Abstract
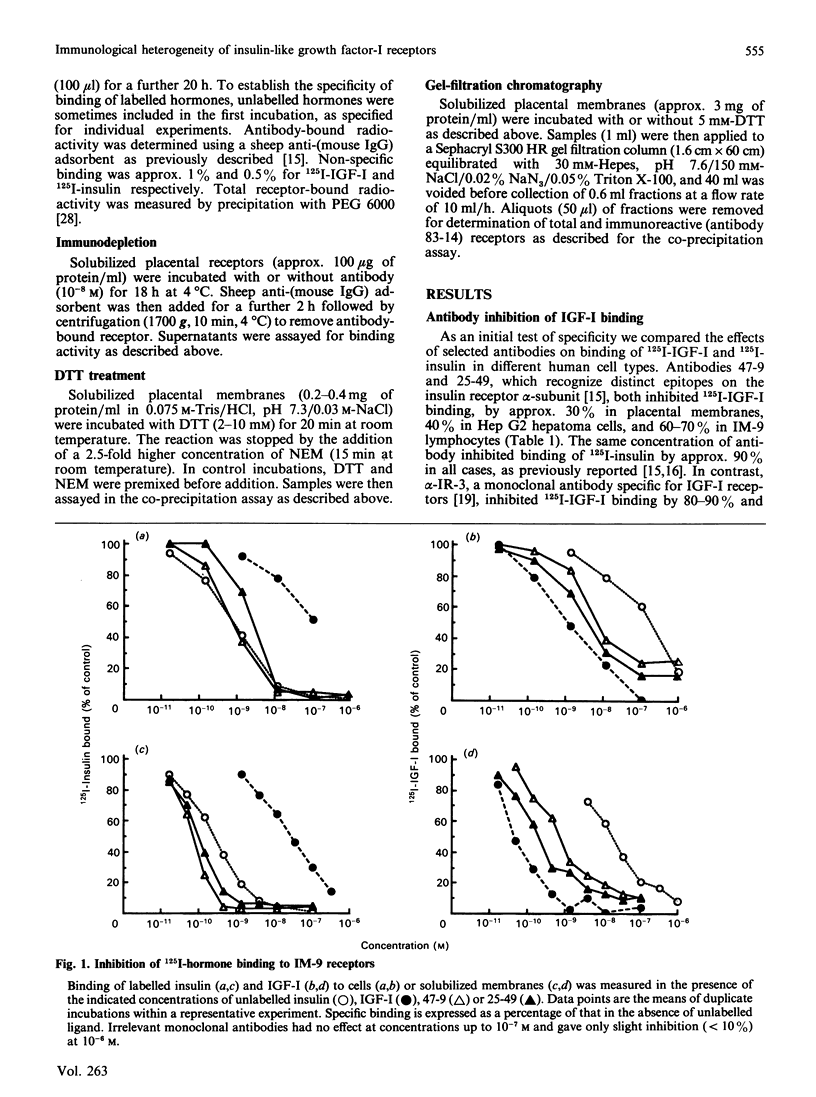
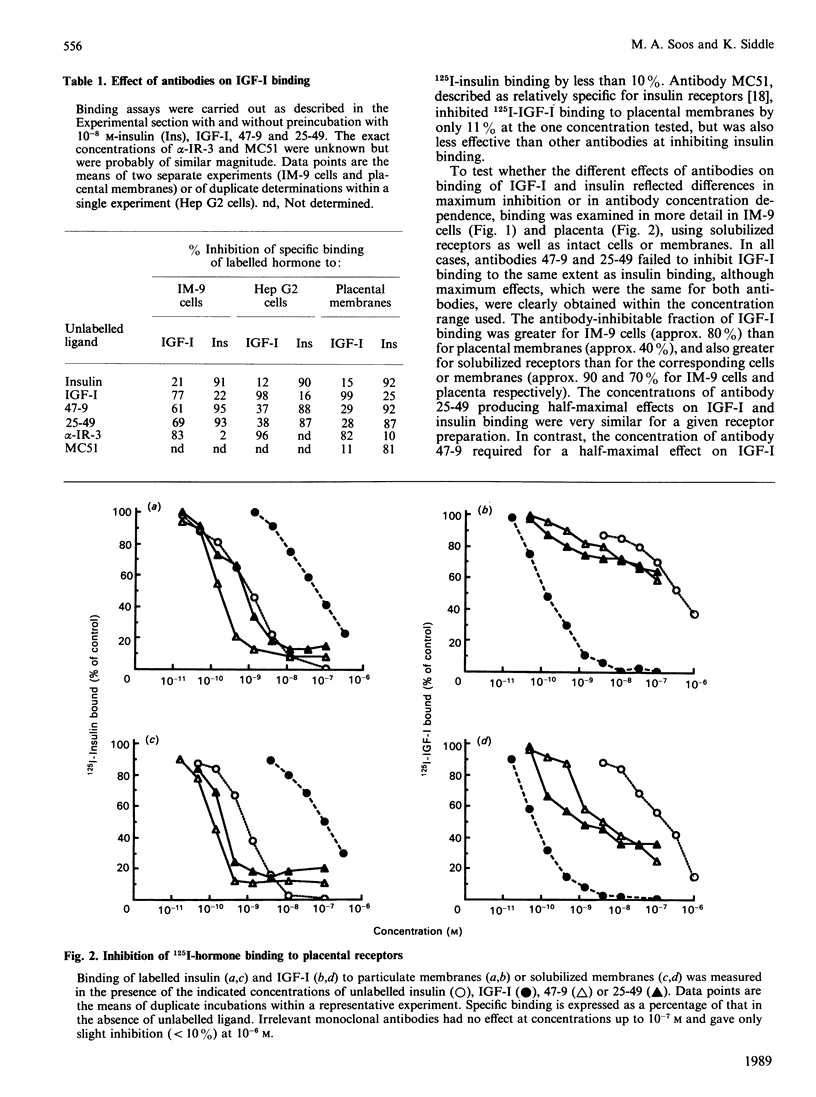
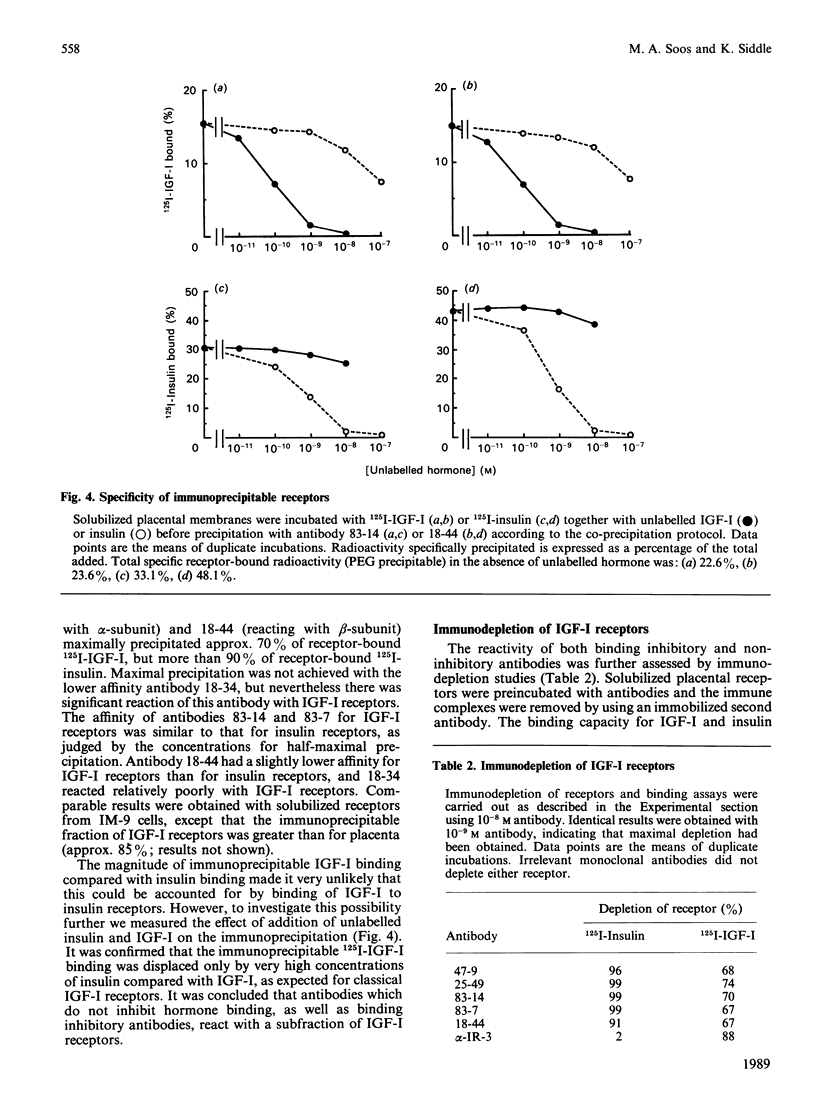
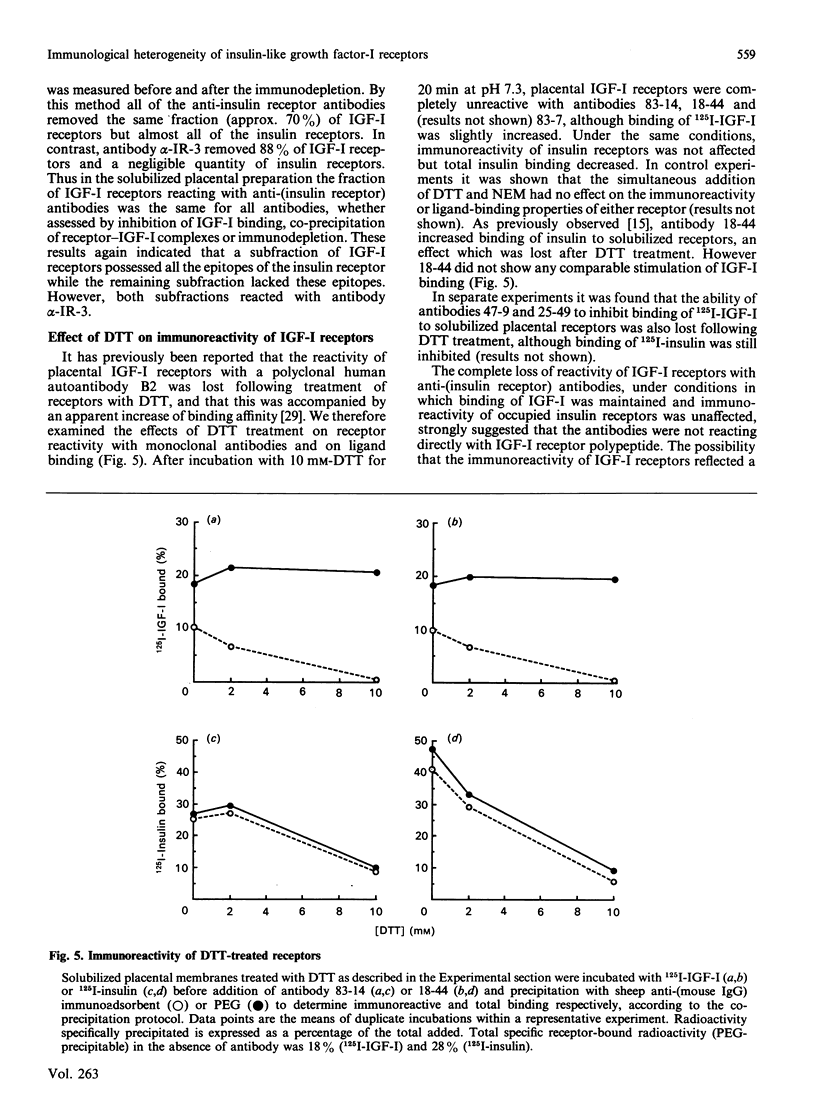
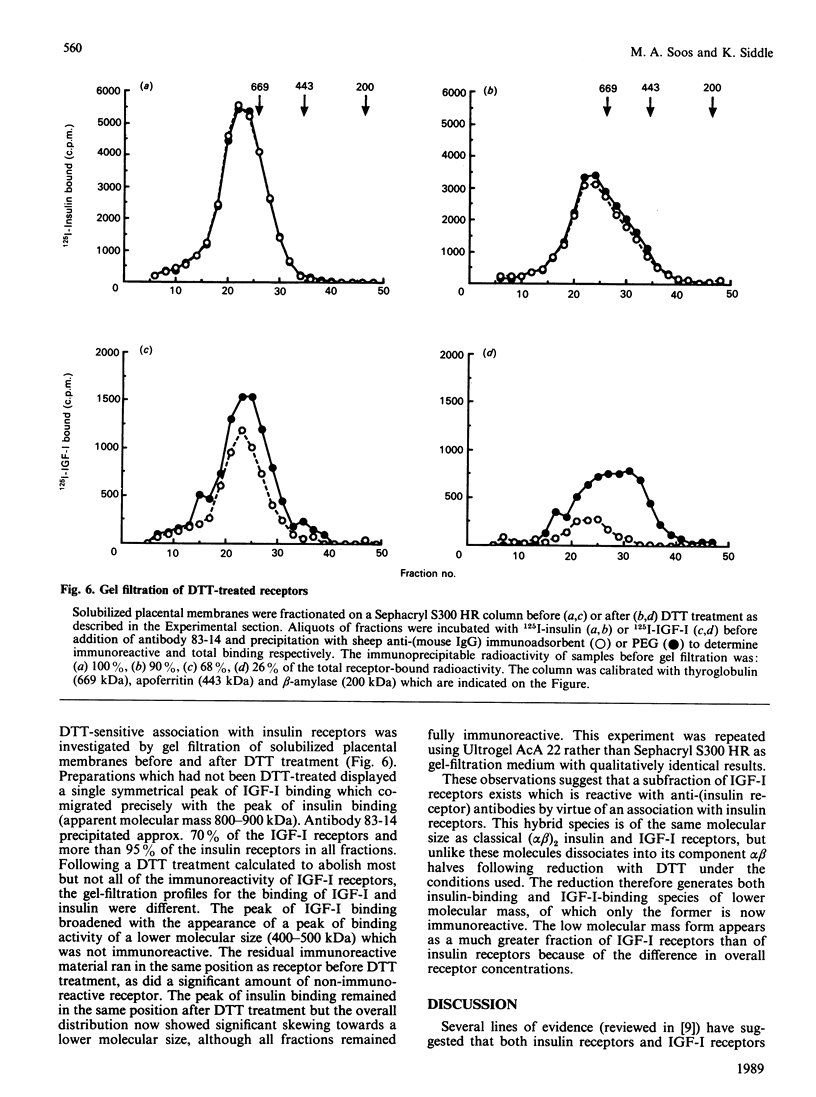
The receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) are closely related in primary sequence and overall structure. We have examined the immunological relationships between these receptors by testing the reactivity of anti-(insulin receptor) monoclonal antibodies with IGF-I receptors in various tissues and cell lines. Antibodies for six distinct epitopes reacted with a subfraction of IGF-I receptors, as shown by inhibition of 125I-IGF-I binding, precipitation of 125I-IGF-I-receptor complexes or immunodepletion of receptor from tissue extracts before binding assays. Both immunoreactive and non-immunoreactive subfractions displayed the expected properties of 'classical' IGF-I receptors, in terms of relative affinities for IGF-I and insulin. The proportion of total IGF-I receptors which was immunoreactive varied in different cell types, being approx. 40% in Hep G2 cells, 35-40% in placental membranes and 75-85% in IM-9 cells. The immunoreactive fraction was somewhat higher in solubilized receptors than in the corresponding intact cells or membranes. A previously described monoclonal antibody, alpha-IR-3, specific for IGF-I receptors, inhibited IGF-I binding by more than 80% in all preparations. When solubilized placental receptors were pretreated with dithiothreitol (DTT) under conditions reported to reduce intramolecular (class I) disulphide bonds, the immunoreactivity of IGF-I receptors was abolished although total IGF-I binding was little affected. Under the same conditions insulin receptors remained fully immunoreactive. When solubilized receptor preparations were fractionated by gel filtration, both IGF-I and insulin receptors ran as symmetrical peaks of identical mobility. After DTT treatment, the IGF-I receptor was partially converted to a lower molecular mass form which was not immunoreactive. The insulin receptor peak showed a much less pronounced skewing and remained fully immunoreactive in all fractions. It is concluded that the anti- (insulin receptor) antibodies do not react directly with IGF-I receptor polypeptide, and that the apparent immunoreactivity of a subfraction of IGF-I receptors reflects their physical association with insulin receptors, both in cell extracts and in intact cells. The most likely basis for this association appears to be a 'hybrid' receptor containing one half (alpha beta) of insulin receptor polypeptide and the other (alpha' beta') of IGF-I receptor polypeptide within the native (alpha beta beta' alpha') heterotetrameric structure.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Siddle K., Dolash S., Boes M., Dake B. Actions of insulin and insulinlike growth factors I and II in cultured microvessel endothelial cells from bovine adipose tissue. Metabolism. 1988 Aug;37(8):714–720. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. D., Sönksen P. H. Characterization of two insulin-binding components of rat-liver plasma membranes. Biosci Rep. 1982 Oct;2(10):785–793. doi: 10.1007/BF01114938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Scott W., Waugh S. M., DiBella E., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor. Structural basis for high affinity ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8395–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. The nature and regulation of the insulin receptor: structure and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Roth J. Cooperativity in ligand binding: a new graphic analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1118–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90473-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz S. M., Swanson M. L., Wemmie J. A., Pessin J. E. Functional properties of an isolated alpha beta heterodimeric human placenta insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor complex. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3234–3242. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Choi S., Sakamoto Y., Itakura K. Purification of insulin receptor with full binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5045–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S. Insulin receptors: binding kinetics and structure-function relationship of insulin. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1321–1378. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. N., Woodhead J. S. Labeled antibodies and their use in the immunoradiometric assay. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):334–355. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Rosen O. M. Antibodies to deduced sequences of the insulin receptor distinguish conserved and nonconserved regions in the IGF-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2489–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cook S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Interaction of the monoclonal antibodies alpha IR-1 and alpha IR-3 with insulin and somatomedin-C receptors. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):223–226. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Effects of hormones and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):934–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Wong M. L., Rutter W. J. Properties of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7516–7520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Baxter R. C., Harrison L. C. Structural differences between insulin and somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors revealed by autoantibodies to the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Nov 30;109(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91744-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Cox A. J., Harrison L. C. Delineation of atypical insulin receptors from classical insulin and type I insulin-like growth factor receptors in human placenta. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 1;257(1):101–107. doi: 10.1042/bj2570101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. Disulphide reduction alters the immunoreactivity and increases the affinity of insulin-like growth-factor-I receptors in human placenta. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):417–423. doi: 10.1042/bj2360417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. The human placenta contains two distinct binding and immunoreactive species of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2288–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Newman J. D., Harrison L. C. An atypical insulin receptor with high affinity for insulin-like growth factors copurified with placental insulin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4124–4128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. The molecular mechanism of insulin action. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:429–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Sasaki N., Kahn C. R., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Antireceptor antibodies as probes of insulinlike growth factor receptor structure. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1459–1469. doi: 10.1172/JCI111102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiess W., Blickenstaff G. D., Sklar M. M., Thomas C. L., Nissley S. P., Sahagian G. G. Biochemical evidence that the type II insulin-like growth factor receptor is identical to the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9339–9344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang U., Kahn C. R., Harrison L. C. Subunit structure of the insulin receptor of the human lymphocyte. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):64–70. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBon T. R., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P., Kathuria S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Purification of insulin-like growth factor I receptor from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7685–7689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde S., Hansen B., Sonne O., Holst J. J., Gliemann J. Tyrosine A14[125I]monoiodoinsulin: Preparation, Biologic Properties, and long-term stability. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa H., Olefsky J. M., Thies S., Boyd D., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Insulin receptors with defective tyrosine kinase inhibit normal receptor function at the level of substrate phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12629–12637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maly P., Lüthi C. Purification of the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor from human placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):695–701. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody which can distinguish between two distinct species of the type I receptor for insulin-like growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1341–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Mapping surface structures of the human insulin receptor with monoclonal antibodies: localization of main immunogenic regions to the receptor kinase domain. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1364–1371. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Shafer J. A. Evidence that insulin receptor from human placenta has a high affinity for only one molecule of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8589–8596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet R. J., Haase B. A., Standaert M. L. Characterization of detergent-solubilized membrane proteins. Hydrodynamic and sedimentation equilibrium properties of the insulin receptor of the cultured human lymphoblastoid cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12118–12126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Methods for assessing immunologic and biologic properties of iodinated peptide hormones. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:223–233. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J., Wong K. Y., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor block insulin binding and inhibit insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7312–7316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Maddux B., Wong K. Y., Styne D. M., Van Vliet G., Humbel R. E., Goldfine I. D. Interactions of a monoclonal antibody to the insulin receptor with receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinology. 1983 May;112(5):1865–1867. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-5-1865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Bell G. I. Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K., Baron M. D., Heward J. M., Luzio J. P., Bellatin J., Lennox E. S. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2350199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Vanderlaan M., Juarez-Salinas H. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascites fluid by hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jan 21;76(1):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins G., Turner J., Edman J. C., Hari J., Pierce S. B., Stover C., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11486–11492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Morrison B. D., Pessin J. E. Isolation of functional alpha beta heterodimers from the purified human placental alpha 2 beta 2 heterotetrameric insulin receptor complex. A structural basis for insulin binding heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6939–6942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Morrison B. D., Wilden P. A., Pessin J. E. Insulin-dependent intermolecular subunit communication between isolated alpha beta heterodimeric insulin receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16730–16738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Soos M. A., Wells A., Argyraki M., Siddle K. Insulin-like and insulin-inhibitory effects of monoclonal antibodies for different epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2420123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl E. J., Roth R. A., Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D. Dual regulation of glycogen metabolism by insulin and insulin-like growth factors in human hepatoma cells (HEP-G2). Analysis with an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1436–1443. doi: 10.1172/JCI111555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


