Abstract
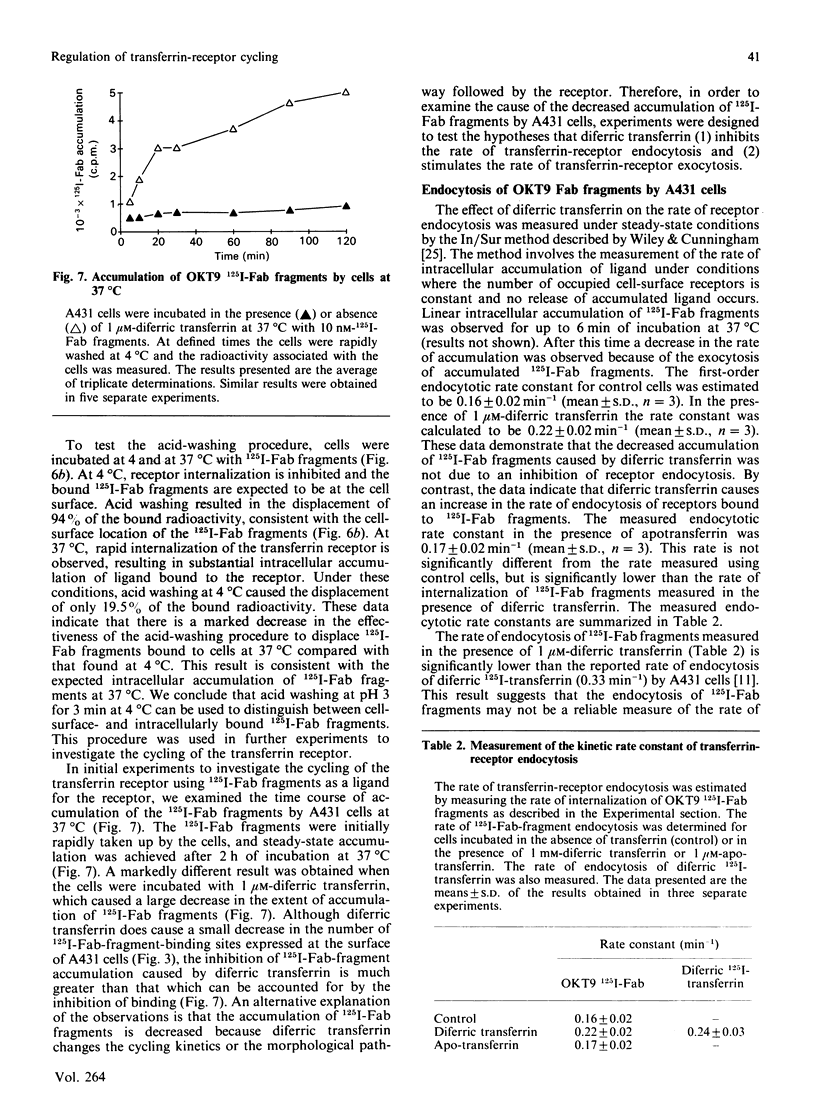
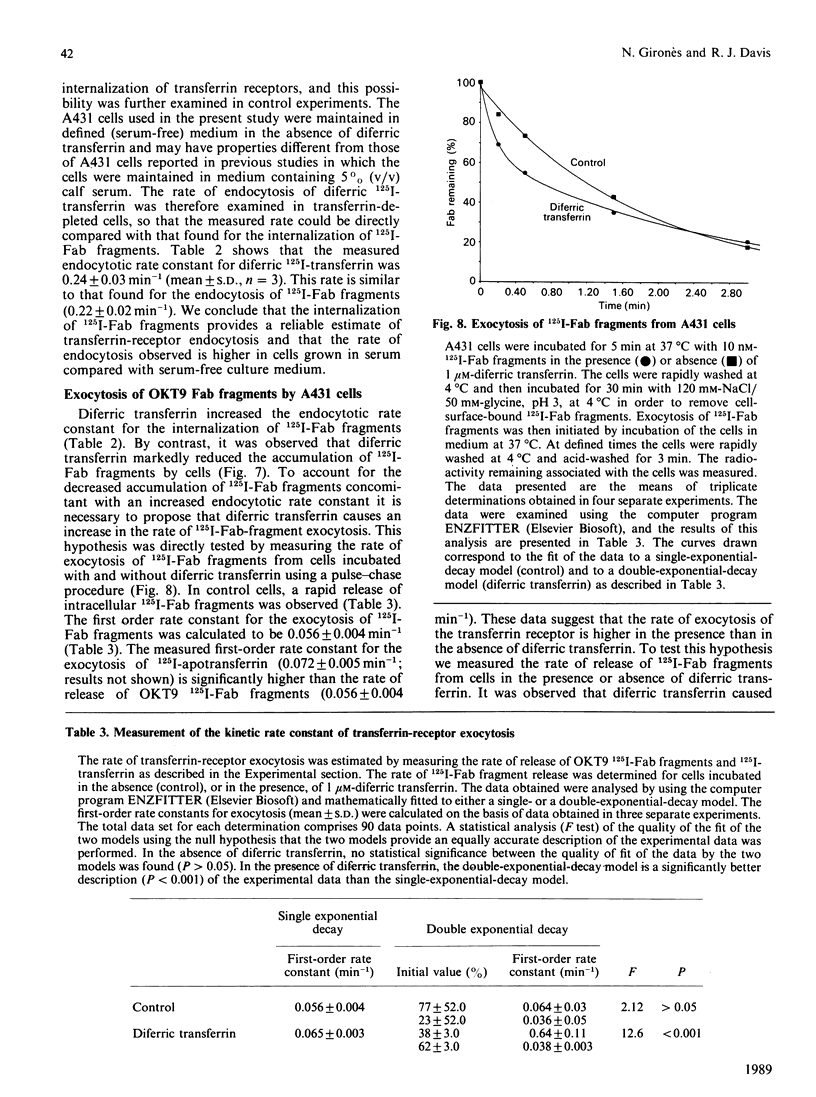
The kinetics of cycling of the transferrin receptor in A431 human epidermoid-carcinoma cells was examined in the presence or absence of bound diferric transferrin. In order to investigate the properties of the receptor in the absence of transferrin, the cells were maintained in defined medium without transferrin. It was demonstrated that Fab fragments of a monoclonal anti-(transferrin receptor) antibody (OKT9) did not alter the binding of diferric 125I-transferrin to the receptor or change the accumulation of [59Fe]diferric transferrin by cells. OKT9 125I-Fab fragments were prepared and used as a probe for the function of the receptor. The first-order rate constants for endocytosis (0.16 +/- 0.02 min-1) and exocytosis (0.056 +/- 0.003 min-1) were found to be significantly lower for control cells than the corresponding rate constants for endocytosis (0.22 +/- 0.02 min-1) and exocytosis (0.065 +/- 0.004 min-1) measured for cells incubated with 1 microM-diferric transferrin (mean +/- S.D., n = 3). The cycling of the transferrin receptor is therefore regulated by diferric transferrin via an increase in both the rate of endocytosis and exocytosis. Examination of the accumulation of OKT9 125I-Fab fragments indicated that diferric transferrin caused a marked decrease in the amount of internalized 125I-Fab fragments associated with the cells after 60 min of incubation at 37 degrees C. Diferric transferrin therefore increases the efficiency of the release of internalized 125I-Fab fragments compared with cells incubated without diferric transferrin. These data indicate that transferrin regulates the sorting of the transferrin receptor at the cell surface and within endosomal membrane compartments.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajioka R. S., Kaplan J. Intracellular pools of transferrin receptors result from constitutive internalization of unoccupied receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6445–6449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Ciechanover A., Lodish H. F. pH and the recycling of transferrin during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Corvera S., Czech M. P. Insulin stimulates cellular iron uptake and causes the redistribution of intracellular transferrin receptors to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8708–8711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Regulation of transferrin receptor expression at the cell surface by insulin-like growth factors, epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):653–658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Faucher M., Racaniello L. K., Carruthers A., Czech M. P. Insulin-like growth factor I and epidermal growth factor regulate the expression of transferrin receptors at the cell surface by distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13126–13134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Kelleher D. J., Anderson J. K., Mole J. E., Czech M. P. Identification of serine 24 as the unique site on the transferrin receptor phosphorylated by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9034–9041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Meisner H. Regulation of transferrin receptor cycling by protein kinase C is independent of receptor phosphorylation at serine 24 in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16041–16047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R. Intracellular routing of transferrin and transferrin receptors in epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R. The appearance and internalization of transferrin receptors at the margins of spreading human tumor cells. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Trowbridge I. S. Internalization and processing of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in human carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):508–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Trowbridge I. S. Internalization and processing of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in human carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):508–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings S. E., Sato G. H. Growth and maintenance of HeLa cells in serum-free medium supplemented with hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):901–904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing S. Q., Trowbridge I. S. Identification of the intermolecular disulfide bonds of the human transferrin receptor and its lipid-attachment site. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):327–331. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Mintz B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in developmentally totipotent mouse teratocarcinoma stem cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3245–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J., van Renswoude J. Rapid internalization of the transferrin receptor in K562 cells is triggered by ligand binding or treatment with a phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Van Renswoude J., Ashwell G., Kempf C., Schechter A. N., Dean A., Bridges K. R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4715–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. E., Ray F., Ward J. H., Kushner J. P., Kaplan J. Internalization and subcellular localization of transferrin and transferrin receptors in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8751–8758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Williams A. F. The kinetics of antibody binding to membrane antigens in solution and at the cell surface. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):1–20. doi: 10.1042/bj1870001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Association of phorbol ester-induced hyperphosphorylation and reversible regulation of transferrin membrane receptors in HL60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P. Transferrin receptor: its biological significance. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(3):205–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01871086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw T. E., Dunn K. W., Maxfield F. R. Phorbol ester treatment increases the exocytic rate of the transferrin receptor recycling pathway independent of serine-24 phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D., Kühn L. C. Noncoding 3' sequences of the transferrin receptor gene are required for mRNA regulation by iron. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Jencks W. P. Energetics of the calcium-transporting ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1629–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K., Harford J. B., Rouault T., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H., Klausner R. D. Transcriptional regulation by iron of the gene for the transferrin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):236–240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberger S., Iacopetta B. J., Kühn L. C. Endocytosis of the transferrin receptor requires the cytoplasmic domain but not its phosphorylation site. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman N. H., Maxfield F. R. Intracellular fusion of sequentially formed endocytic compartments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1083–1091. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Sutherland R., Newman R., Greaves M. Structural features of the cell surface receptor for transferrin that is recognized by the monoclonal antibody OKT9. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8516–8522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider M. D., Rogers O. C. Intracellular movement of cell surface receptors after endocytosis: resialylation of asialo-transferrin receptor in human erythroleukemia cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):826–834. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Sussman H. H. Demonstration of two distinct transferrin receptor recycling pathways and transferrin-independent receptor internalization in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10319–10331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner L. I., Lienhard G. E. Insulin elicits a redistribution of transferrin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through an increase in the rate constant for receptor externalization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):8975–8980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Kaplan J. Mitogenic agents induce redistribution of transferrin receptors from internal pools to the cell surface. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):721–728. doi: 10.1042/bj2380721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts C. Rapid endocytosis of the transferrin receptor in the absence of bound transferrin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):633–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman A. M., Klausner R. D., Rao K., Harford J. B. Exposure of K562 cells to anti-receptor monoclonal antibody OKT9 results in rapid redistribution and enhanced degradation of the transferrin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):951–958. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S. Anomalous binding of epidermal growth factor to A431 cells is due to the effect of high receptor densities and a saturable endocytic system. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):801–810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. A steady state model for analyzing the cellular binding, internalization and degradation of polypeptide ligands. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Kaplan J. Epidermal growth factor rapidly induces a redistribution of transferrin receptor pools in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7456–7460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Hanover J. A., Dickson R. B., Pastan I. Morphologic characterization of the pathway of transferrin endocytosis and recycling in human KB cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):175–179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. W., Doriaux M., Farquhar M. G. Transferrin receptors recycle to cis and middle as well as trans Golgi cisternae in Ig-secreting myeloma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):277–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Suomalainen M., Zanetti-Schneider M., Schneider C., Garoff H. Phosphorylation of the human transferrin receptor by protein kinase C is not required for endocytosis and recycling in mouse 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2661–2667. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]