Abstract
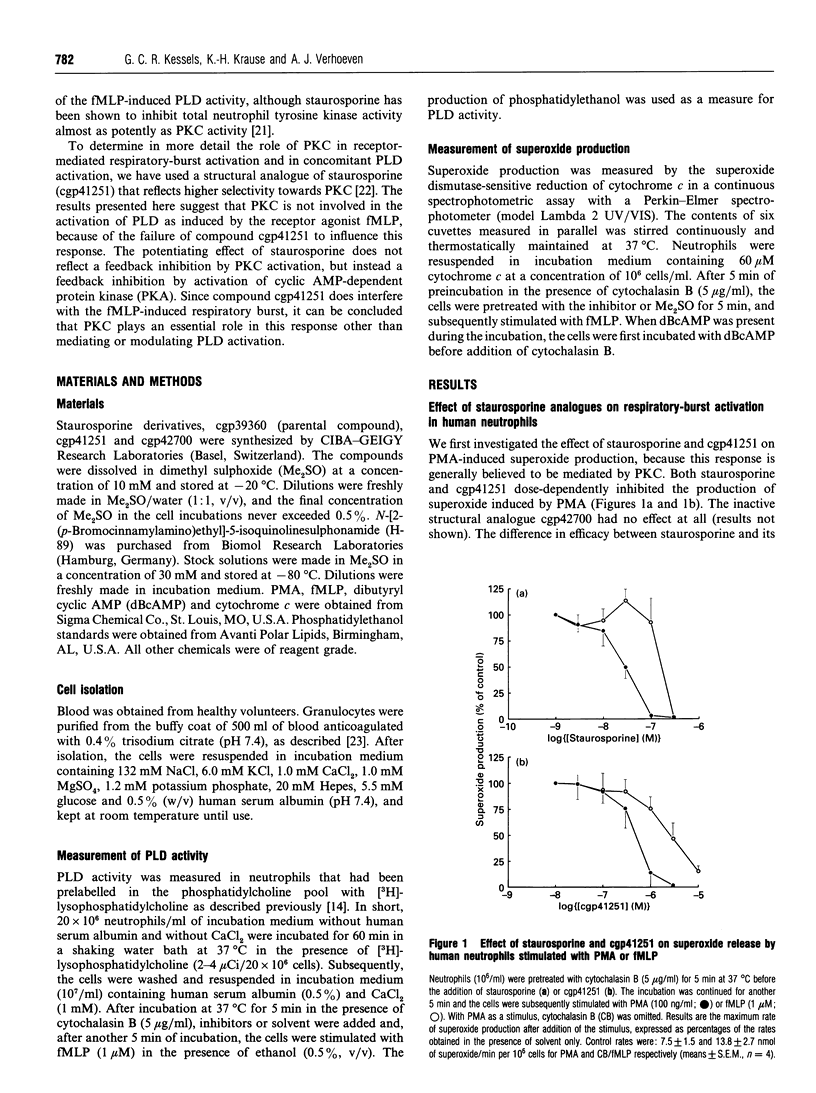
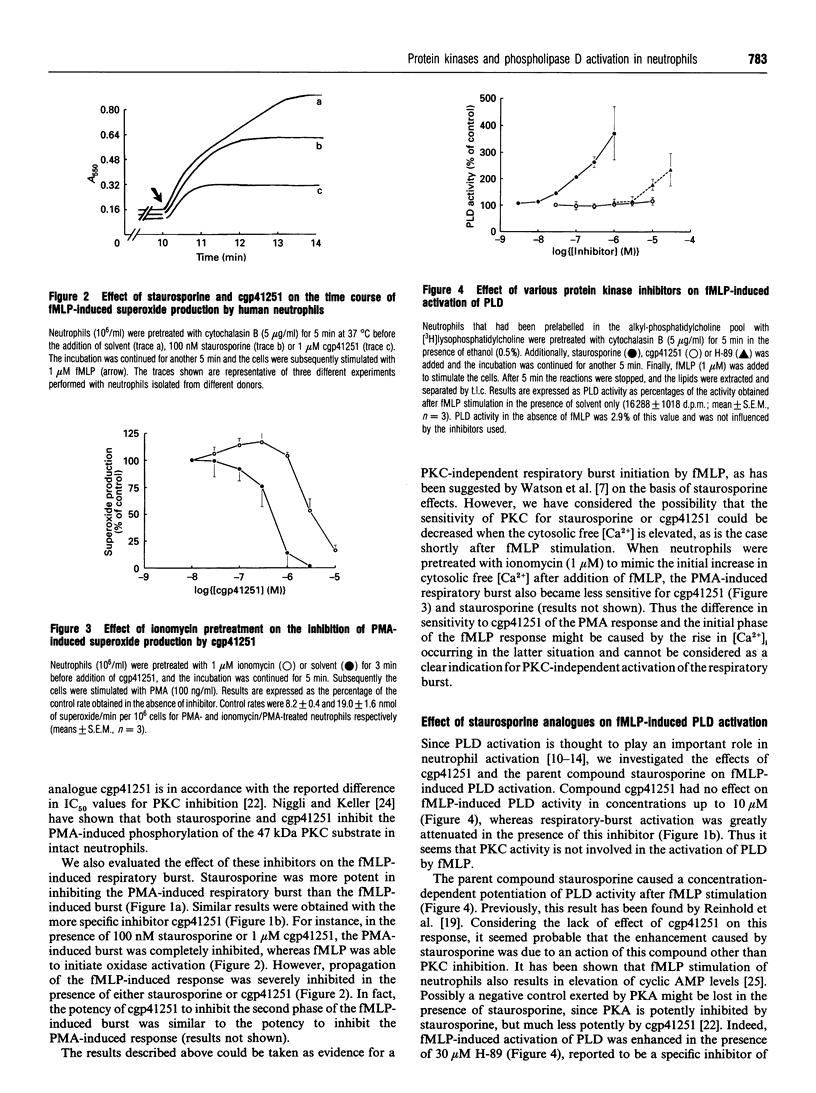
Stimulation of human neutrophils by the receptor agonist N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) results in a respiratory burst, catalysed by an NADPH oxidase. Concomitantly, phospholipase D (PLD) is activated. To investigate the role of protein kinase C (PKC) in these neutrophil responses, we have compared the effects of staurosporine and a structural analogue of staurosporine (cgp41251), that reflects a higher selectivity towards PKC [Meyer, Regenass, Fabbro, Alteri, Rösel, Müller, Caravatti and Matter (1989) Int. J. Cancer 43, 851-856]. Both staurosporine and cgp41251 dose-dependently inhibited the production of superoxide induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Both compounds also caused inhibition of the fMLP-induced respiratory burst, but with a lower efficacy during the initiation phase of this response. This latter observation cannot be taken as evidence against PKC involvement in the activation of the respiratory burst, because pretreatment of neutrophils with ionomycin before PMA stimulation also results in a lower efficacy of inhibition. Activation of PLD by fMLP was enhanced in the presence of staurosporine, but not in the presence of cgp41251. Enhancement of PLD activation was also observed in the presence of H-89, an inhibitor of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). Both staurosporine and H-89 reversed the dibutyryl-cyclic-AMP-induced inhibition of PLD activation, whereas cgp41251 was without effect. These results indicate that the potentiating effect of staurosporine on PLD activation induced by fMLP does not reflect a feedback inhibition by PKC activation, but instead a feedback inhibition by PKC activation. Taken together, our results indicate that in human neutrophils: (i) PKC activity is not essential for fMLP-induced activation of PLD; (ii) PKC activity does play an essential role in the activation of the respiratory burst by fMLP, other than mediating or modulating PLD activation; (iii) there exists a negative-feedback mechanism on fMLP-induced PLD activation by concomitant activation of PKA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agwu D. E., McCall C. E., McPhail L. C. Regulation of phospholipase D-induced hydrolysis of choline-containing phosphoglycerides by cyclic AMP in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3895–3903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agwu D. E., McPhail L. C., Sozzani S., Bass D. A., McCall C. E. Phosphatidic acid as a second messenger in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Effects on activation of NADPH oxidase. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):531–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI115336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Erickson R. W., Curnutte J. T. Staurosporine inhibits the soluble and membrane-bound protein tyrosine kinases of human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90124-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauldry S. A., Bass D. A., Cousart S. L., McCall C. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha priming of phospholipase D in human neutrophils. Correlation between phosphatidic acid production and superoxide generation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4173–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W., Kraft A. S. The effect of a protein kinase C inhibitor, H-7, on human neutrophil oxidative burst and degranulation. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 May;41(5):441–446. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Pai J. K., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Regulation of phospholipase D in HL-60 granulocytes. Activation by phorbol esters, diglyceride, and calcium ionophore via protein kinase- independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9069–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonser R. W., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Garland L. G. Phospholipase D activation is functionally linked to superoxide generation in the human neutrophil. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2640617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgoin S., Grinstein S. Peroxides of vanadate induce activation of phospholipase D in HL-60 cells. Role of tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11908–11916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa T., Mishima A., Hagiwara M., Sano M., Hayashi K., Inoue T., Naito K., Toshioka T., Hidaka H. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5267–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combadière C., Hakim J., Giroud J. P., Périanin A. Staurosporine, a protein kinase inhibitor, up-regulates the stimulation of human neutrophil respiratory burst by N-formyl peptides and platelet activating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91675-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conricode K. M., Brewer K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of phospholipase D by protein kinase C. Evidence for a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7199–7202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Thelen M., Baggiolini M. Two transduction sequences are necessary for neutrophil activation by receptor agonists. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16179–16184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forehand J. R., Pabst M. J., Phillips W. A., Johnston R. B., Jr Lipopolysaccharide priming of human neutrophils for an enhanced respiratory burst. Role of intracellular free calcium. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):74–83. doi: 10.1172/JCI113887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard C., McPhail L. C., Marfat A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Bass D. A., McCall C. E. Role of protein kinases in stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte oxidative metabolism by various agonists. Differential effects of a novel protein kinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):61–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI112302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessels G. C., Gervaix A., Lew P. D., Verhoeven A. J. The chymotrypsin inhibitor carbobenzyloxy-leucine-tyrosine-chloromethylketone interferes with phospholipase D activation induced by formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15870–15875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessels G. C., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. fMet-Leu-Phe-induced activation of phospholipase D in human neutrophils. Dependence on changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration and relation with respiratory burst activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23152–23156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenderman L., Tool A., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. 1,2-Diacylglycerol accumulation in human neutrophils does not correlate with respiratory burst activation. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):399–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., Verhoeven A. J., van der Bend R. L., Weening R. S., Roos D. Purified protein kinase C phosphorylates a 47-kDa protein in control neutrophil cytoplasts but not in neutrophil cytoplasts from patients with the autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2352–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., van der Bend R. L., Tool A. T., van Blitterswijk W. J., Roos D., Verhoeven A. J. 1-O-hexadecyl-2-Q-methylglycerol, a novel inhibitor of protein kinase C, inhibits the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5876–5884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Regenass U., Fabbro D., Alteri E., Rösel J., Müller M., Caravatti G., Matter A. A derivative of staurosporine (CGP 41 251) shows selectivity for protein kinase C inhibition and in vitro anti-proliferative as well as in vivo anti-tumor activity. Int J Cancer. 1989 May 15;43(5):851–856. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muid R. E., Dale M. M., Davis P. D., Elliott L. H., Hill C. H., Kumar H., Lawton G., Twomey B. M., Wadsworth J., Wilkinson S. E. A novel conformationally restricted protein kinase C inhibitor, Ro 31-8425, inhibits human neutrophil superoxide generation by soluble, particulate and post-receptor stimuli. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81178-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullmann T. J., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate activation of phospholipase D in human neutrophils leads to the production of phosphatides and diglycerides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1197–1202. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90520-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Keller H. On the role of protein kinases in regulating neutrophil actin association with the cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7927–7932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. C., Bowman E. P., Lambeth J. D. Phospholipase D activation in a cell-free system from human neutrophils by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). Activation is calcium dependent and requires protein factors in both the plasma membrane and cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17236–17242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Grzeskowiak M., Della Bianca V., Calzetti F., Gandini G. Phosphatidic acid and not diacylglycerol generated by phospholipase D is functionally linked to the activation of the NADPH oxidase by FMLP in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91711-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Särndahl E., Lindroth M., Bengtsson T., Fällman M., Gustavsson J., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Association of ligand-receptor complexes with actin filaments in human neutrophils: a possible regulatory role for a G-protein. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2791–2799. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I. Protein kinase C and the activation of the human neutrophil NADPH-oxidase. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):711–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi S. R., Olson S. C., Burnham D. N., Lambeth J. D. Cyclic AMP-elevating agents block chemoattractant activation of diradylglycerol generation by inhibiting phospholipase D activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3498–3504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uings I. J., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Spacey G. D., Bonser R. W., Hudson A. T., Garland L. G. Tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in receptor coupling to phospholipase D but not phospholipase C in the human neutrophil. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):597–600. doi: 10.1042/bj2810597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Fox K., McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant-elicited alterations of cAMP levels in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes require a Ca2+-dependent mechanism which is independent of transmembrane activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6769–6775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven A. J., van Schaik M. L., Roos D., Weening R. S. Detection of carriers of the autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. Blood. 1988 Feb;71(2):505–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson F., Robinson J., Edwards S. W. Protein kinase C-dependent and -independent activation of the NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7432–7439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie M. S., Dubyak G. R. Guanine-nucleotide- and adenine-nucleotide-dependent regulation of phospholipase D in electropermeabilized HL-60 granulocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):81–89. doi: 10.1042/bj2780081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


