Abstract
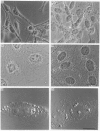
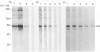
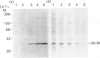
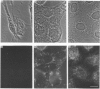
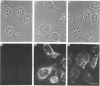
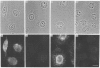
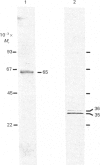
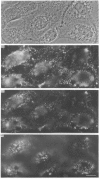
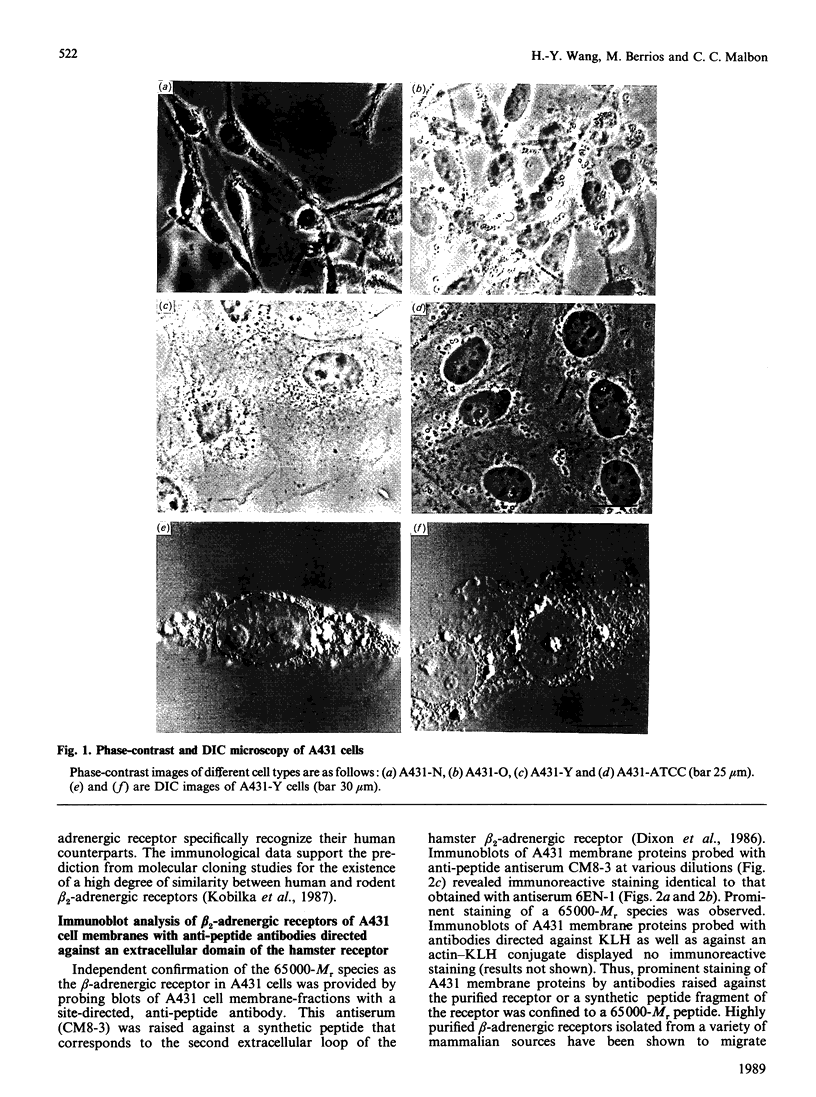
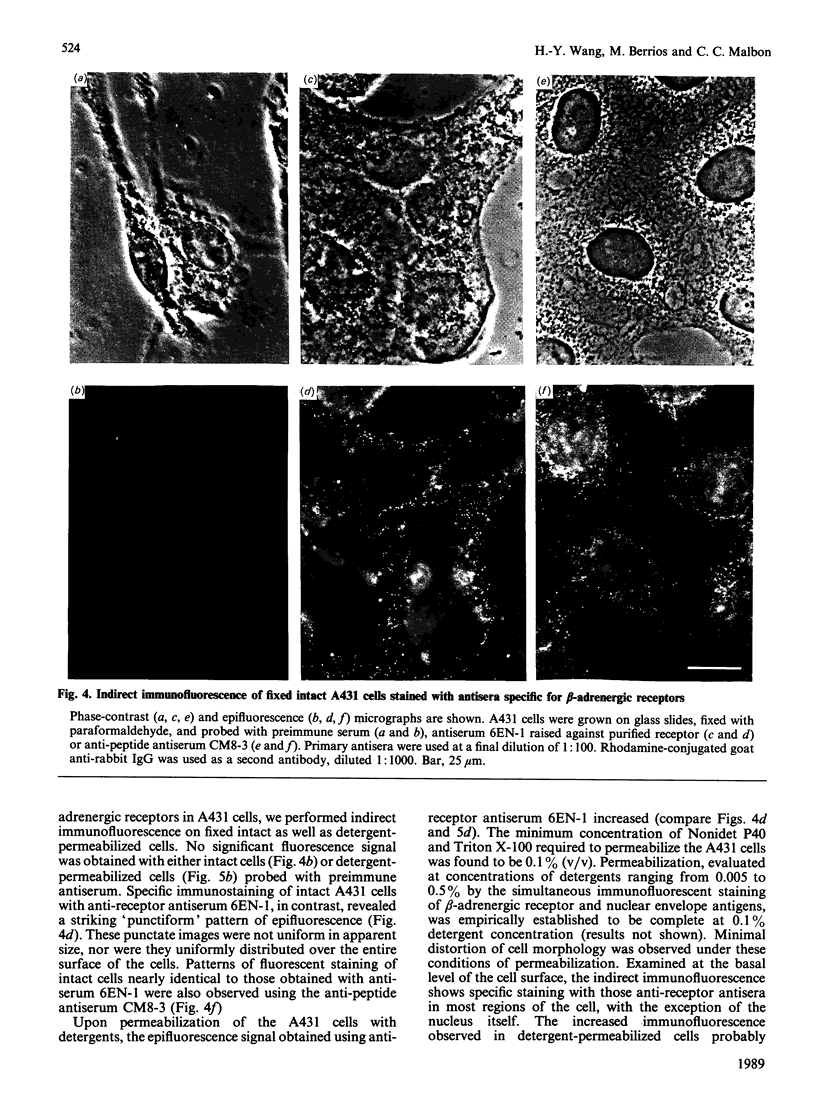
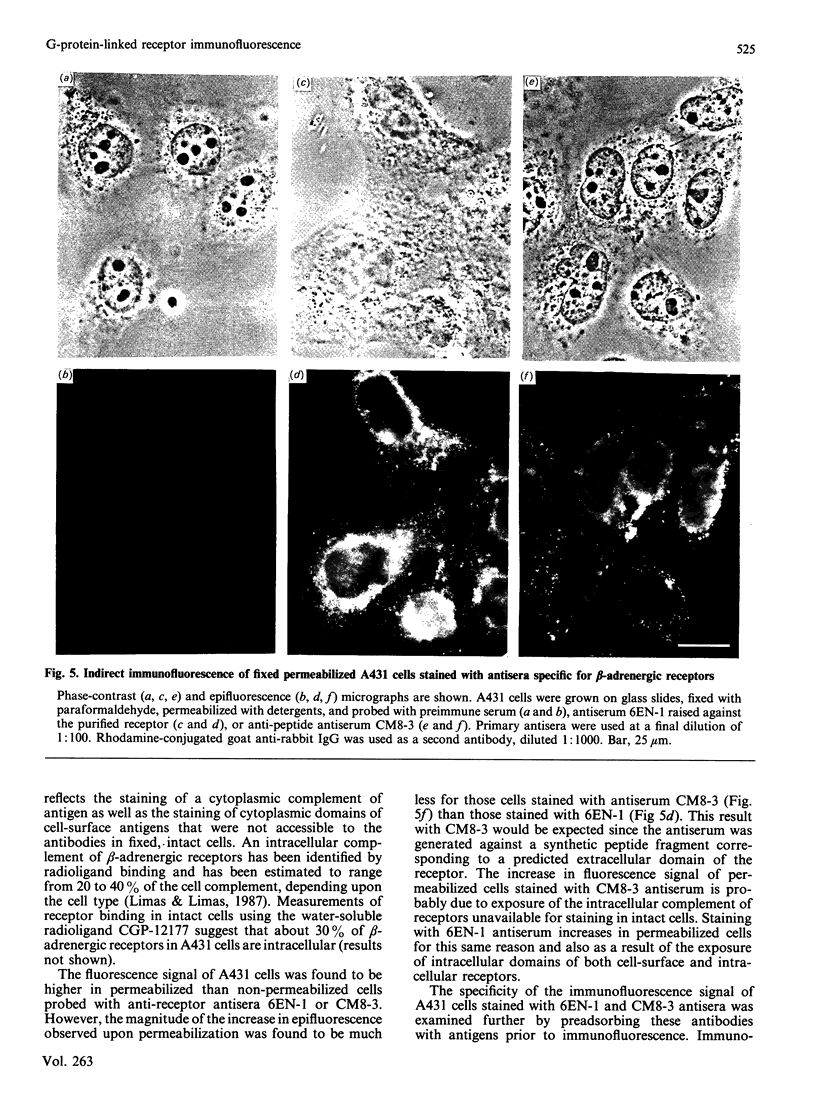
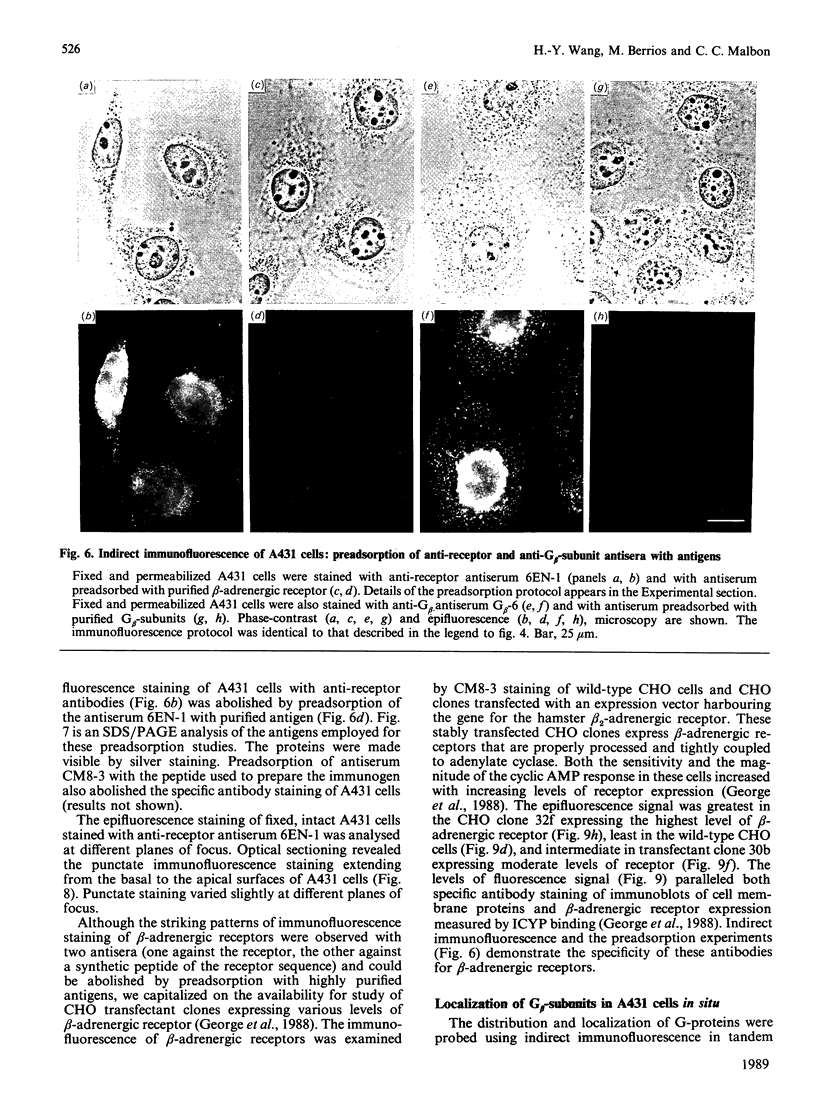
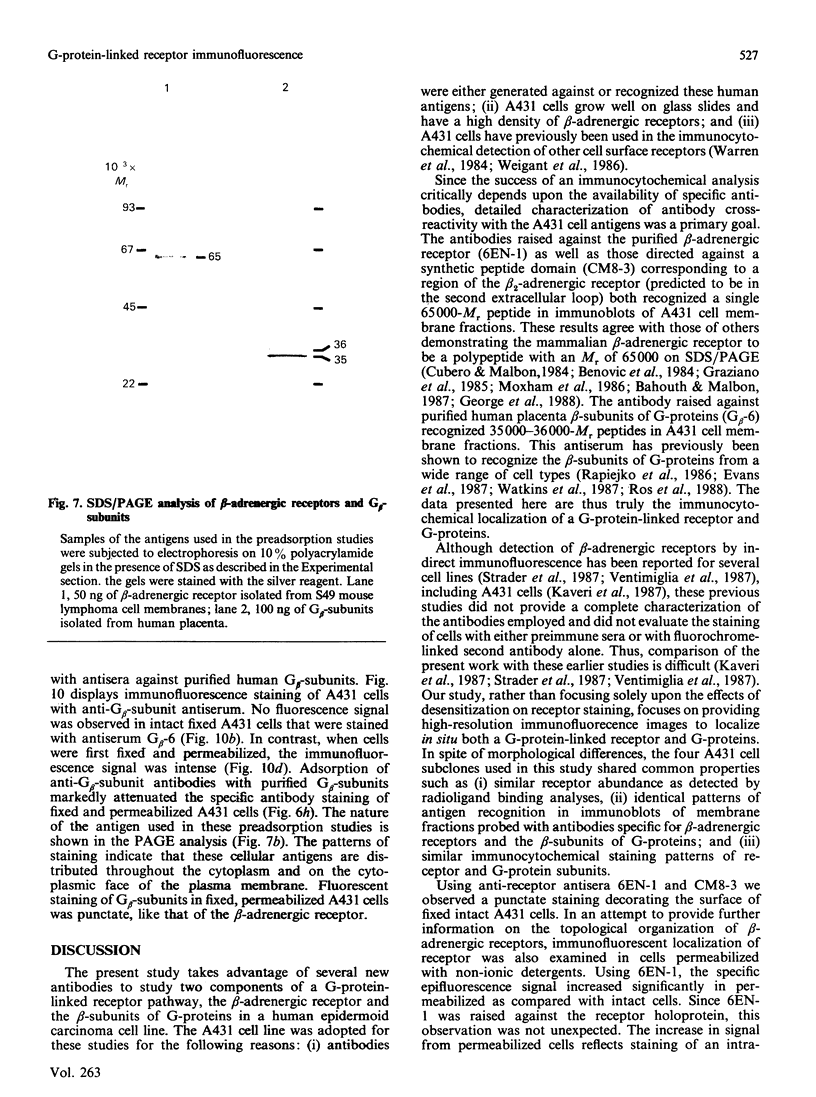
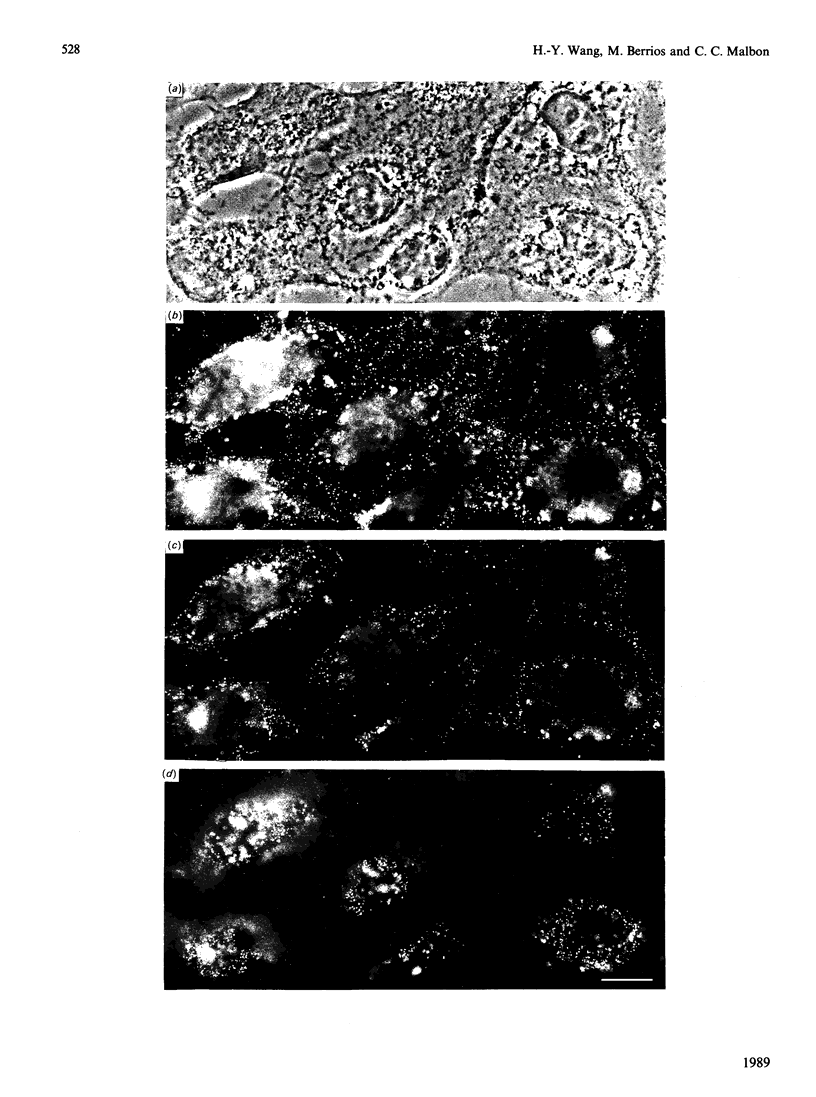
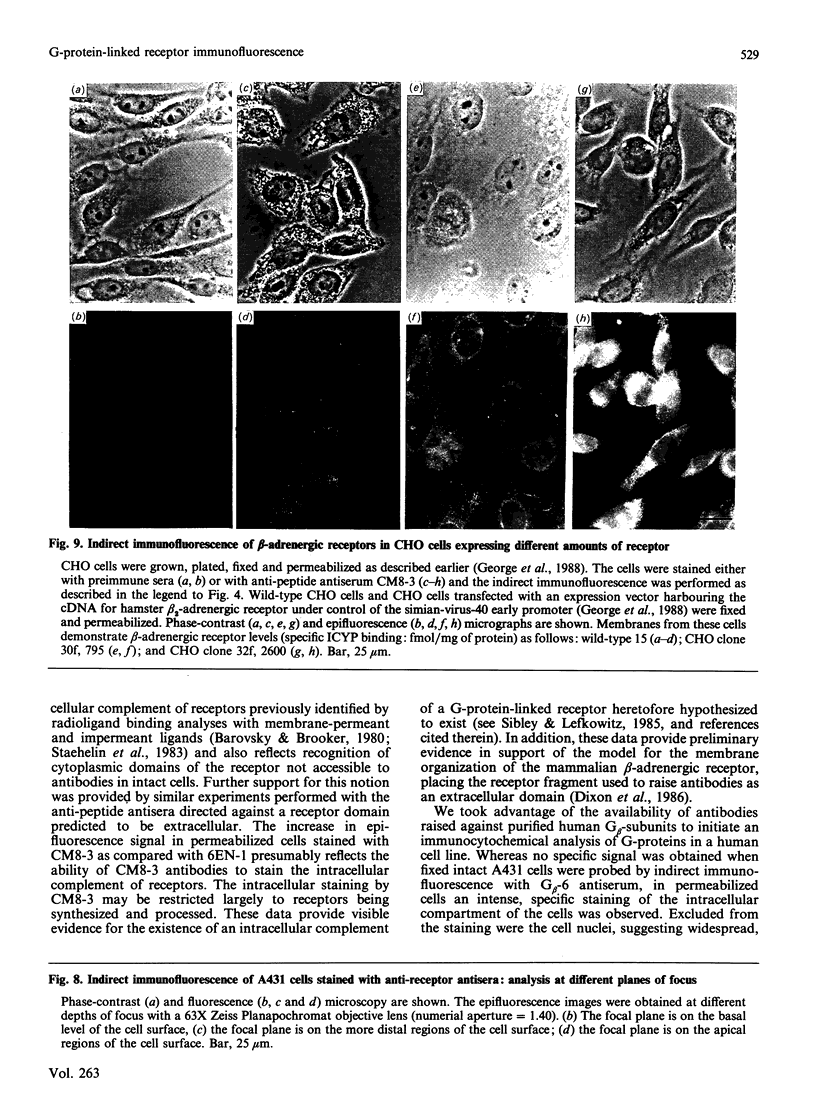
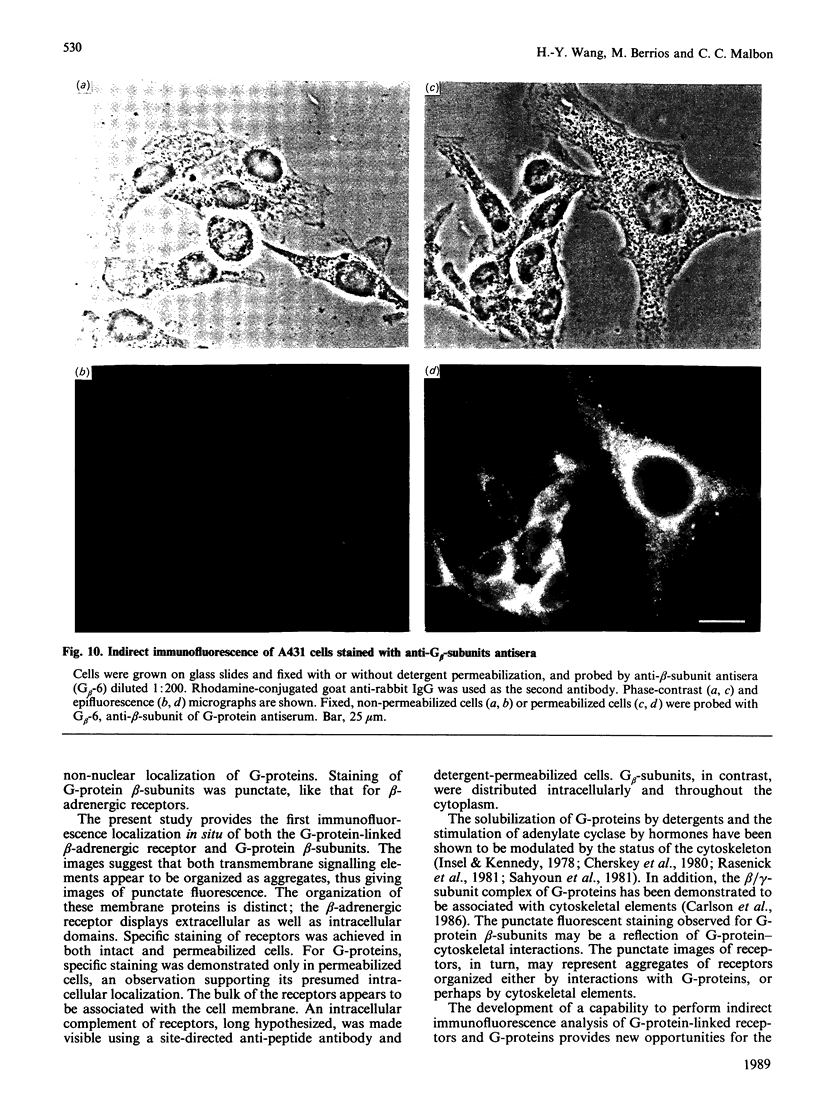
Polyclonal antibodies directed against (i) rodent lung beta 2-adrenergic receptor, (ii) a synthetic fragment of an extracellular domain of the receptor, and (iii) human placenta G-protein beta-subunits, were used to localize these antigens in situ in intact and permeabilized human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Antibodies directed against beta 2-adrenergic receptors showed a punctate immunofluorescence staining throughout the cell surface of fixed intact cells. Punctate staining was also observed in clones of Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with an expression vector harbouring the gene for the hamster beta 2-adrenergic receptor. The immunofluorescence observed with anti-receptor antibodies paralleled the level of receptor expression. In contrast, the beta-subunits common to G-proteins were not stained in fixed intact cells, presumably reflecting their intracellular localization. In detergent-permeabilized fixed cells, strong punctate staining of G beta-subunits was observed throughout the cytoplasm. This is the first indirect immunofluorescence localization of beta-adrenergic receptors and G-proteins. Punctate immunofluorescence staining suggests that both antigens are distributed in clusters.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alho H., Dillion-Carter O., Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C., Chuang D. M. Changes in immunohistochemical properties of beta-adrenergic receptors in frog erythrocytes by isoproterenol-induced desensitization. Life Sci. 1988;42(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bigay J., Deterre P., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Tissue expression and phylogenetic appearance of the beta and gamma subunits of GTP binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80830-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahouth S. W., Malbon C. C. Human beta-adrenergic receptors. Simultaneous purification of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic-receptor peptides. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):557–566. doi: 10.1042/bj2480557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barovsky K., Brooker G. (-)-[125I]-iodopindolol, a new highly selective radioiodinated beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist: measurement of beta-receptors on intact rat astrocytoma cells. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(4):297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Shorr R. G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptor: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4510–4518. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. E., Woolkalis M. J., Newhouse M. G., Manning D. R. Fractionation of the beta subunit common to guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins with the cytoskeleton. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherksey B. D., Zadunaisky J. A., Murphy R. B. Cytoskeletal constraint of the beta-adrenergic receptor in frog erythrocyte membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6401–6405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero A., Malbon C. C. The fat cell beta-adrenergic receptor. Purification and characterization of a mammalian beta 1-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1344–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delavier-Klutchko C., Hoebeke J., Strosberg A. D. The human carcinoma cell line A431 possesses large numbers of functional beta-adrenergic receptors. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 24;169(2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80308-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson P. F., Minier L. N., Lasher R. S. Quantitative electrophoretic transfer of polypeptides from SDS polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: a method for their re-use in immunoautoradiographic detection of antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Jun 11;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B., Pappin D. J. The opsin family of proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):625–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2380625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Berrios M., Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Receptor density and cAMP accumulation: analysis in CHO cells exhibiting stable expression of a cDNA that encodes the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Malbon C. C. Large-scale purification of beta-adrenergic receptors from mammalian cells in culture. Prep Biochem. 1985;15(5):349–366. doi: 10.1080/00327488508062451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C. Purified rat hepatic beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Structural similarities to the rat fat cell beta 1-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7665–7674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Kaveri S. V., Durieu O., Delavier C., Hoebeke J., Strosberg A. D. beta-Adrenergic agonist activity of a monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1781–1784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Malbon C. C. Down-regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors: agonist-induced reduction in receptor mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Kennedy M. S. Colchicine potentiates beta-adrenoreceptor-stimulated cyclic AMP in lymphoma cells by an action distal to the receptor. Nature. 1978 Jun 8;273(5662):471–473. doi: 10.1038/273471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Levitzki A. Characterization of the beta 2-adrenoceptor-dependent adenylate cyclase of A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 May 1;36(9):1531–1538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaveri S. V., Cervantes-Olivier P., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the human A431 beta 2-adrenergic receptor recognize two major polypeptide chains. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):449–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Dixon R. A., Frielle T., Dohlman H. G., Bolanowski M. A., Sigal I. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):46–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A. From epinephrine to cyclic AMP. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):800–806. doi: 10.1126/science.2841758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limas C. J., Limas C. Altered intracellular adrenoceptor distribution in myocardium of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):H904–H908. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.4.H904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Simon M. I. G protein multiplicity in eukaryotic signal transduction systems. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4957–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Mangano T. J., Watkins D. C. Heart contains two substrates (Mr = 40,000 and 41,000) for pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation that co-purify with Ns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):809–815. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Watkins D. C. Permissive hormone regulation of hormone-sensitive effector systems. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Malbon C. C. Fat cell beta 1-adrenergic receptor: structural evidence for existence of disulfide bridges essential for ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6072–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Ross E. M., George S. T., Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic receptors display intramolecular disulfide bridges in situ: analysis by immunoblotting and functional reconstitution. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., Northup J. K., Evans T., Brown J. E., Malbon C. C. G-proteins of fat-cells. Role in hormonal regulation of intracellular inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2400035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasenick M. M., Stein P. J., Bitensky M. W. The regulatory subunit of adenylate cyclase interacts with cytoskeletal components. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):560–562. doi: 10.1038/294560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros M., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Steady-state levels of G-proteins and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat fat cells. Permissive effects of thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4362–4368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N. E., LeVine H., 3rd, Davis J., Hebdon G. M., Cuatrecasas P. Molecular complexes involved in the regulation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6158–6162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel M. B., Sinha Y. N., VanderLaan W. P. Production of antibodies by inoculation into lymph nodes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:3–12. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Gruenbaum Y., Berrios M., Fisher P. A. Biosynthesis and interconversion of Drosophila nuclear lamin isoforms during normal growth and in response to heat shock. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):771–790. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Sklar P. B., Pevsner J. Molecular mechanisms of olfaction. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):13971–13974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin M., Simons P., Jaeggi K., Wigger N. CGP-12177. A hydrophilic beta-adrenergic receptor radioligand reveals high affinity binding of agonists to intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3496–3502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol Rev. 1984 Apr;64(2):661–743. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.2.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Blake A. D., Cheung A. H., Register R. B., Rands E., Zemcik B. A., Candelore M. R., Dixon R. A. The carboxyl terminus of the hamster beta-adrenergic receptor expressed in mouse L cells is not required for receptor sequestration. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):855–863. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90623-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the beta-subunit of bovine transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Liao Y. C., Alborzi A., Beiderman B., Chang F. H., Masters S. B., Levinson A. D., Bourne H. R. Inhibitory and stimulatory G proteins of adenylate cyclase: cDNA and amino acid sequences of the alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventimiglia R., Greene M. I., Geller H. M. Localization of beta-adrenergic receptors on differentiated cells of the central nervous system in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5073–5077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. Y., Berrios M., Malbon C. C. Localization of beta-adrenergic receptors in A431 cells in situ. Effect of chronic exposure to agonist. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):533–538. doi: 10.1042/bj2630533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G., Davoust J., Cockcroft A. Recycling of transferrin receptors in A431 cells is inhibited during mitosis. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2217–2225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Regulation of G-proteins in differentiation. Altered ratio of alpha- to beta-subunits in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. R., Hadcock J. R., Johnson G. L., Malbon C. C. Antipeptide antibodies directed against cytoplasmic rhodopsin sequences recognize the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4319–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegant F. A., Blok F. J., Defize L. H., Linnemans W. A., Verkley A. J., Boonstra J. Epidermal growth factor receptors associated to cytoskeletal elements of epidermoid carcinoma (A431) cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):87–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Rodriguez H., Wong S. K., Brandt D. R., May D. C., Burnier J., Harkins R. N., Chen E. Y., Ramachandran J., Ullrich A. The avian beta-adrenergic receptor: primary structure and membrane topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]