Abstract
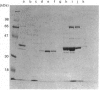
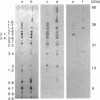
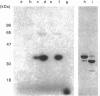
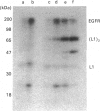
We have characterized a 68 kDa lipocortin from human placenta that was identified as a covalently linked homodimer of lipocortin-1 by peptide mapping and sequence analysis. The site of cross-linking was localized within the 3 kDa N-terminal tail region, an exposed domain that contains the phosphorylation sites for protein tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C and is sensitive to proteolysis. Sequence analysis of the corresponding peptide revealed that glutamine-18 was modified, suggesting that the cross-link may be generated by a transglutaminase. By incubating lipocortin-1 with placental membranes and with labelled glycine ethyl ester we observed a Ca2+-dependent labelling of lipocortin-1 within the tail region, supporting this notion. Like lipocortin-1, the dimer inhibits phospholipase Ad2 activity, is a substrate for the epidermal-growth-factor (EGF) receptor/kinase, and display Ca2+-dependent binding to phosphatidylserine-containing vesicles. In preparations from human placenta the dimer is particularly abundant, accounting for approx. 20% of the lipocortin-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanquet P. R., Paillard S., Courtois Y. Influence of fibroblast growth factor on phosphorylation and activity of a 34 kDa lipocortin-like protein in bovine epithelial lens cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Zaks W. J., Hamman H. C., Crane S., Martin W. H., Gould K. L., Oddie K. M., Parsons S. J. Identification of chromaffin granule-binding proteins. Relationship of the chromobindins to calelectrin, synhibin, and the tyrosine kinase substrates p35 and p36. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1860–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M. R., Owens R. J., Totty N. F., Moss S. E., Waterfield M. D., Crumpton M. J. Primary structure of the human, membrane-associated Ca2+-binding protein p68 a novel member of a protein family. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):21–27. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J. Eleventh Gaddum memorial lecture. Lipocortin and the mechanism of action of the glucocorticoids. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):987–1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Boudreau M., Galyean R., Hunter T., Tack B. Association of the S-100-related calpactin I light chain with the NH2-terminal tail of the 36-kDa heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10485–10488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J., Zokas L. Antibodies to the N-terminus of calpactin II (p35) affect Ca2+ binding and phosphorylation by the epidermal growth factor receptor in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2069–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Schlaepfer D. D., Burgess W. H. Characterization of lipocortin I and an immunologically unrelated 33-kDa protein as epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase substrates and phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6921–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Owada M. K., Sonobe S., Kakunaga T., Kawakatsu H., Yano J. A 32-kDa protein associated with phospholipase A2-inhibitory activity from human placenta. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F. The regulation of lipomodulin, a phospholipase inhibitory protein, in rabbit neutrophils by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7730–7733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., McGray P., Mattaliano R. J., Burne C., Chow E. P., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Purification and characterization of proteolytic fragments of lipocortin I that inhibit phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7639–7645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson N., Marriott G., Weber K. p36, the major cytoplasmic substrate of src tyrosine protein kinase, binds to its p11 regulatory subunit via a short amino-terminal amphiphatic helix. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2435–2442. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasik A., Pepinsky R. B., Shoelson S. E., Kahn C. R. Lipocortins 1 and 2 as substrates for the insulin receptor kinase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11862–11867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna N. C., Hee-Chong M., Severson D. L., Tokuda M., Chong S. M., Waisman D. M. Inhibition of phospholipase A2 by protein I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):455–460. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Creutz C. E. Cell biology. Consensus in exocytosis. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):573–573. doi: 10.1038/320573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Levin A., Branton D. Copper staining: a five-minute protein stain for sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):308–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B. Localization of lipid-protein and protein-protein interactions within the murine retrovirus gag precursor by a novel peptide-mapping technique. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11229–11235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K. Epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):81–84. doi: 10.1038/321081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Tizard R., Mattaliano R. J., Sinclair L. K., Miller G. T., Browning J. L., Chow E. P., Burne C., Huang K. S., Pratt D. Five distinct calcium and phospholipid binding proteins share homology with lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10799–10811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfäffle M., Ruggiero F., Hofmann H., Fernández M. P., Selmin O., Yamada Y., Garrone R., von der Mark K. Biosynthesis, secretion and extracellular localization of anchorin CII, a collagen-binding protein of the calpactin family. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2335–2342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. A., Glenney J. R. Regulation of calpactin I phospholipid binding by calpactin I light-chain binding and phosphorylation by p60v-src. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):321–328. doi: 10.1042/bj2470321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy-Choudhury S., Mishra V. S., Low M. G., Das M. A phospholipid is the membrane-anchoring domain of a protein growth factor of molecular mass 34 kDa in placental trophoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):2014–2018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato E. F., Morimoto Y. M., Matsuno T., Miyahara M., Utsumi K. Neutrophil specific 33 kDa protein: its Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent intracellular translocation. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Characterization of Ca2+-dependent phospholipid binding and phosphorylation of lipocortin I. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6931–6937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadle P. J., Gerke V., Weber K. Three Ca2+-binding proteins from porcine liver and intestine differ immunologically and physicochemically and are distinct in Ca2+ affinities. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16354–16360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets E. E., Giugni T. D., Coates G. G., Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Epidermal growth factor dependent phosphorylation of a 35-kilodalton protein in placental membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Feb 24;26(4):1164–1172. doi: 10.1021/bi00378a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. Enzymatic cross-linking of involucrin and other proteins by keratinocyte particulates in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. The glutamine residues reactive in transglutaminase-catalyzed cross-linking of involucrin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18093–18098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. L., Dedman J. R. An immunological comparison of several novel calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15815–15818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Slaughter C. A., Leznicki I., Barjon P., Reynolds G. A. Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait J. F., Sakata M., McMullen B. A., Miao C. H., Funakoshi T., Hendrickson L. E., Fujikawa K. Placental anticoagulant proteins: isolation and comparative characterization four members of the lipocortin family. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6268–6276. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi K., Hotta H., Suketa Y. Changes of phospholipase A2 inhibitory activity in the K+-sensitive actin gelation factor during the differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 1;930(3):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Chahwala S. B., Whitman M., Cantley L., Schindler D., Chow E. P., Sinclair L. K., Pepinsky R. B. Location of sites in human lipocortin I that are phosphorylated by protein tyrosine kinases and protein kinases A and C. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3682–3690. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb P. D., Mahadevan L. C. Calcium-dependant binding proteins associated with human placental syncytiotrophoblast microvillous cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 18;916(3):288–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]