Abstract
Cleavage of ovalbumin and angiotensinogen at sites homologous to the reactive centre loop of alpha 1-antitrypsin is not accompanied by the increase in heat-stability associated with the transition from the native stressed (S) structure to a cleaved relaxed (R) form that is typical of other serpins. Failure to undergo the S-R change in ovalbumin is not due to phosphorylation of Ser-344 near the sites of cleavage on the loop. The suggested explanation is the unique presence of bulky side chains at the P10-P12 site in ovalbumin and angiotensinogen.
Full text
PDF


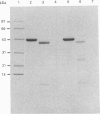
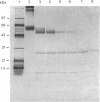
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruch M., Weiss V., Engel J. Plasma serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins) exhibit major conformational changes and a large increase in conformational stability upon cleavage at their reactive sites. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16626–16630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Owen M. C. Plakalbumin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, antithrombin and the mechanism of inflammatory thrombosis. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):730–732. doi: 10.1038/317730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Pemberton P. A., Boswell D. R. The serpins: evolution and adaptation in a family of protease inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:527–535. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Angiotensinogen is related to the antitrypsin-antithrombin-ovalbumin family. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6604942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gettins P., Harten B. Properties of thrombin- and elastase-modified human antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3634–3639. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin-III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 31;95(2):864–871. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90867-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Primary structure of human preangiotensinogen deduced from the cloned cDNA sequence. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3603–3609. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 15;177(3):531–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisbet A. D., Saundry R. H., Moir A. J., Fothergill L. A., Fothergill J. E. The complete amino-acid sequence of hen ovalbumin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):335–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLMANN G. E. Enzymatic dephosphorylation of ovalbumin and plakalbumin. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;35(5):711–726. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton P. A., Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J., Carrell R. W. The structural basis for neutrophil inactivation of C1 inhibitor. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj2580193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton P. A., Stein P. E., Pepys M. B., Potter J. M., Carrell R. W. Hormone binding globulins undergo serpin conformational change in inflammation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):257–258. doi: 10.1038/336257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewksbury D. A., Dart R. A., Travis J. The amino terminal amino acid sequence of human angiotensinogen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. O., Fisher W. K. Amino acid sequences containing half-cystine residues in ovalbumin. Aust J Biol Sci. 1978 Oct;31(5):433–442. doi: 10.1071/bi9780433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. J., Bridger W. A. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the two phosphoserine residues of hen egg white ovalbumin. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5825–5831. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. T. Ovalbumin is an elastase substrate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14335–14336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]