Abstract
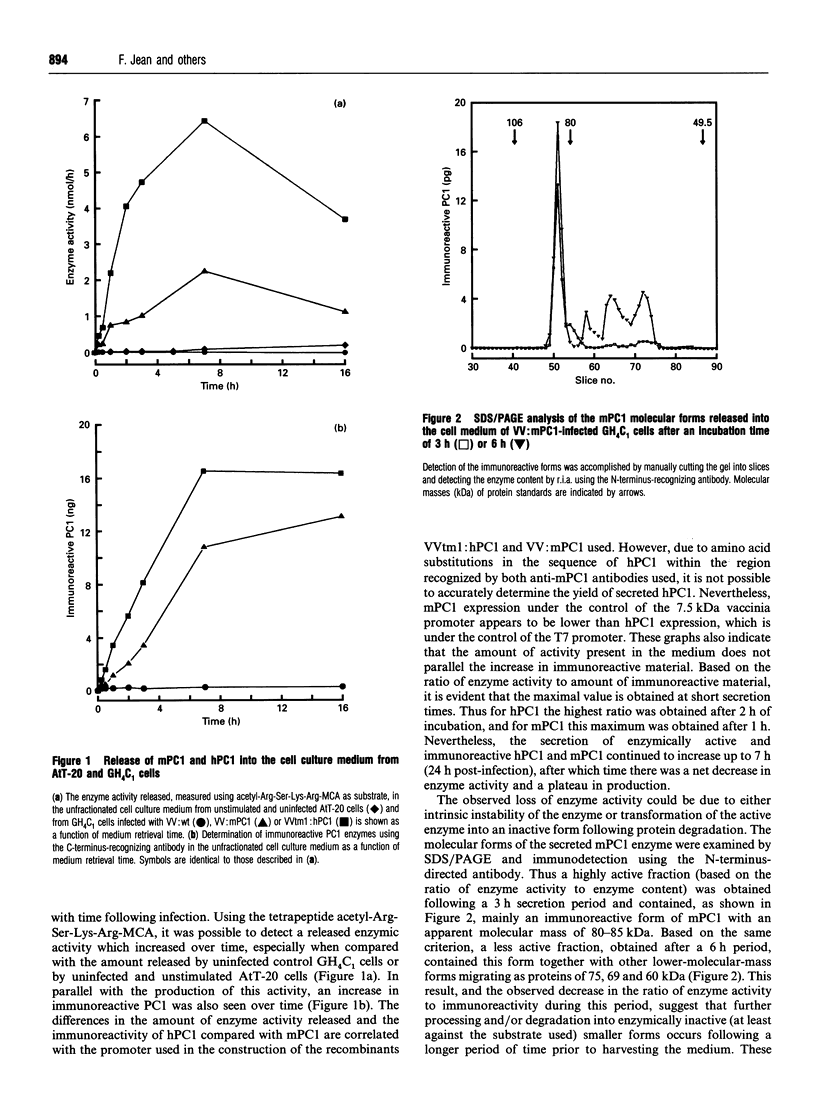
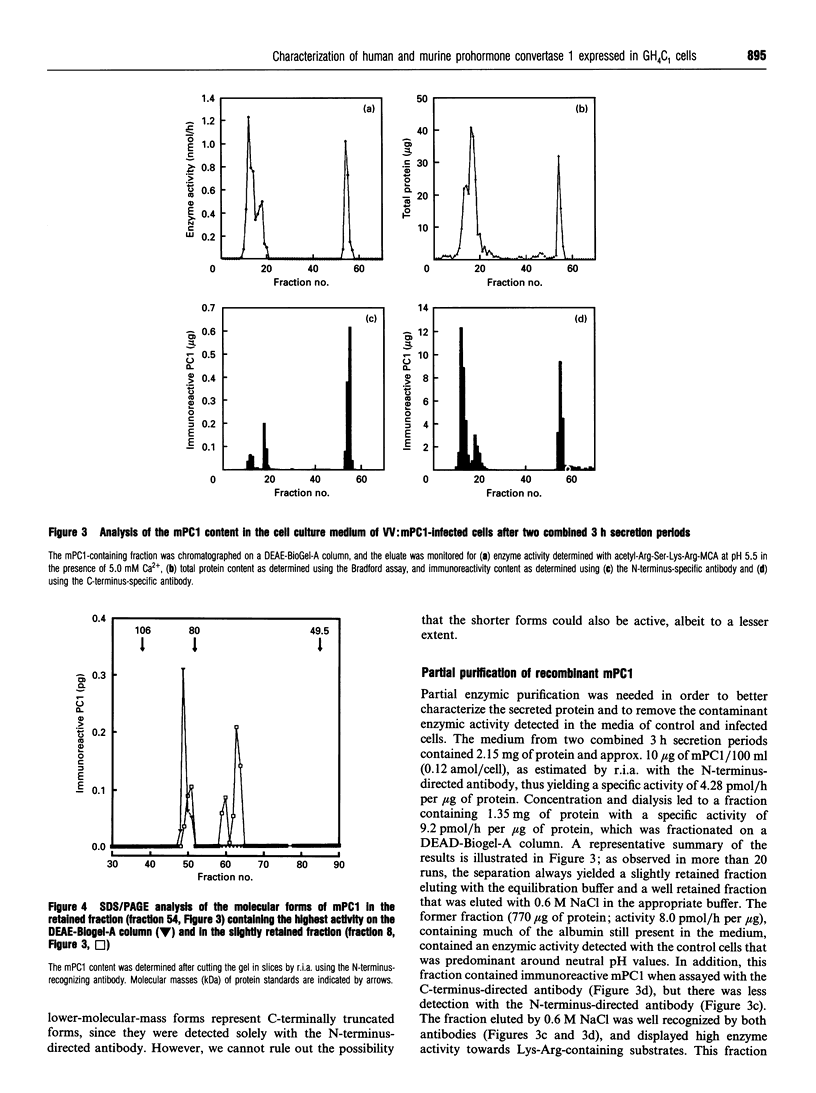
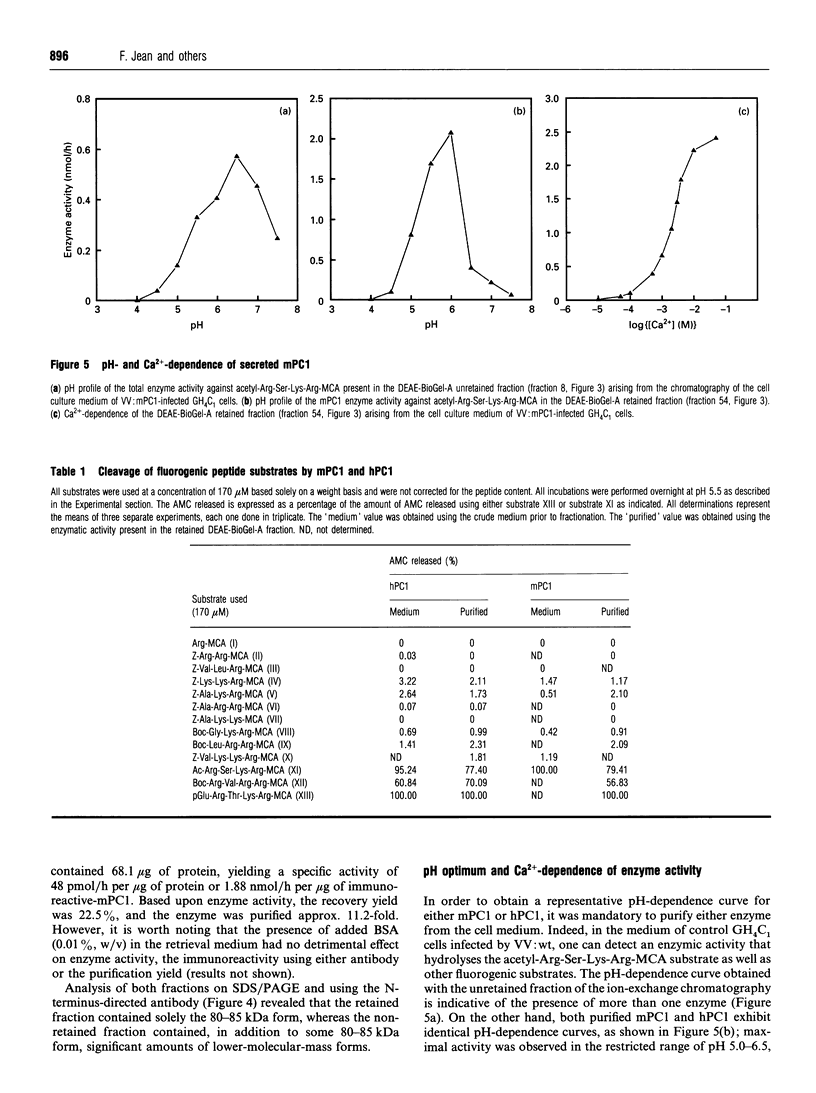
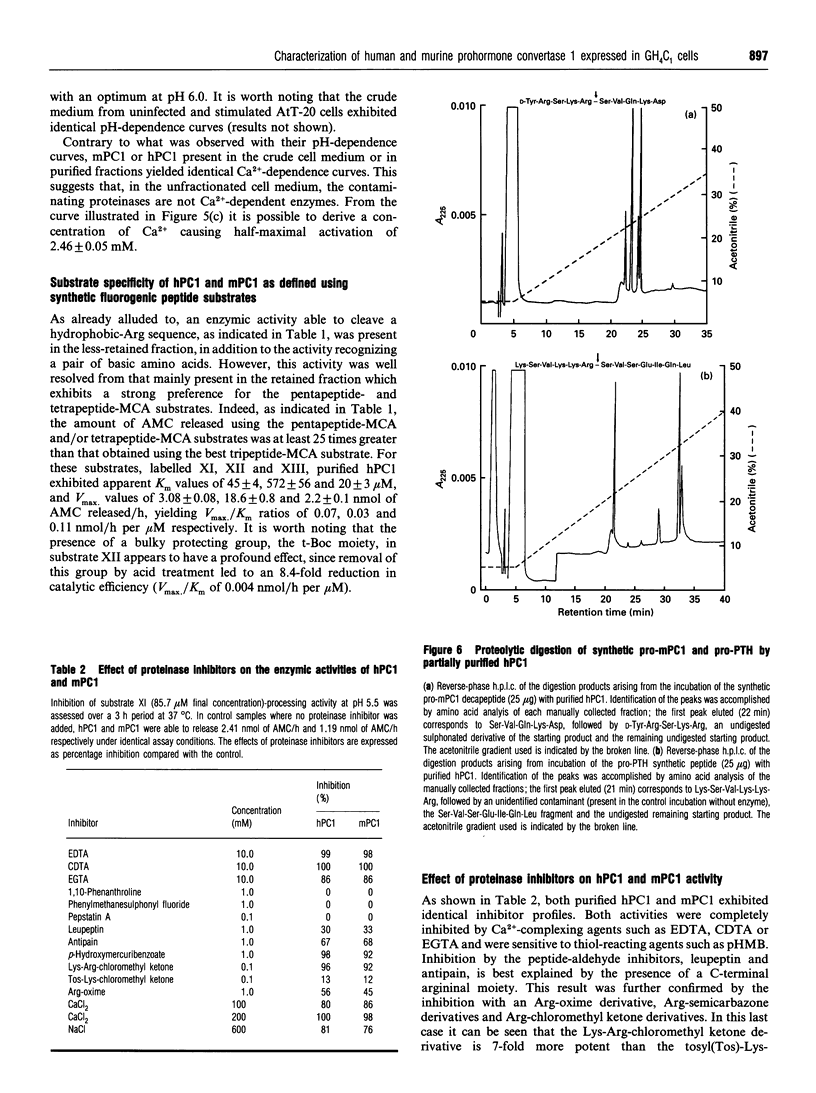
Prohormone convertase-1 (PC1), an endopeptidase that is structurally related to the yeast subtilisin-like Kex2 gene product, has been proposed to be involved in mammalian tissue-specific prohormone processing at pairs of basic residues. To better study this enzyme, a rat somatomammotroph cell line, GH4C1, was infected with vaccinia virus recombinants of murine PC1 (mPC1) and human PC1 (hPC1). An enzymically active form of each protein was secreted into the cell medium and partially purified by anion-exchange chromatography. The 80-85 kDa enzyme was shown to be Ca(2+)-dependent and exhibited a pH optimum of 6.0 when assayed against a synthetic fluorogenic substrate, acetyl-Arg-Ser-Lys-Arg-4-methylcoumaryl-1-amide. mPC1 and hPC1 displayed identical cleavage selectivity towards a number of fluorogenic substrates, and those incorporating an Arg at the P4 site were most favoured. Synthetic peptides, encompassing the junction between the putative pro-region and the active enzyme, and between the pro-region and the biologically active parathyroid hormone, were shown to be recognized and cleaved specifically at the pair of basic residues by both enzymes. Group-specific proteinase inhibitors such as metal ion chelators and p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, but not phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride and pepstatin, strongly inhibit the PC1-associated activity. In addition, it is shown that an enzyme activity displaying identical properties is present in the cell medium of uninfected corticotroph AtT-20 cells and that its level is increased following stimulation of secretion by the secretagogue 8-bromo cyclic AMP.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailyes E. M., Shennan K. I., Seal A. J., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Hutton J. C., Docherty K. A member of the eukaryotic subtilisin family (PC3) has the enzymic properties of the type 1 proinsulin-converting endopeptidase. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):391–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2850391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basak A., Gong Y. T., Cromlish J. A., Paquin J. A., Jean F., Seidah N. G., Lazure C., Chrétien M. Syntheses of argininal semicarbazone containing peptides and their applications in the affinity chromatography of serine proteinases. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Jul;36(1):7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Reudelhuber T., Mercure C., Rondeau N., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Proprotein conversion is determined by a multiplicity of factors including convertase processing, substrate specificity, and intracellular environment. Cell type-specific processing of human prorenin by the convertase PC1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11417–11423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Rondeau N., Day R., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. PC1 and PC2 are proprotein convertases capable of cleaving proopiomelanocortin at distinct pairs of basic residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3564–3568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. L., Bailyes E. M., Nielsen E., Guest P. C., Rutherford N. G., Arden S. D., Hutton J. C. Identification of the type 2 proinsulin processing endopeptidase as PC2, a member of the eukaryote subtilisin family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15229–15236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo M. J., Nakajima K., Zimmerman M., Powers J. C. Sensitive substrates for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: a study of the merits of various chromophoric and fluorogenic leaving groups in assays for serine proteases. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Oliva A. A., Jr, LaMendola J., Grens A., Bode H., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the prohormone convertase gene family in metazoa: analysis of cDNAs encoding a PC3-like protein from hydra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Batchelor D. C., Palmer D. J. Identification of kex2-related proteases in chromaffin granules by partial amino acid sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15679–15683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic beta cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):93–96. doi: 10.1038/333093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R., Schafer M. K., Watson S. J., Chrétien M., Seidah N. G. Distribution and regulation of the prohormone convertases PC1 and PC2 in the rat pituitary. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):485–497. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A., Thorner J. Yeast prohormone processing enzyme (KEX2 gene product) is a Ca2+-dependent serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco L., Daly L., Kim S., Devi L. Dynorphin-processing endopeptidase in the rat anterior pituitary lactotrophic cell line, GH4C1. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 Mar;55(3):351–356. doi: 10.1159/000126136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Nagase M., Shoda A., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Structure and expression of mouse furin, a yeast Kex2-related protease. Lack of processing of coexpressed prorenin in GH4C1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22075–22078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Molecular and enzymatic properties of furin, a Kex2-like endoprotease involved in precursor cleavage at Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):296–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J. S., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A., Thomas G. A unique Kex2-like endoprotease from Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in the central nervous system during early embryogenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):705–717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Thomas G., Herbert E., Franke C. A. Use of vaccinia virus as a neuropeptide expression vector. Methods Enzymol. 1986;124:295–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)24022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean F., Basak A., Chrétien M., Lazure C. Detection of endopeptidase activity and analysis of cleavage specificity using a radiometric solid-phase enzymatic assay. Anal Biochem. 1991 May 1;194(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90248-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Tucker J. E., Joh R., Landsberg K. E., Saltman D., Barr P. J. Identification of a second human subtilisin-like protease gene in the fes/fps region of chromosome 15. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;10(10):757–769. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. S., Fields C. G., Fields G. B. A cleavage method which minimizes side reactions following Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Sep;36(3):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmair R., Egger C., Gee P., Hogue-Angeletti R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Laslop A., Winkler H. Differential subcellular distribution of PC1, PC2 and furin in bovine adrenal medulla and secretion of PC1 and PC2 from this tissue. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Aug 31;143(1-2):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchmair R., Gee P., Hogue-Angeletti R., Laslop A., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Immunological characterization of the endoproteases PC1 and PC2 in adrenal chromaffin granules and in the pituitary gland. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 10;297(3):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner J., Chun J., Harter D., Axel R. Isolation and functional expression of a mammalian prohormone processing enzyme, murine prohormone convertase 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6834–6838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Pélaprat D., Chrétien M. Proteases and posttranslational processing of prohormones: a review. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;61(7):501–515. doi: 10.1139/o83-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg I., Lincoln B., Rhodes C. J. Fluorometric assay of a calcium-dependent, paired-basic processing endopeptidase present in insulinoma granules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91599-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackin R. B., Noe B. D., Spiess J. Identification of a somatostatin-14-generating propeptide converting enzyme as a member of the kex2/furin/PC family. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2263–2265. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Nakamura T., Ohshima T., Tanaka S., Matsuo H. Yeast KEX2 genes encodes an endopeptidase homologous to subtilisin-like serine proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):246–254. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Hosaka M., Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K. Cloning and functional expression of a novel endoprotease involved in prohormone processing at dibasic sites. J Biochem. 1991 Jun;109(6):803–806. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Kim W. S., Torii S., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Baba T., Murakami K. Identification of the fourth member of the mammalian endoprotease family homologous to the yeast Kex2 protease. Its testis-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5897–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Watanabe T., Nakagawa T., Kim W. S., Nagahama M., Hosaka M., Hatsuzawa K., Kondoh-Hashiba K., Murakami K. Consensus sequence for precursor processing at mono-arginyl sites. Evidence for the involvement of a Kex2-like endoprotease in precursor cleavages at both dibasic and mono-arginyl sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16335–16340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehemtulla A., Kaufman R. J. Preferred sequence requirements for cleavage of pro-von Willebrand factor by propeptide-processing enzymes. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2349–2355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Pauli I. G., Zhang Y., van de Ven W. J. cDNA sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster gene, Dfur1, encoding a protein structurally related to the subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Oomen P. P., Wagenaar S. S., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. fur gene expression as a discriminating marker for small cell and nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI113240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Hamelin J., Gaspar A., Collard M. W., Chrétien M. Testicular expression of PC4 in the rat: molecular diversity of a novel germ cell-specific Kex2/subtilisin-like proprotein convertase. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1559–1570. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1448111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Chrétien M. Mammalian neural and endocrine pro-protein and pro-hormone convertases belonging to the subtilisin family of serine proteinases. Enzyme. 1991;45(5-6):271–284. doi: 10.1159/000468901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Hamelin J., Gaspar A. M., Day R., Chrétien M. The cDNA sequence of the human pro-hormone and pro-protein convertase PC1. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 May;11(4):283–289. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan K. I., Seal A. J., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Docherty K. Site-directed mutagenesis and expression of PC2 in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24011–24017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shennan K. I., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Docherty K. Characterization of PC2, a mammalian Kex2 homologue, following expression of the cDNA in microinjected Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 24;284(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M., Leunissen J. A., Dijkstra B. W. Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinases. Protein Eng. 1991 Oct;4(7):719–737. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.7.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas L., Leduc R., Thorne B. A., Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F., Thomas G. Kex2-like endoproteases PC2 and PC3 accurately cleave a model prohormone in mammalian cells: evidence for a common core of neuroendocrine processing enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindrola O., Lindberg I. Biosynthesis of the prohormone convertase mPC1 in AtT-20 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1088–1094. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1508222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


