Abstract
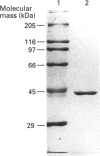
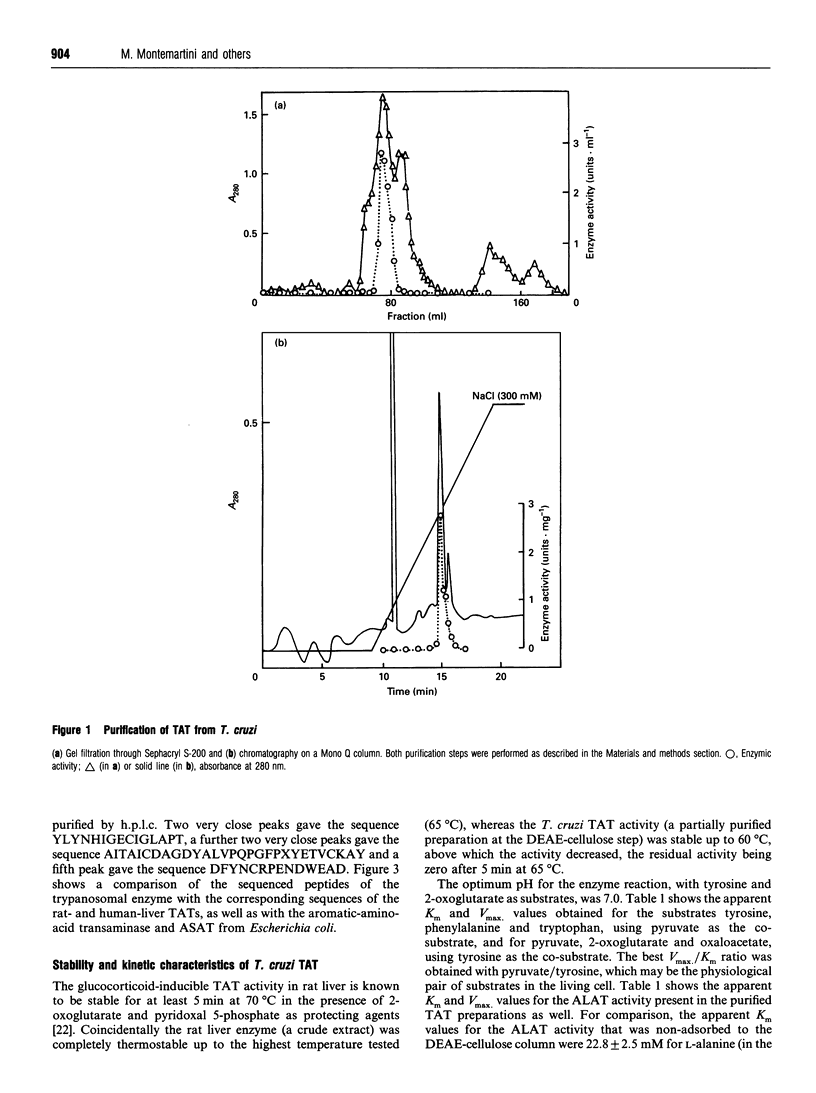
Tyrosine aminotransferase was purified to homogeneity from epimastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi by a method involving chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, gel filtration on Sephacryl S-200 and chromatography on Mono Q in an f.p.l.c. system. The purified enzyme showed a single band in SDS/PAGE, with an apparent molecular mass of 45 kDa. Since the apparent molecular mass of the native enzyme, determined by gel filtration, is 91 kDa, the native enzyme is a dimer of similar subunits. The amino-acid composition was determined, as well as the sequences of three internal peptides obtained by CNBr cleavage at Met residues. Both criteria suggest considerable similarity with the tyrosine aminotransferases from rat and from human liver. The enzyme contains nine 1/2 Cys residues, three free and the others forming three disulphide bridges. The enzyme is not N-glycosylated. The isoelectric point is 4.6-4.8. The optimal pH for the reaction of the enzyme with tyrosine as a substrate is 7.0. The apparent Km values for tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan, with pyruvate as a co-substrate, were 6.8, 17.9 and 21.4 mM, respectively, whereas those for pyruvate, alpha-oxoglutarate and oxaloacetate, with tyrosine as a substrate, were 0.5, 38 and 16 mM respectively. The purified tyrosine aminotransferase acts as an alanine aminotransferase as well and the activity seems to reside in the same enzyme molecule. The results suggest that the enzyme is a general aromatic-amino-acid transaminase, with high sequence similarity to tyrosine aminotransferases from rat and human liver.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE A. N., GHOSH J. J. Transaminases of Leishmania donovani, the causative organism of kala-azar. Nature. 1957 Dec 21;180(4599):1425–1425. doi: 10.1038/1801425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Franke de Cazzulo B. M., Engel J. C., Cannata J. J. End products and enzyme levels of aerobic glucose fermentation in trypanosomatids. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Sep;16(3):329–343. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Hellman U., Couso R., Parodi A. J. Amino acid and carbohydrate composition of a lysosomal cysteine proteinase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Absence of phosphorylated mannose residues. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jan 1;38(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzulo J. J., Juan S. M., Segura E. L. Glutamate dehydrogenase and aspartate aminotransferase in Trypanosoma cruzi. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977;56(3):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(77)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantsas N. S., Levis G. M., Vakirtzi-Lemonias C. S. Crithidia fasciculata tyrosine transaminase. I. Development, characterization and differentiation from alanine transaminase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 26;230(1):137–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham I. G., Dacey S. A., Taylor P. P., Smith T. J., Hunter M. G., Finlay M. E., Primrose S. B., Parker D. M., Edwards R. M. The cloning and sequence analysis of the aspC and tyrB genes from Escherichia coli K12. Comparison of the primary structures of the aspartate aminotransferase and aromatic aminotransferase of E. coli with those of the pig aspartate aminotransferase isoenzymes. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):593–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2340593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., Guénet C., Dietrich J. B., Chasserot S., Fromont M., Befort N., Jami J., Beck G., Pictet R. Complete complementary DNA of rat tyrosine aminotransferase messenger RNA. Deduction of the primary structure of the enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Granner D. K. Purification of the native form of tyrosine aminotransferase from rat liver. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Mackin R. B. Organ specificity of glucocorticoid-sensitive tyrosine aminotransferase. Separation from aspartate aminotransferase isoenzymes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Scoble H. A., Mathews W. R., Baumstark B. R., Biemann K. The structure of tyrosine aminotransferase. Evidence for domains involved in catalysis and enzyme turnover. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):45–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S. I., Granner D. K., Tomkins G. M. Tyrosine aminotransferase. Purificaton and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):3998–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Okuno S., Ogawa T., Ogawa H., Kagamiyama H. Aspartate aminotransferase of Escherichia coli: nucleotide sequence of the aspC gene. J Biochem. 1985 Apr;97(4):1259–1262. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Lanham S. M. Aspartate aminotransferase in Leishmania is a broad-spectrum transaminase. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(3):373–375. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrides C., D'Iorio A. The regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. K., Hale T. I., Christen P. Evolutionary relationships among aminotransferases. Tyrosine aminotransferase, histidinol-phosphate aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase are homologous proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):249–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki C., Montemartini M., Duschak V., Santomé J. A., Cazzulo J. J. Presence and subcellular localization of tyrosine aminotransferase and p-hydroxyphenyllactate dehydrogenase in epimastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 15;71(2):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90498-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T., Morrison J. F. The purification and properties of the aspartate aminotransferase and aromatic-amino-acid aminotransferase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rege A. A. Purification and characterization of a tyrosine aminotransferase from Crithidia fasciculata. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Aug;25(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmeier R., Natt E., Zentgraf H., Scherer G. Isolation and characterization of the human tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3853–3861. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbs H. H., Seed J. R. Elevated serum and hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase in voles chronically infected with Trypanosoma brucei gambiense. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Feb;39(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbs H. H., Seed J. R. Further studies on the metabolism of tryptophan in Trypanosoma brucei gambiense: cofactors, inhibitors, and end-products. Experientia. 1975 Mar 15;31(3):274–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01922536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]