Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn T. G., Cohn D. V., Gorr S. U., Ornstein D. L., Kashdan M. A., Levine M. A. Primary structure of bovine pituitary secretory protein I (chromogranin A) deduced from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5043–5047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeletti R. H., Hickey W. F. A neuroendocrine marker in tissues of the immune system. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):89–90. doi: 10.1126/science.3898368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps D. K., Phillips J. H., Purves F. C. Glycoproteins of the chromaffin-granule matrix: use of lectin blotting to distinguish several separate classes. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., García A. G., Aunis D. Chromaffin cell calcium channel kinetics measured isotopically through fast calcium, strontium, and barium fluxes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):915–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Hesketh J. E., Devilliers G. Immunohistochemical and immunocytochemical localization of myosin, chromogranin A and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in nerve cells in culture and in adrenal glands. J Neurocytol. 1980 Apr;9(2):255–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01205161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLASCHKO H., BORN G. V., D'IORIO A., EADE N. R. Observations on the distribution of catechol amines and adenosinetriphosphate in the bovine adrenal medulla. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):548–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S., Margolis R. U. Peptide mapping studies of the chromogranins and of two chromaffin granule proteoglycans. J Neurochem. 1982 Dec;39(6):1700–1703. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks P., Helle K. B., Mayor D. Evidence for the presence of a chromogranin-like protein in bovine splenic nerve granules. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;5(2):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgun C., Martinez de Muñoz D., Aunis D. Osmotic fragility of chromaffin granules prepared under isoosmotic or hyperosmotic conditions and localization of acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 8;839(3):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Hodgson A. J., White G. H. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyzes substance P. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2065–2072. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Millar T. J. Is intracellular acetylcholinesterase involved in the processing of peptide neurotransmitters? Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1984;6(1-2):79–89. doi: 10.3109/10641968409062552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Ranieri E., White G. H., Hodgson A. J. The enkephalins are amongst the peptides hydrolyzed by purified acetylcholinesterase. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1369–1377. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Elting J. J., Frick M., Elde R. Selective localization of the parathyroid secretory protein-I/adrenal medulla chromogranin A protein family in a wide variety of endocrine cells of the rat. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):1963–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Zangerle R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Chu L. L., Elting J. J., Hamilton J. W., Winkler H. Similarity of secretory protein I from parathyroid gland to chromogranin A from adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6056–6059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté A., Doucet J. P., Trifaró J. M. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of chromaffin cell proteins in response to stimulation. Neuroscience. 1986 Oct;19(2):629–645. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90286-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels A. J., Williams R. J., Wright P. E. The character of the stored molecules in chromaffin granules of the adrenal medulla: a nuclear magnetic resonance study. Neuroscience. 1978;3(6):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Björnsson B. T., Burton D. W., O'Connor D. T., Copp D. H. Chromogranin A is present in and released by fish endocrine tissue. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 1;40(22):2133–2136. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Murray S. S., Burton D. W., Parmer R. J., O'Connor D. T., Delegeane A. M., Mellon P. L. A cloned chromogranin A (CgA) cDNA detects a 2.3Kb mRNA in diverse neuroendocrine tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):418–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diliberto D. J., Jr, Veiveros O. H., Axelrod J. Subcellualr distribution of protein carboxymethylase and its endogenous substrates in the adrenal medulla: possible role in excitation-secretion coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4050–4054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart M., Grube D., Bader M. F., Aunis D., Gratzl M. Chromogranin A in the pancreatic islet: cellular and subcellular distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Dec;34(12):1673–1682. doi: 10.1177/34.12.2878021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Huttner W. B., Mallet J., O'Connor D. T., Winkler H., Zanini A. A nomenclature proposal for the chromogranin/secretogranin proteins. Neuroscience. 1987 Jun;21(3):1019–1021. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Iacangelo A., Hsu C. M., Hotchkiss A. J., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromogranin A synthesis and secretion in chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):65–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E. Is chromogranin a prohormone? Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):301–301. doi: 10.1038/325301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista R., Ray P., Lewis R. V. A "trypsin-like" enzyme in adrenal chromaffin granules: a proenkephalin processing enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 15;106(3):895–902. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91795-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facer P., Bishop A. E., Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Hennessy R. J., Polak J. M. Chromogranin: a newly recognized marker for endocrine cells of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1366–1373. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90657-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkensammer G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Richter K., Winkler H. Cell-free and cellular synthesis of chromogranin A and B of bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkensammer G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Biogenesis of chromaffin granules: incorporation of sulfate into chromogranin B and into a proteoglycan. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1475–1480. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Frischenschlager I. Immunological characterization of secretory proteins of chromaffin granules: chromogranins A, chromogranins B, and enkephalin-containing peptides. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1854–1861. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Schober M. Chromogranins A, B, and C: widespread constituents of secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:120–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Iacangelo A., Eiden L. E. Neural and humoral factors separately regulate neuropeptide Y, enkephalin, and chromogranin A and B mRNA levels in rat adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Lassmann H., Hagn C., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the distribution of chromogranin A and B in endocrine and nervous tissues. Neuroscience. 1985 Nov;16(3):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M. Isolation and characterization of chromogranins A, B, and C from bovine chromaffin granules and a rat pheochromocytoma. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):262–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Enkephalin convertase: purification and characterization of a specific enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase localized to adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3886–3890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauweiler B., Weihe E., Hartschuh W., Yanaihara N. Presence and coexistence of chromogranin A and multiple neuropeptides in Merkel cells of mammalian oral mucosa. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 29;89(2):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzl M., Krieger-Brauer H., Ekerdt R. Latent acetylcholinesterase in secretory vesicles isolated from adrenal medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 7;649(2):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes M., Iacangelo A., Eiden L. E., Godfrey B., Herbert E. Chromogranin A: the primary structure deduced from cDNA clones reveals the presence of pairs of basic amino acids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:351–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
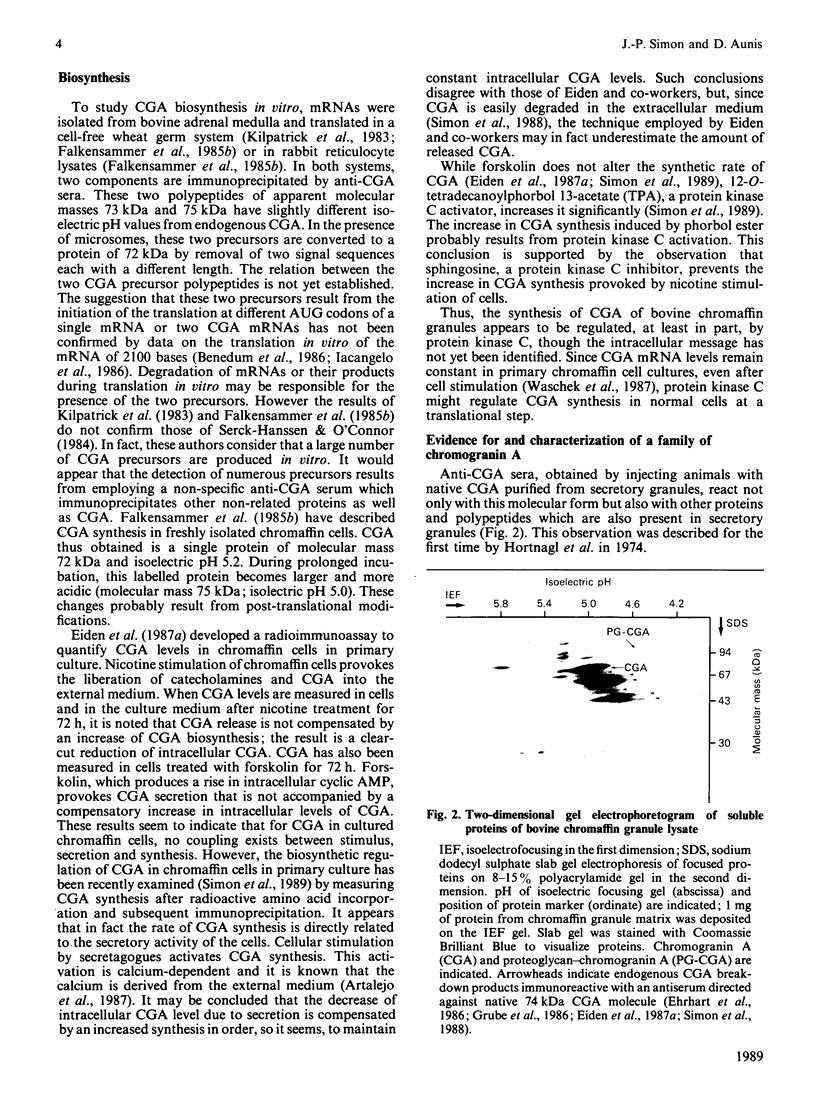
- Grube D., Aunis D., Bader F., Cetin Y., Jörns A., Yoshie S. Chromogranin A (CGA) in the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. I. CGA in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Histochemistry. 1986;85(6):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00508425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagn C., Klein R. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Douglas B. H., 2nd, Winkler H. An immunological characterization of five common antigens of chromaffin granules and of large dense-cored vesicles of sympathetic nerve. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 30;67(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90325-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagn C., Schmid K. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Chromogranin A, B, and C in human adrenal medulla and endocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):405–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Chu L. L., Rouse J. B., Reddig K., MacGregor R. R. Structural characterization of adrenal chromogranin A and parathyroid secretory protein-I as homologs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jan;244(1):16–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn S. A. Electron microscopic localization of chromogranin A in osmium-fixed neuroendocrine cells with a protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Jul;35(7):795–801. doi: 10.1177/35.7.3295032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B. Biochemical studies of the chromaffin granule. I. Distribution of chromagranin A and dopamine- -hydroxylase activity in the membrane and water-soluble granule fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):80–93. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B., Reed R. K., Pihl K. E., Serck-Hanssen G. Osmotic properties of the chromogranins and relation to osmotic pressure in catecholamine storage granules. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Jan;123(1):21–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B. Some chemical and physical properties of the soluble protein fraction of bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Jul;2(4):298–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman L. J., Ahn T. G., Levine M. A., Allison A., Cohen P. S., Cooper M. J., Cohn D. V., Israel M. A. Molecular cloning and primary structure of human chromogranin A (secretory protein I) cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11559–11563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook V. Y., Eiden L. E., Brownstein M. J. A carboxypeptidase processing enzyme for enkephalin precursors. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):341–342. doi: 10.1038/295341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Grimaldi K. A., Peshavaria M. Biosynthesis of betagranin in pancreatic beta-cells. Identification of a chromogranin A-like precursor and its parallel processing with proinsulin. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2440449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M. Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A in purified insulin granules. Formation of a 20 kDa N-terminal fragment (betagranin) by the concerted action of a Ca2+-dependent endopeptidase and carboxypeptidase H (EC 3.4.17.10). Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):457–464. doi: 10.1042/bj2440457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Hansen F., Peshavaria M. beta-Granins: 21 kDa co-secreted peptides of the insulin granule closely related to adrenal medullary chromogranin A. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Nielsen E., Kastern W. The molecular cloning of the chromogranin A-like precursor of beta-granin and pancreastatin from the endocrine pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 29;236(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Lochs H., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the acidic chromogranins and on dopamine beta-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.2.1) of bovine chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1974 Jan;22(1):197–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb12201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J., Eiden L. E. The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2339–2341. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Okayama H., Eiden L. E. Primary structure of rat chromogranin A and distribution of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismael Z., Millar T. J., Small D. H., Chubb I. W. Acetylcholinesterase generates enkephalin-like immunoreactivity when it degrades the soluble proteins (chromogranins) from adrenal chromaffin granules. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao L. S., Schneider A. S. Calcium mobilization and catecholamine secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells. A Quin-2 fluorescence study. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4881–4888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiang W. L., Krusius T., Finne J., Margolis R. U., Margolis R. K. Glycoproteins and proteoglycans of the chromaffin granule matrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1651–1659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick L., Gavine F., Apps D., Phillips J. Biosynthetic relationship between the major matrix proteins of adrenal chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner N. Molecular organization of the chromaffin vesicles of the adrenal medulla. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1974;2:265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Benedum U. M., Gerdes H. H., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human chromogranin A and pancreastatin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17026–17030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostron H., Winkler H., Geissler D., König P. Uptake of calcium by chromaffin granules in vitro. J Neurochem. 1977 Mar;28(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruggel W., O'Connor D. T., Lewis R. V. The amino terminal sequences of bovine and human chromogranin A and secretory protein I are identical. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):380–383. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Hagn C., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Presence of chromogranin A, B and C in bovine endocrine and nervous tissues: a comparative immunohistochemical study. Histochem J. 1986 Jul;18(7):380–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01675219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., van Ranst L., Lloyd R. V., O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine cells. Immunocytochemical detection in human, monkey, and pig respiratory mucosa. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Jan;35(1):113–118. doi: 10.1177/35.1.3098831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. W., Huttner W. B. (Glu62, Ala30, Tyr8)n serves as high-affinity substrate for tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase: a Golgi enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6143–6147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg I., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Further characterization of an enkephalin-generating enzyme from adrenal medullary chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1984 May;42(5):1411–1419. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Kovacs K., Ryan N. Immunohistochemical localization of chromogranin in human hypophyses and pituitary adenomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Jun;109(6):515–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. S., Burton D. W., Deftos L. J. The coregulation of secretion and cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid of chromogranin-A and calcitonin by phorbol ester in cells that produce both substances. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):495–499. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. S., Deaven L. L., Burton D. W., O'Connor D. I., Mellon P. L., Deftos L. J. The gene for human chromogranin A (CgA) is located on chromosome 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman B., Wiedermann C. J., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M., Sperk G., Winkler H. Biochemical and functional properties of large and small dense-core vesicles in sympathetic nerves of rat and ox vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1984 Nov;13(3):921–931. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M. H., Harbour D., Gagnon C. Secretory proteins from adrenal medullary cells are carboxyl-methylated in vivo and released under their methylated form by acetylcholine. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):38–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Hogue-Angeletti R. Neurons and neuroendocrine cells contain chromogranin: detection of the molecule in normal bovine tissues by immunochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Aug;33(8):791–798. doi: 10.1177/33.8.3894497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Bernstein K. N. Radioimmunoassay of chromogranin A in plasma as a measure of exocytotic sympathoadrenal activity in normal subjects and patients with pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 20;311(12):764–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409203111204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Chromogranin A: immunohistology reveals its universal occurrence in normal polypeptide hormone producing endocrine glands. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 24;33(17):1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90721-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Immunoreactive human chromogranin A in diverse polypeptide hormone producing human tumors and normal endocrine tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):1084–1086. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin: widespread immunoreactivity in polypeptide hormone producing tissues and in serum. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Deftos L. J. How sensitive and specific is measurement of plasma chromogranin A for the diagnosis of neuroendocrine neoplasia? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:379–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Deftos L. J. Secretion of chromogranin A by peptide-producing endocrine neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 1;314(18):1145–1151. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605013141803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Frigon R. P. Chromogranin A, the major catecholamine storage vesicle soluble protein. Multiple size forms, subcellular storage, and regional distribution in chromaffin and nervous tissue elucidated by radioimmunoassay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3237–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzak A., Aunis D., Langley K. Membrane recycling after exocytosis: an ultrastructural study of cultured chromaffin cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Aug;171(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Nelson D. L., Ling E., Angeletti R. H. Chromogranin A-like proteins in the secretory granules of a protozoan, Paramecium tetraurelia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17264–17267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryde J. G., Phillips J. H. Fractionation of membrane proteins by temperature-induced phase separation in Triton X-114. Application to subcellular fractions of the adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj2330525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian J., Hickey W. F., Angeletti R. H. Neuroendocrine cells in intestinal lamina propria. Detection with antibodies to chromogranin A. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jan;17(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiffen F. U., Gratzl M. Ca2+ binding to chromaffin vesicle matrix proteins: effect of pH, Mg2+, and ionic strength. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4402–4406. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiffen F. U., Gratzl M. Chromogranins, widespread in endocrine and nervous tissue, bind Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieker S., Fischer-Colbrie R., Eiden L., Winkler H. Phylogenetic distribution of peptides related to chromogranins A and B. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1066–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindi G., Buffa R., Sessa F., Tortora O., Solcia E. Chromogranin A, B and C immunoreactivities of mammalian endocrine cells. Distribution, distinction from costored hormones/prohormones and relationship with the argyrophil component of secretory granules. Histochemistry. 1986;85(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00508649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundle S., Somogyi P., Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Winkler H., Chubb I. W. Chromogranin A, B and C: immunohistochemical localization in ovine pituitary and the relationship with hormone-containing cells. Regul Pept. 1986 Dec 30;16(3-4):217–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Jasani B., Williams E. D., Winkler H. Chromogranin A and B and secretogranin II in medullary carcinomas of the thyroid. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987 Jul;11(7):551–556. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198707000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schober M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schmid K. W., Bussolati G., O'Connor D. T., Winkler H. Comparison of chromogranins A, B, and secretogranin II in human adrenal medulla and pheochromocytoma. Lab Invest. 1987 Oct;57(4):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Hendy G. N., Hamelin J., Paquin J., Lazure C., Metters K. M., Rossier J., Chrétien M. Chromogranin A can act as a reversible processing enzyme inhibitor. Evidence from the inhibition of the IRCM-serine protease 1 cleavage of pro-enkephalin and ACTH at pairs of basic amino acids. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya K., Ghatei M. A., Minamino N., Bretherton-Watt D., Matsuo H., Bloom S. R. Isolation of human pancreastatin fragment containing the active sequence from a glucagonoma. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80606-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serck-Hanssen G., O'Connor D. T. Immunological identification and characterization of chromogranins coded by poly(A) mRNA from bovine adrenal medulla and pituitary gland and human phaeochromocytoma. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11597–11600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Fonseca R., Nolan J., Angeletti R. H. Relationship of multiple forms of chromogranin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1645–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Nolan J., Angeletti R. H. Chromogranin, an integral membrane protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1641–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R. R., Sen R. Molecular mobilities in chromaffin granules. Magnetic field dependence of proton T1 relaxation times. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 3;538(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietzen M., Schober M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Scherman D., Sperk G., Winkler H. Rat adrenal medulla: levels of chromogranins, enkephalins, dopamine beta-hydroxylase and of the amine transporter are changed by nervous activity and hypophysectomy. Neuroscience. 1987 Jul;22(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Effect of secretagogues on chromogranin A synthesis in bovine cultured chromaffin cells. Possible regulation by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):915–922. doi: 10.1042/bj2600915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Secretion from chromaffin cells is controlled by chromogranin A-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. H., Ismael Z., Chubb I. W. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyses chromogranin A to yield low molecular weight peptides. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. Purification and properties of an acidic protein from chromaffin granules of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):483–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1030483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Chubb I. W., Smith A. D. A possible structural basis for the extracellular release of acetylcholinesterase. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 18;191(1103):271–283. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., DePotter R. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M., Winkler H., Chubb I. W. Chromogranin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Immunochemical characterisation, distribution and relationship to catecholamine and enkephalin pathways. Brain Res. 1984 Dec;320(2-3):193–230. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Aborg C. H. In vitro studies on a two-pool stage of adrenaline and noradrenaline in granule material from bovine adrenal medulla. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Aug;109(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Aborg C. H. The ability of ATP-free granule material from bovine adrenal medulla to bind inorganic cations and biogenic amines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Apr;99(4):476–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Polak J. M. Ultrastructural localization of chromogranin: a potential marker for the electron microscopical recognition of endocrine cell secretory granules. Histochem J. 1985 Sep;17(9):981–992. doi: 10.1007/BF01417947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veeraragavan K., Coulombe R., Gagnon C. Stoichiometric carboxyl methylation of chromogranins from bovine adrenal medullary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):732–738. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volknandt W., Schober M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Zimmermann H., Winkler H. Cholinergic nerve terminals in the rat diaphragm are chromogranin A immunoreactive. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Oct 29;81(3):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90389-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waschek J. A., Pruss R. M., Siegel R. E., Eiden L. E., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Regulation of enkephalin, VIP, and chromogranin biosynthesis in actively secreting chromaffin cells. Multiple strategies for multiple peptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:308–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Feichtinger H., Schmid K. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Grimelius L., Cedermark B., Papotti M., Bussolati G., Winkler H. Chromogranin A and B and secretogranin II in bronchial and intestinal carcinoids. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;412(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00716181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Lloyd R. V. Detection of chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells with a monoclonal antibody. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):458–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Apps D. K., Fischer-Colbrie R. The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules: established facts and unresolved topics. Neuroscience. 1986 Jun;18(2):261–290. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Hörtnagl H., Smith A. D. Membranes of the adrenal medulla. Behaviour of insoluble proteins of chromaffin granules on gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(2):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1180303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. The composition of adrenal chromaffin granules: an assessment of controversial results. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Westhead E. The molecular organization of adrenal chromaffin granules. Neuroscience. 1980;5(11):1803–1823. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfarter T., Fischer-Colbrie R., Hogue-Angeletti R., Eiden L. E., Winkler H. Processing of chromogranin A within chromaffin granules starts at C- and N-terminal cleavage sites. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie S., Hagn C., Ehrhart M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Grube D., Winkler H., Gratzl M. Immunological characterization of chromogranins A and B and secretogranin II in the bovine pancreatic islet. Histochemistry. 1987;87(2):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00533393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]