Abstract
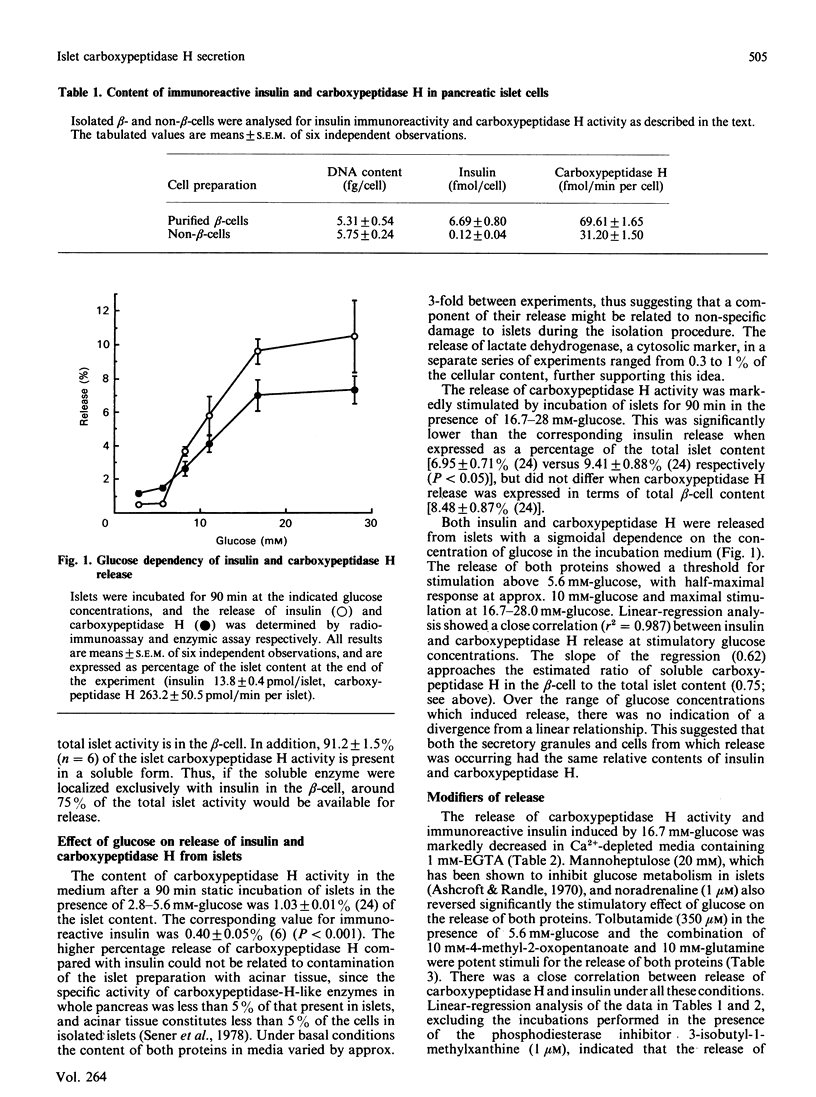
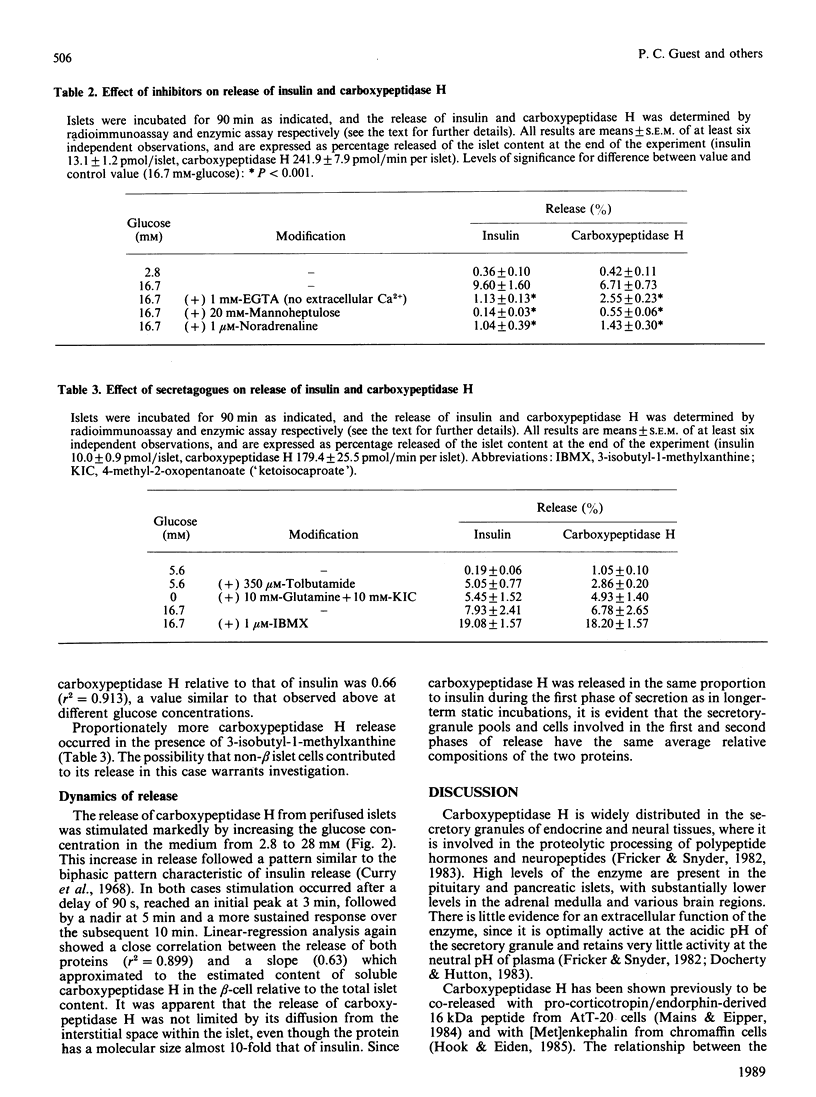
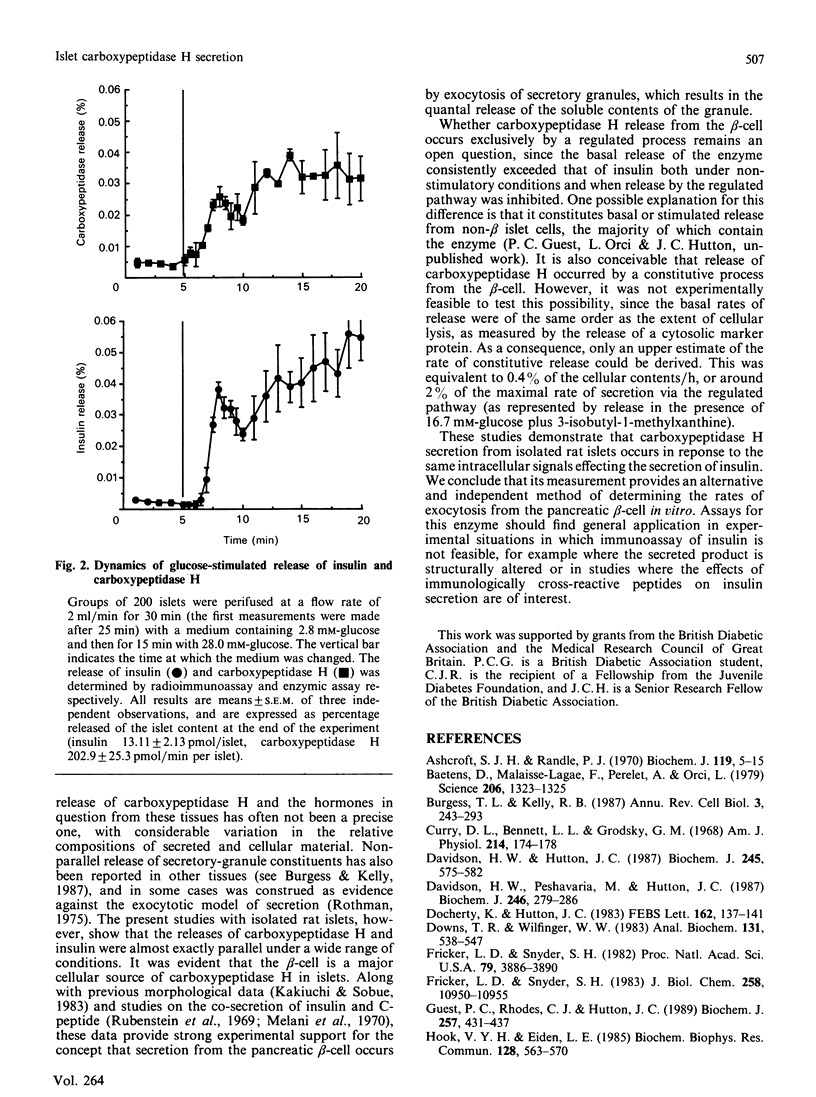
The release of carboxypeptidase H activity from isolated rat islets was determined and compared to the secretion of immunoreactive insulin. Analysis of pancreatic islet cells sorted into beta and non-beta types indicated that approx. 80% of islet carboxypeptidase H activity is present in the beta cell. The release of both insulin and carboxypeptidase H was stimulated markedly by increasing the glucose concentration in the medium from 2.8 to 28 mM. The fractional release was in accordance with the observed cellular distribution of both proteins. The secretory response was biphasic with time, with an initial rapid transient phase of release within 5 min, followed by a more sustained response. The concentration-dependencies of glucose stimulation of release of insulin and carboxypeptidase H were similar, with a threshold for stimulation around 5.6 mM-glucose and maximal stimulatory response at 16.7-28 mM-glucose. The release of both proteins was inhibited by 20 mM-mannoheptulose, removal of Ca2+ from the medium and addition of 1 microM-noradrenaline. The combination of 10 mM-4-methyl-2-oxopentanoate and 10 mM-glutamine stimulated the release of carboxypeptidase H and insulin, as did 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and 350 microM-tolbutamide in the presence of glucose. It is evident that carboxypeptidase H is released from the pancreatic beta-cell by an exocytotic process from the same intracellular compartment as insulin. The release of carboxypeptidase H by a constitutive process was at best equivalent to 0.4%/h, or less than 2% of the maximal rate of release via the regulated pathway. It is concluded that carboxypeptidase H can be used as a sensitive index of beta-cell secretion and an alternative marker to the insulin-related peptides.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft S. J., Randle P. J. Enzymes of glucose metabolism in normal mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;119(1):5–15. doi: 10.1042/bj1190005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetens D., Malaisse-Lagae F., Perrelet A., Orci L. Endocrine pancreas: three-dimensional reconstruction shows two types of islets of langerhans. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.390711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Kelly R. B. Constitutive and regulated secretion of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:243–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Requirement for calcium ion in insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):174–178. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Hutton J. C. The insulin-secretory-granule carboxypeptidase H. Purification and demonstration of involvement in proinsulin processing. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):575–582. doi: 10.1042/bj2450575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Peshavaria M., Hutton J. C. Proteolytic conversion of proinsulin into insulin. Identification of a Ca2+-dependent acidic endopeptidase in isolated insulin-secretory granules. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj2460279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Hutton J. C. Carboxypeptidase activity in the insulin secretory granule. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 3;162(1):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs T. R., Wilfinger W. W. Fluorometric quantification of DNA in cells and tissue. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):538–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Enkephalin convertase: purification and characterization of a specific enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase localized to adrenal chromaffin granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3886–3890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of enkephalin convertase, an enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10950–10955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest P. C., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. Regulation of the biosynthesis of insulin-secretory-granule proteins. Co-ordinate translational control is exerted on some, but not all, granule matrix constituents. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):431–437. doi: 10.1042/bj2570431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook V. Y., Eiden L. E. (Met)enkephalin and carboxypeptidase processing enzyme are co-released from chromaffin cells by cholinergic stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C. Secretory granules. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1091–1098. doi: 10.1007/BF01971456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. Secretion and regulation of two biosynthetic enzyme activities, peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase and a carboxypeptidase, by mouse pituitary corticotropic tumor cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1683–1690. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Identification of proinsulin and C-peptide in human serum by a specific immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., in't Veld P. A., Van de Winkel M., Maes E., Schuit F. C., Gepts W. A new in vitro model for the study of pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):806–816. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. The biosociology of pancreatic B cells. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):277–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00299019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Barrès E., Hutton J. C., Bicknell R. J. Radiometric assay for carboxypeptidase H (EC 3.4.17.10) and other carboxypeptidase B-like enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1989 Apr;178(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. S. Protein transport by the pancreas. Science. 1975 Nov 21;190(4216):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.1105785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Kawazu S., Hutton J. C., Boschero A. C., Devis G., Somers G., Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Effect of exogenous pyruvate on islet function. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):217–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1760217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobey W. J., Beer S. F., Carrington C. A., Clark P. M., Frank B. H., Gray I. P., Luzio S. D., Owens D. R., Schneider A. E., Siddle K. Sensitive and specific two-site immunoradiometric assays for human insulin, proinsulin, 65-66 split and 32-33 split proinsulins. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):535–541. doi: 10.1042/bj2600535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Winkle M., Maes E., Pipeleers D. Islet cell analysis and purification by light scatter and autofluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


