Abstract
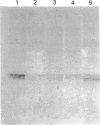
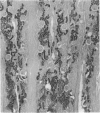
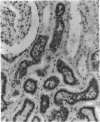
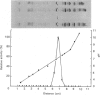
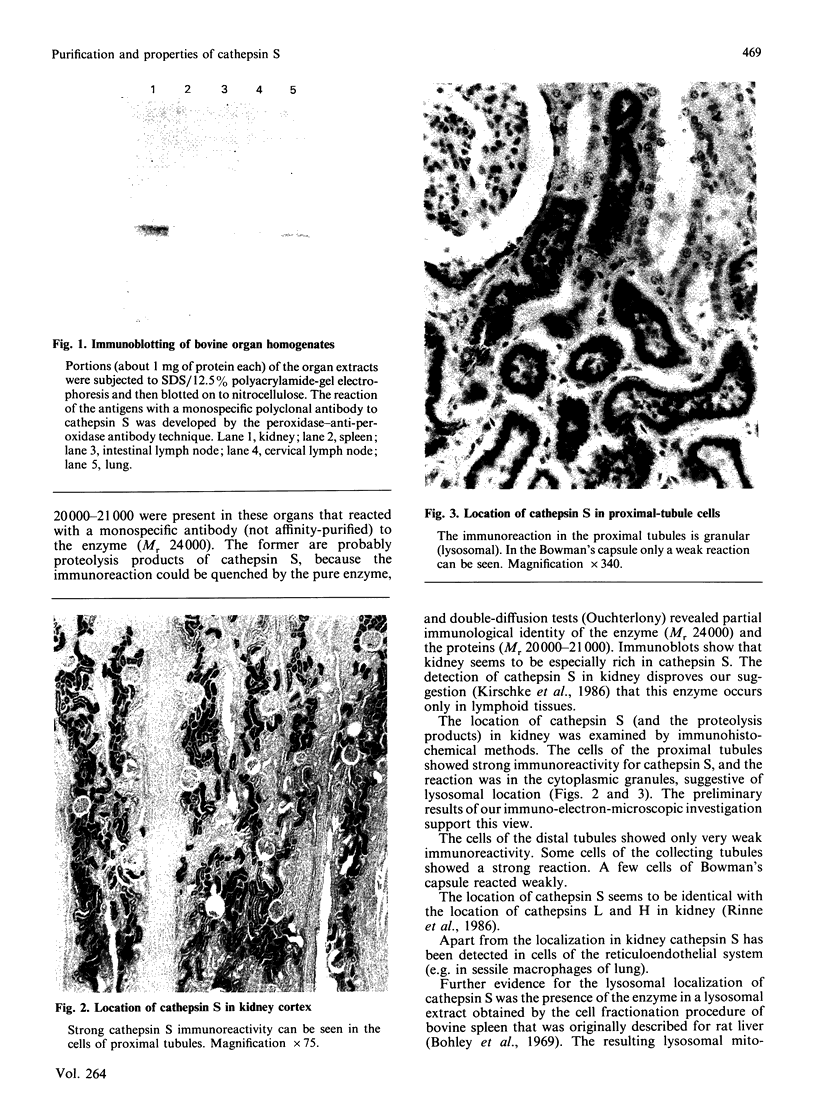
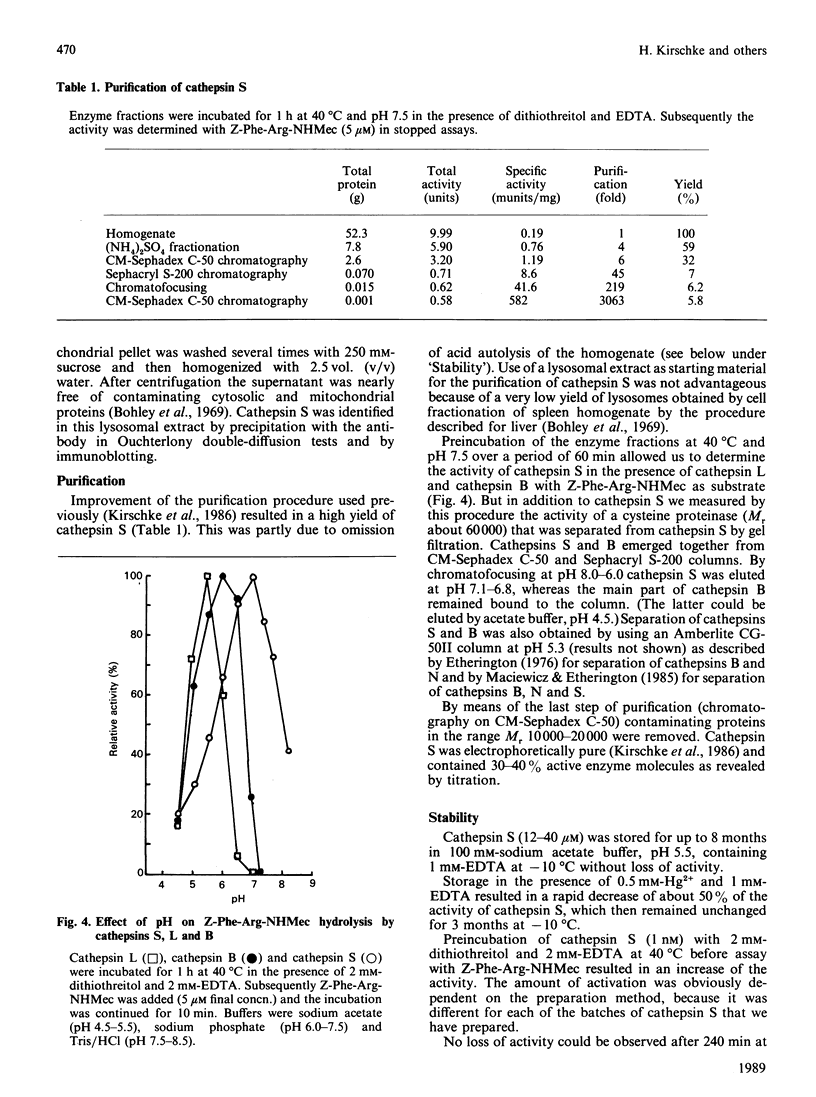
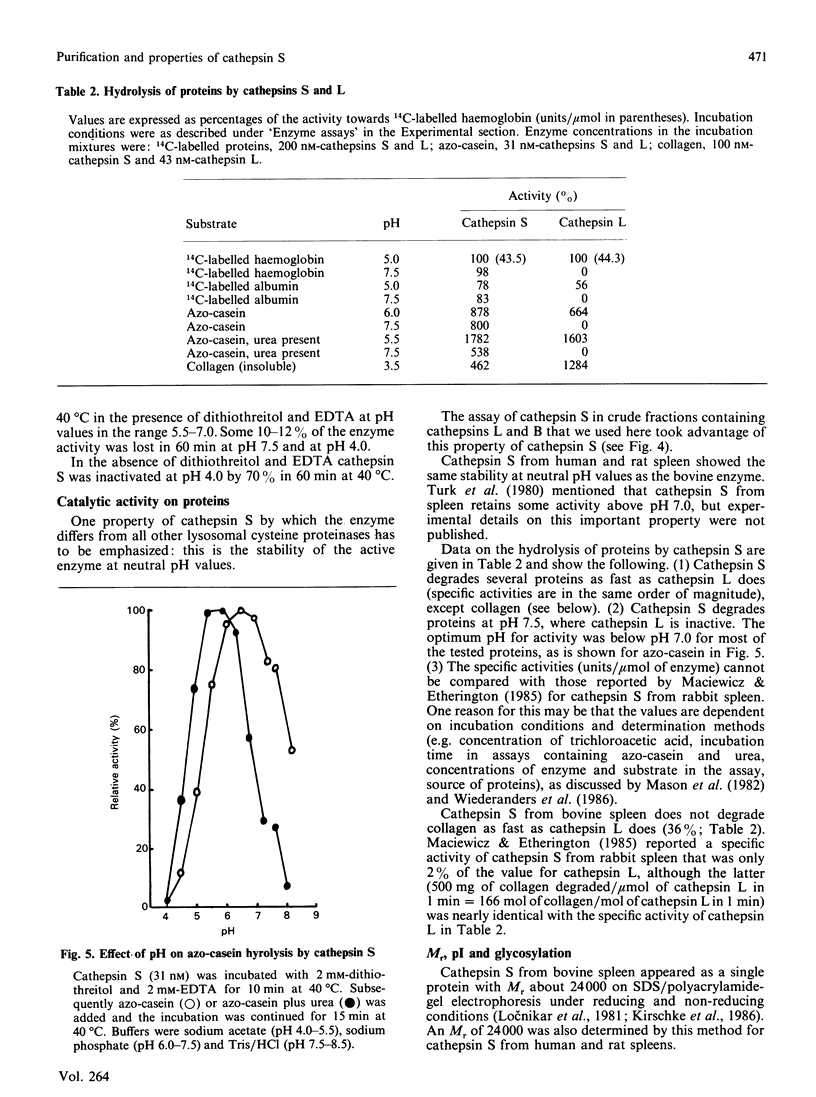
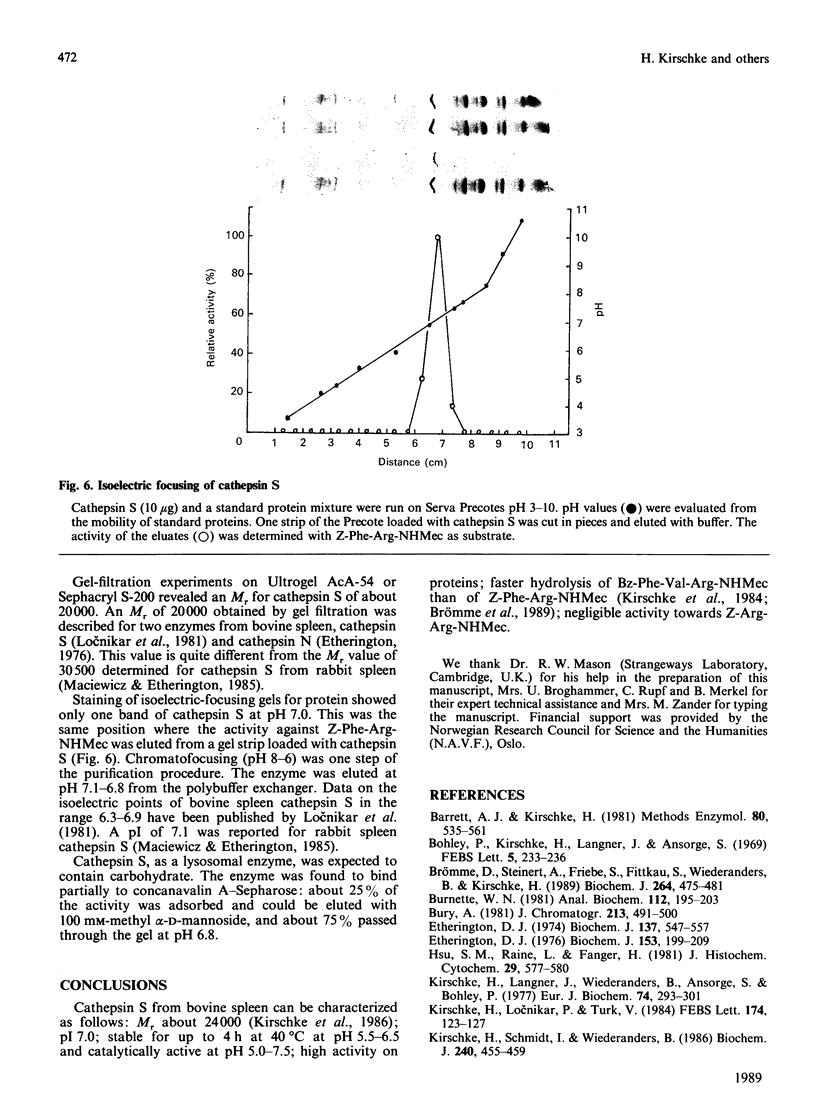
Cathepsin S was detected in bovine kidney, spleen, lymph nodes and lung by immunochemical methods. The immunostaining of cathepsin S in kidney was concentrated to the cells of the proximal tubule, where the enzyme was present in cytoplasmic granules. The purification method for cathepsin S from bovine spleen involved (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, chromatography on CM-Sephadex C-50, gel filtration on Sephacryl S-200 and chromatofocusing (pH 8.0-6.0). The enzyme was partially destroyed by autolysis of the homogenate at pH 4.2. The isoelectric point of cathepsin S was 7.0. Cathepsin S was found to hydrolyse proteins at a similar rate to cathepsin L below pH 7.0. At pH values of 7.0-7.5 cathepsin S retained most of its activity, whereas cathepsin L was completely inactive.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett A. J., Kirschke H. Cathepsin B, Cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):535–561. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohley P., Kirschke H., Langner J., Ansorge S. Präparative gewinnung hochgereinigter lysosomenenzyme aus rattenlebern. FEBS Lett. 1969 Nov 12;5(3):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brömme D., Steinert A., Friebe S., Fittkau S., Wiederanders B., Kirschke H. The specificity of bovine spleen cathepsin S. A comparison with rat liver cathepsins L and B. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):475–481. doi: 10.1042/bj2640475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. Bovine spleen cathepsin B1 and collagenolytic cathepsin. A comparative study of the properties of the two enzymes in the degradation of native collagen. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):199–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1530199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. The purification of bovine cathepsin B1 and its mode of action on bovine collagens. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):547–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1370547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P. Cathepsin L. A new proteinase from rat-liver lysosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Locnikar P., Turk V. Species variations amongst lysosomal cysteine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Schmidt I., Wiederanders B. Cathepsin S. The cysteine proteinase from bovine lymphoid tissue is distinct from cathepsin L (EC 3.4.22.15). Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):455–459. doi: 10.1042/bj2400455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregar I., Locnikar P., Popović T., Suhar A., Lah T., Ritonja A., Gubensek F., Turk V. Bovine intracellular cysteine proteinases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1433–1438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner J., Ansorge S., Bohhley P., Kirschke H., Hanson H. Intracellular protein breakdown. I. Activity determinations of endoipeptidases using protein substrates. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;26(5):935–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciewicz R. A., Etherington D. J. A comparison of four cathepsins (B, L, N and S) with collagenolytic activity from rabbit spleen. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2560433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Taylor M. A., Etherington D. J. Purification and characterisation of collagenolytic cathepsins from rabbit liver. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80699-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne A., Järvinen M., Kirschke H., Wiederanders B., Hopsu-Havu V. K. Demonstration of cathepsins H and L in rat tissues. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1465–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Audran R. The isolation of IgG from mammalian sera with the aid of caprylic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnsek T., Kregar I., Lebez D. Acid sulphydryl protease from calf lymph nodes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):514–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:440–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederanders B., Kirschke H. Antibodies to rat liver cathepsins: characterization and use for the identification of enzyme precursors. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1421–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederanders B., Kirschke H., Schaper S. The azocasein-urea-pepstatin assay discriminates between lysosomal proteinases. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederanders B., Schaper S., Kirschke H. Isolation and some properties of a cathepsin E type proteinase from rat spleen. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1989;48(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]