) purified from dysmyelinating mutant and different stages of normal myelinating mouse brains have been studied by using h.p.l.c. with a highly sensitive post-column o-phthaldialdehyde derivative-formation method. All three naturally occurring derivatives (NG-monomethylarginine (MeArg), NGN'G-dimethylarginine [Me2(sym)Arg] and NGNG-dimethylarginine [Me2(asym)Arg]) were found in MBP; however, their relative concentrations varied significantly with the age of the animal. The amounts of MeArg and Me2(sym)Arg in MBP increased as a function of the age of the brain, whereas that of Me2(asym)Arg decreased. MBP from early-myelinating mouse brain was shown to contain a high proportion of Me2(asym)Arg, which was hardly detectable in older brain MBP. This derivative, Me2(asym)Arg, was also absent from MBP embedded in the most compact multilamellar myelin, but was present in MBP in the least compact myelin (P3B). Comparing the extent of total methylation in vivo (sum of all three arginine derivatives), MBP extracted from less-compact myelin (P3A and P3B) showed a level approx. 40% higher than that from compact myelin. MBPs isolated from dysmyelinating mutant mouse brains, such as jimpy (jp/y) and quaking (qk/qk), contained a much higher level of Me2(asym)Arg relative to the other two methyl derivatives and also in comparison with those levels in the mother brain MBP. SDS/PAGE analysis of MBPs extracted from the mutant (both jp/y and qk/qk) as well as young normal (6-13 days old) mouse brains indicated the presence of a high-molecular-mass isoform of MBP (about 32 kDa), but this isoform was not found in adult brains. These results therefore indicate that structural integrity of myelin membrane in which MBP is embedded appears to play a pivotal role in determining the extent and the kind of Me2Arg formation in MBP at the post-translational level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., Agrawal D., Jenkins R. P. Immunochemical evidence of phosphorylation of a new 23K basic protein in rat brain myelin. Neurochem Res. 1986 Mar;11(3):375–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00965011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amur S. G., Shanker G., Pieringer R. A. Regulation of myelin basic protein (arginine) methyltransferase by thyroid hormone in myelinogenic cultures of cells dissociated from embryonic mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):494–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Carnegie P. R. Isolation and partial characterization of methylated arginines from the encephalitogenic basic protein of myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1230069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. S., Carnegie P. R. Specific enzymic methylation of an arginine in the experimental allergic encephalomyelitis protein from human myelin. Science. 1971 Feb 12;171(3971):579–581. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3971.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Braun P. E., Carson J. H. Identification of prelarge and presmall basic proteins in mouse myelin and their structural relationship to large and small basic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Rosegay A., Vandenheuvel W. J. Identification of N G , N G -dimethylarginine and N G , N G -dimethylarginine in the basic A1 protein from bovine myelin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jan;148(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S., Eylar E. H. Localization of methylated arginine in the A1 protein from myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni A. T. Molecular biology of myelin proteins from the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanderkar L. P., Paik W. K., Kim S. Studies on myelin-basic-protein methylation during mouse brain development. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2400471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Navickas I. J., Chang C. N., Dancis B. M. Methylation of ribosomal proteins in HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. H., Chou F. C., Kowalski T. J., Shapira R., Kibler R. F. The major site of guinea-pig myelin basic protein encephalitogenic in Lewis rats. J Neurochem. 1977 Jan;28(1):115–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb07716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crang A. J., Jacobson W. The relationship of myelin basic protein (arginine) methyltransferase to myelination in mouse spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1982 Jul;39(1):244–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz T. F., Moscarello M. A. Characterization of myelin fractions from human brain white matter. J Neurochem. 1985 May;44(5):1411–1418. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E. Determination of methylated basic amino acids with the amino acid analyzer. Application to total acid hydrolyzates of myelin basic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2387–2391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fannon A. M., Moscarello M. A. Characterization of myelin basic protein charge isomers from adult mouse brain. Neuroreport. 1991 Mar;2(3):135–138. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199103000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fannon A. M., Moscarello M. A. Myelin basic protein is affected by reduced synthesis of myelin proteolipid protein in the jimpy mouse. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):105–110. doi: 10.1042/bj2680105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Paik W. K., Kim S. Purification and molecular identification of two protein methylases I from calf brain. Myelin basic protein- and histone-specific enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19024–19033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Rawal N., Syed S. K., Paik W. K., Kim S. D. Enzymic methylation of myelin basic protein in myelin. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):381–387. doi: 10.1042/bj2750381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass W. F., 2nd, Briggs R. C., Hnilica L. S. Identification of tissue-specific nuclear antigens transferred to nitrocellulose from polyacrylamide gels. Science. 1981 Jan 2;211(4477):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.7003713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Allfrey V. G. Characterization of the non-histone nuclear proteins associated with rapidly labeled heterogeneous nuclear RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7307–7322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlero de Rosbo N., Tsang S., Bernard C. C. Comparative study of myelin basic protein isoforms in developing vertebrate central nervous system: absence of 21.5- and 20.2-kilodalton myelin basic proteins in chicken may point to their importance in mammalian myelinogenesis. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(1):34–40. doi: 10.1159/000112138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Tuck M., Kim M., Campagnoni A. T., Paik W. K. Studies on myelin basic protein-specific protein methylase I in various dysmyelinating mutant mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90254-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs R. L., Reddy R., Cook R. G., Yeoman L. C., Tan E. M., Reichlin M., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of a nucleolar scleroderma antigen (Mr = 34,000; pI, 8.5) rich in NG,NG-dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14304–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Roberts K. D., Yeoman L. C., Busch H. Nucleolar specific acidic phosphoprotein C23 is highly methylated. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14600–14602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowden J. A., Moscarello M. A., Morecki R. The isolation and characterization of an acid-soluble protein from myelin. Can J Biochem. 1966 May;44(5):567–577. doi: 10.1139/o66-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E., Gaitonde M. K. Electrophoretic analysis of the highly basic proteins of the rat brain fraction which induces experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):333–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Quarles R. H., Brady R. O., Webster H. de F. Variation of proteins, enzyme markers and gangliosides in myelin subfractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 5;329(2):305–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaurin J., Moscarello M. A. The preparation of antibodies reactive against citrulline-containing charge isomers of myelin basic protein but not against the arginine-containing charge isomers. Anal Biochem. 1990 Dec;191(2):272–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90219-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake M. Methylases of myelin basic protein and histone in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1975 May;24(5):909–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscarello M. A., Brady G. W., Fein D. B., Wood D. D., Cruz T. F. The role of charge microheterogeneity of basic protein in the formation and maintenance of the multilayered structure of myelin: a possible role in multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci Res. 1986;15(1):87–99. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490150109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawal N., Paik W. K., Kim S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for myelin basic protein-specific protein methylase I. J Neurosci Methods. 1991 Apr;37(2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(91)90123-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reporterer M., Corbin J. L. N G ,N G ,-dimethylarginine in myosin during muscle development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90663-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. H., Carnegie P. R., Anderson R. M. Cycloleucine-induced vacuolation of myelin is associated with inhibition of protein methylation. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Feb 6;21(3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Snyder D. S. Studies of autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. CRC Crit Rev Clin Neurobiol. 1984;1(1):45–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Stone K. L., LoPresti M. B., Merrill B. M., Planck S. R. Amino acid sequence of the UP1 calf thymus helix-destabilizing protein and its homology to an analogous protein from mouse myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5666–5670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman A. W., Quarles R. H., de Webster H., Matthieu J. M., Brady R. O. Characterization and protein analysis of myelin subfractions in rat brain: developmental and regional comparisons. J Neurochem. 1975 Dec;25(6):749–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





