Abstract
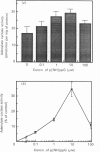
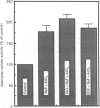
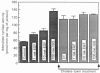
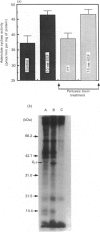
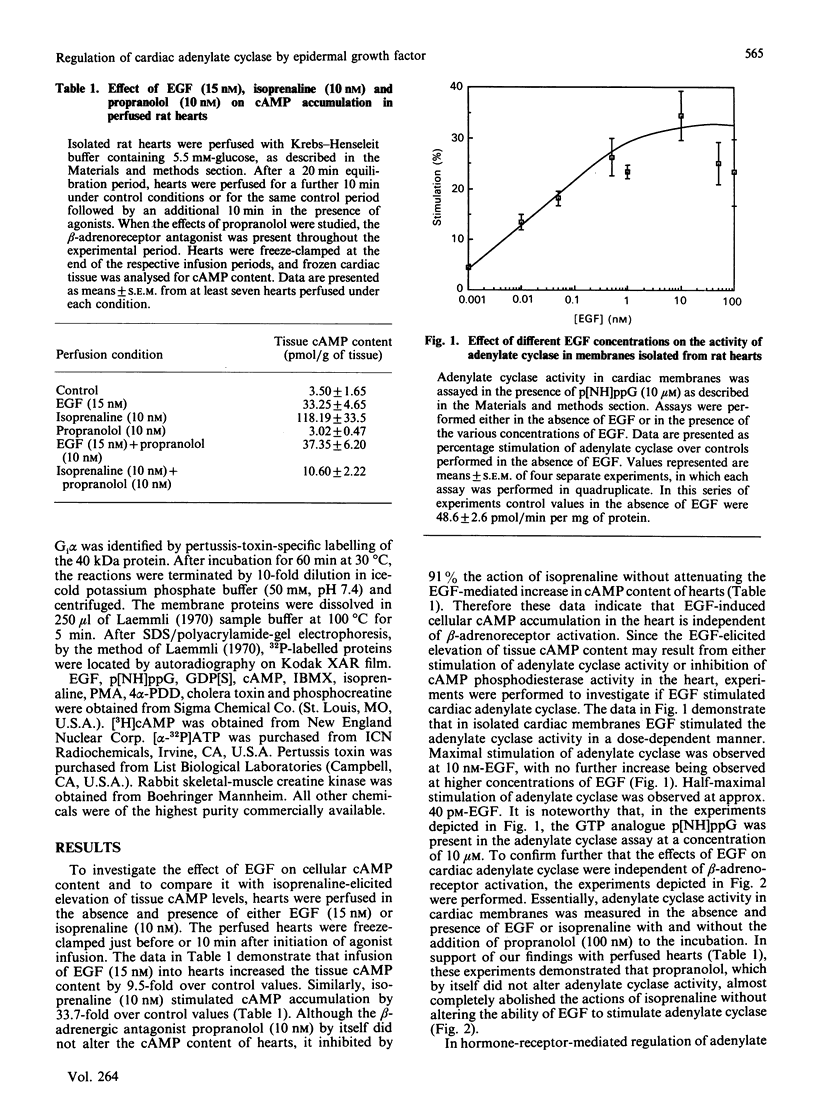
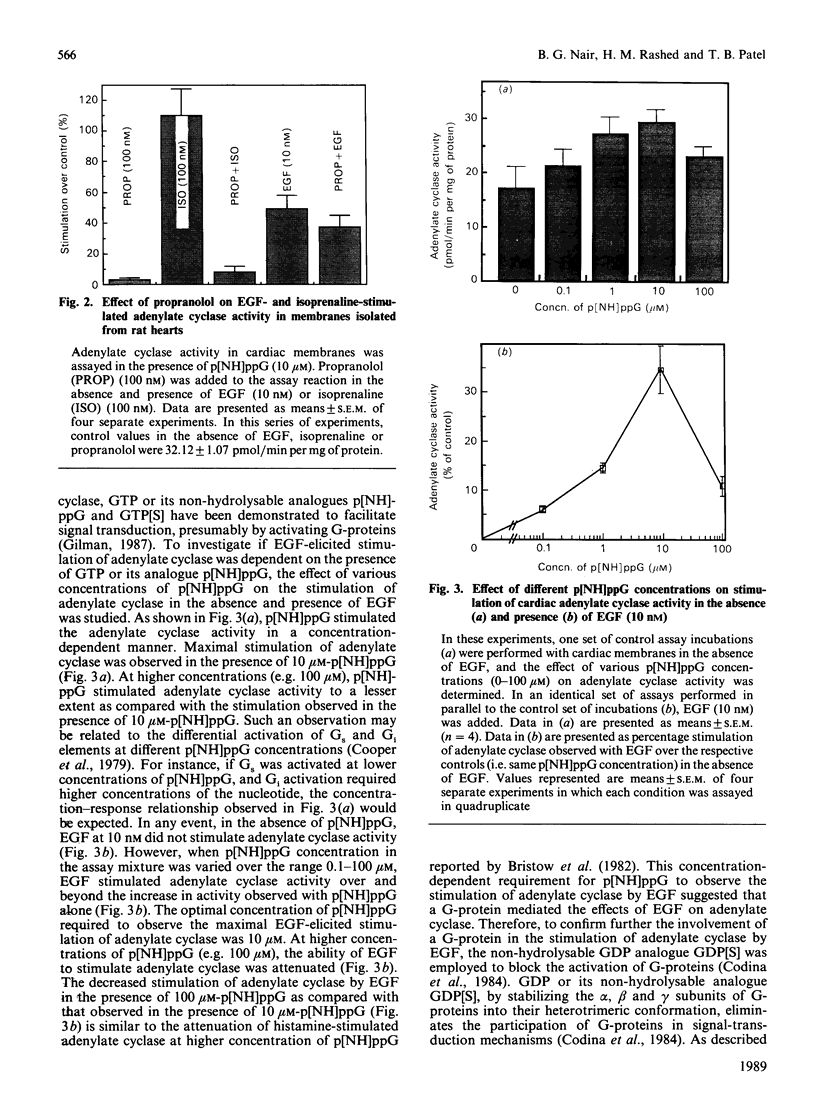
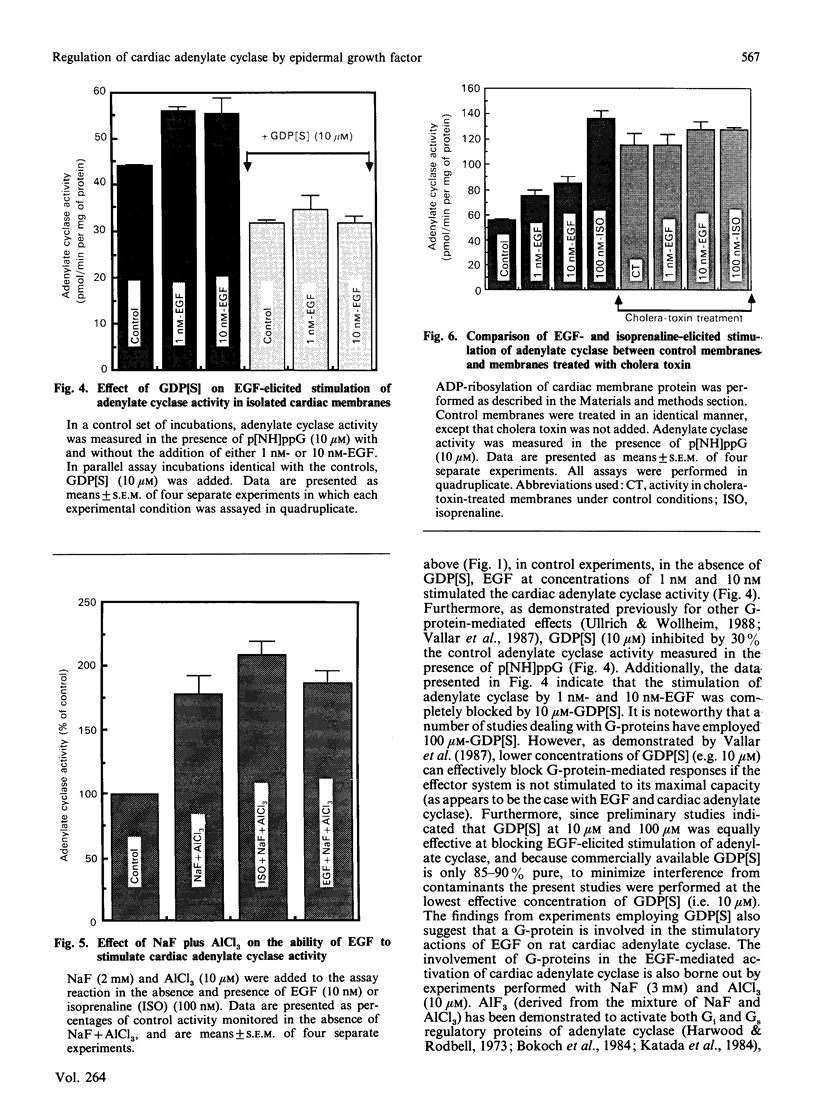
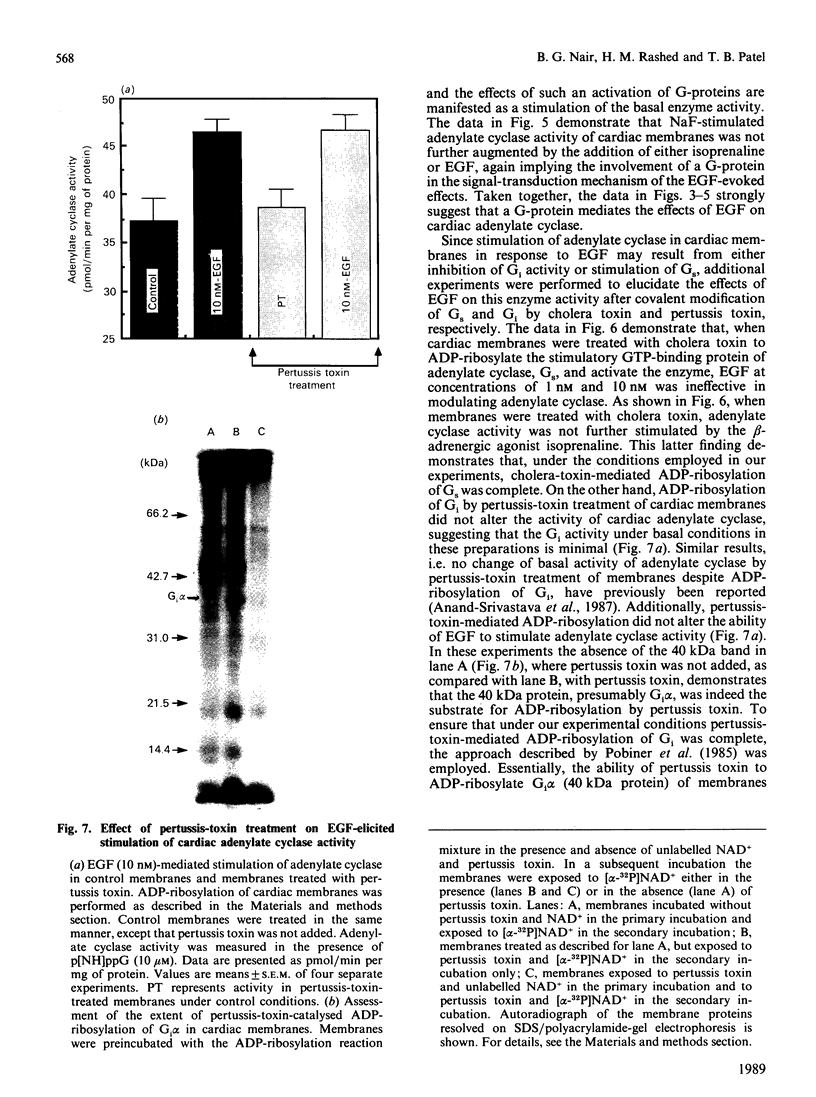
In isolated perfused rat hearts, epidermal growth factor (EGF; 15 nM) increased cellular cyclic AMP (cAMP) content by 9.5-fold. In rat cardiac membranes, EGF also stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in a dose-dependent manner, with maximal stimulation (35% above control) being observed at 10 nM-EGF. Half-maximal stimulation of adenylate cyclase was observed at 40 pM-EGF. Although the beta-adrenergic-receptor antagonist propranolol markedly attenuated the isoprenaline-mediated increase in cAMP content of perfused hearts and stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity, it did not alter the ability of EGF to elevate tissue cAMP content and stimulate adenylate cyclase. The involvement of a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein) in the activation of adenylate cyclase by EGF was indicated by the following evidence. First, the EGF-mediated stimulation of adenylate cyclase required the presence of the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue, guanyl-5'-yl-imidodiphosphate (p[NH]ppG). Maximal stimulation was observed in the presence of 10 microM-p[NH]ppG. Secondly, in the presence of 10 microM-p[NH]ppG, the stable GDP analogue guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate at a concentration of 10 microM blocked the stimulation of the adenylate cyclase by 1 nM- and 10 nM-EGF. Third, NaF + AlCl3-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity was not altered by EGF. The ability of EGF to stimulate adenylate cyclase was not affected by pertussis-toxin treatment of cardiac membranes. However, in cholera-toxin-treated cardiac membranes, when the adenylate cyclase activity was stimulated by 2-fold, EGF was ineffective. Finally, PMA by itself did not alter the activity of cardiac adenylate cyclase, but abolished the EGF-mediated stimulation of this enzyme activity. The experimental evidence in the present paper demonstrates, for the first time, that EGF stimulates adenylate cyclase in rat cardiac membranes through a stimulatory GTP-binding regulatory protein, and this effect is manifested in elevated cellular cAMP levels in perfused hearts exposed to EGF.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand-Srivastava M. B., Srivastava A. K., Cantin M. Pertussis toxin attenuates atrial natriuretic factor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Involvement of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4931–4934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. B., Gallo M., Wilson J., Lovelace E., Pastan I. Effect of epidermal growth factor on prostaglandin E1-stimulated accumulation of cyclic AMP in fibroblastic cells. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 15;102(2):329–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balk S. D., Riley T. M., Gunther H. S., Morisi A. Heparin-treated, v-myc-transformed chicken heart mesenchymal cells assume a normal morphology but are hypersensitive to epidermal growth factor (EGF) and brain fibroblast growth factor (bFGF); cells transformed by the v-Ha-ras oncogene are refractory to EGF and bFGF but are hypersensitive to insulin-like growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F., Bouscarel B., Slaton J., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Epidermal growth factor mimics insulin effects in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):523–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2390523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow M. R., Cubicciotti R., Ginsburg R., Stinson E. B., Johnson C. Histamine-mediated adenylate cyclase stimulation in human myocardium. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):671–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L., Patel U., Cohen S. Hormonal factors and liver growth. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1977 Oct 3;16:205–213. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(78)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J., Sunyer T., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L. Mechanisms in the vectorial receptor-adenylate cyclase signal transduction. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:111–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. M., Schlegel W., Lin M. C., Rodbell M. The fat cell adenylate cyclase system. Characterization and manipulation of its bimodal regulation by GTP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8927–8931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher M., Gironès N., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M., Davis R. J. Regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation state by sphingosine in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5319–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. L. Role of cyclic nucleotides in cell growth and differentiation. Physiol Rev. 1976 Oct;56(4):652–708. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Rodbell M. Inhibition by fluoride ion of hormonal activation of fat cell adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4901–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Connelly P. A., Sisk R. B., Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Pertussis toxin or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate can distinguish between epidermal growth factor- and angiotensin-stimulated signals in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2032–2036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Garrison J. C. Epidermal growth factor and angiotensin II stimulate formation of inositol 1,4,5- and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in hepatocytes. Differential inhibition by pertussis toxin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17285–17293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotersztajn S., Pavoine C., Mallat A., Stengel D., Insel P. A., Pecker F. Cholera toxin blocks glucagon-mediated inhibition of the liver plasma membrane (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3114–3117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G. Activation of 45Ca2+ influx and 22Na+/H+ exchange by epidermal growth factor and vanadate in A431 cells is independent of phosphatidylinositol turnover and is inhibited by phorbol ester and diacylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9321–9327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnaldo I., Pouysségur J., Paris S. Thrombin exerts a dual effect on stimulated adenylate cyclase in hamster fibroblasts, an inhibition via a GTP-binding protein and a potentiation via activation of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):711–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2530711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Aerts R. J., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. The epidermal growth factor-induced calcium signal in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):279–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moule S. K., McGivan J. D. Epidermal growth factor, like glucagon, exerts a short-term stimulation of alanine transport in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):233–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2470233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II in vitro by the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10335–10338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. B., Olson M. S. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in ischemic rat heart. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):H858–H864. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.246.6.H858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Eakes A. T. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the production of phosphatidylinositol monophosphate and the breakdown of polyphosphoinositides in A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1644–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Role of Ni in coupling angiotensin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16200–16209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin S. W., Sunga P., Myrdal S. The effect of epidermal growth factor on chronotropic response in cardiac cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):889–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashed H. M., Patel T. B. Glucagon-stimulated calcium efflux in the isolated perfused rat liver is dependent on cellular redox potential. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15953–15958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Sachs L. Enhancement of hormone action by a phorbol ester and anti-tubulin alkaloids involves different mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 29;720(2):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Epidermal-growth-factor-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human A431 cells. Differences from the effect of bradykinin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2520857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. GTP-dependent inhibition of insulin secretion by epinephrine in permeabilized RINm5F cells. Lack of correlation between insulin secretion and cyclic AMP levels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8615–8620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine-Braun K. A., Northup J. K., Hollenberg M. D. Epidermal growth factor (urogastrone)-mediated phosphorylation of a 35-kDa substrate in human placental membranes: relationship to the beta subunit of the guanine nucleotide regulatory complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):236–240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Patten S. M., Heisermann G. J., Cheng H. C., Walsh D. A. Tyrosine kinase catalyzed phosphorylation and inactivation of the inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3398–3403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Nishibe S., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M., Carpenter G. Regulation of epidermal growth factor-stimulated formation of inositol phosphates in A-431 cells by calcium and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7581–7590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]