Abstract
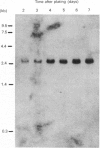
We showed previously that the levels of type I regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase increase during differentiation of L6 skeletal myoblasts as a result of a specific decrease in its rate of degradation. Studies on the rates of degradation of the catalytic subunit show that unlike the type I regulatory subunit, catalytic subunit is degraded very slowly in myoblasts (t1/2 = 29 h) and more rapidly in myotubes (t1/2 = 14 h). As with the regulatory subunit, the degradation of catalytic subunit is increased by treatment of myoblasts with cyclic AMP analogues. These results suggest that the overall increase in the amount of type I cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme during myogenesis is due to the increase in levels of mRNA for the catalytic subunit. This probably leads to an increase in the amount of catalytic subunit, which then stabilizes the regulatory subunit, thereby causing an increase in the levels of this protein also.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhanaty E., Patinkin J., Tauber-Finkelstein M., Shaltiel S. Degradative inactivation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by a membranal proteinase is restricted to the free catalytic subunit in its native conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3492–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Nelson W. J., Moon R. T., Lazarides E. Synthesis and assembly of spectrin during avian erythropoiesis: stoichiometric assembly but unequal synthesis of alpha and beta spectrin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. H., Zalin R. J. Regulation of muscle differentiation: stimulation of myoblast fusion in vitro by catecholamines. Science. 1981 Dec 18;214(4527):1355–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6274017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulis B. H. Regulation of protein expression in differentiation by subunit assembly. Human membrane and secreted IgM. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2181–2187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings B. A. cAMP mediated proteolysis of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):126–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Moon R. T. Assembly and topogenesis of the spectrin-based membrane skeleton in erythroid development. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):354–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehnert M. E., Lodish H. F. Unequal synthesis and differential degradation of alpha and beta spectrin during murine erythroid differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):413–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer I. A., Mason M. E., Sanwal B. D. Levels of type I cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit are regulated by changes in turnover rate during skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17200–17205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen O., Frøysa A., Sandberg M., Eskild W., Joseph D., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Cellular localization and age-dependent changes in mRNA for cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in rat testis. Biol Reprod. 1987 Nov;37(4):947–956. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod37.4.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. E., Narindrasorasak S., Cates G. A., Sanwal B. D. Regulation of protein kinase and its regulatory subunits during skeletal myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8002–8007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showers M. O., Maurer R. A. A cloned bovine cDNA encodes an alternate form of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16288–16291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Carmichael D. F., Lee D. C., Chrivia J. C., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the catalytic subunit of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1300–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Chrivia J. C., McKnight G. S. Evidence for a second isoform of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15360–15363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Expression of cDNAs for two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15202–15207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahrmann J. P., Winand R., Luzzati D. Effect of cyclic AMP on growth and morphological differentiation of an established myogenic cell line. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 26;245(143):112–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio245112a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]