Abstract
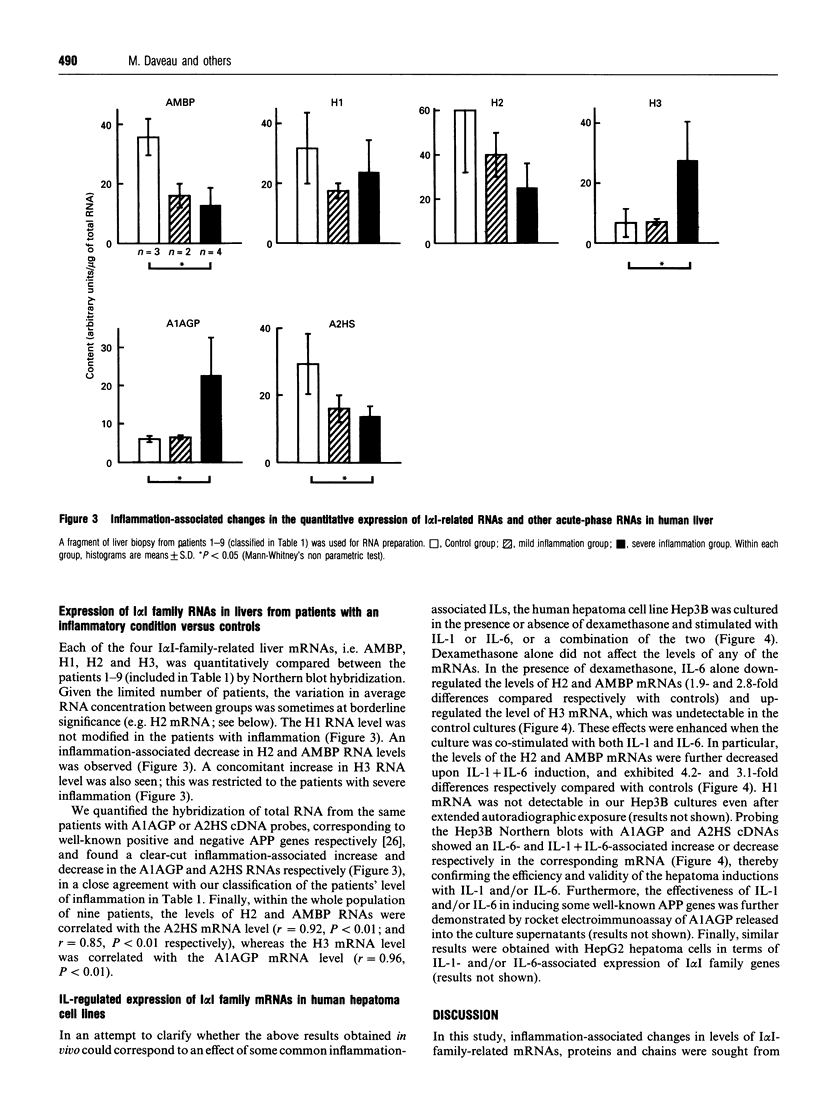
The inter-alpha-inhibitor (I alpha I) family encompasses four plasma proteins, namely free bikunin as well as I alpha I, pre-alpha-inhibitor (P alpha I) and inter-alpha-like inhibitor (I alpha LI). Each of the last three proteins is a distinct assembly of one bikunin chain with one or more unique heavy (H) chains designated H1, H2 and H3. The three H chains and the bikunin chain are encoded by four distinct mRNAs. These molecules and chains, as well as the corresponding mRNAs, were quantified in sera and liver biopsies from a series of patients with or without mild or severe acute infection. The decrease or increase observed for a given molecule or chain in the serum was in agreement with a similar change in the corresponding liver mRNA. In acute inflammation the H2 and bikunin chains are down-regulated and the relevant molecules (I alpha I, I alpha LI) behave as negative acute-phase proteins, whereas the H3 chain is up-regulated and the corresponding P alpha I molecule is a positive acute-phase protein. Also, P alpha I displays a higher-than-usual M(r); this is probably due to ligand binding. The H1 gene does not seem to be affected by the inflammatory condition. The quantitative changes in RNA levels seen in vivo were confirmed in vitro in the human hepatoma Hep3B cell line prior to or after induction with the acute-phase mediators interleukin-1 and/or -6. These results provide the first example in humans of positive and negative acute-phase proteins that are encoded by evolutionary related genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerström B., Lögdberg L. An intriguing member of the lipocalin protein family: alpha 1-microglobulin. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90037-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann H., Richards C., Gauldie J. Interaction among hepatocyte-stimulating factors, interleukin 1, and glucocorticoids for regulation of acute phase plasma proteins in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4122–4128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Andus T., Geiger T., Trullenque R., Fabra R., Heinrich P. C. Interleukin-6 is the major regulator of acute phase protein synthesis in adult human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80476-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell J. V., Gómez-Lechón M. J., David M., Fabra R., Trullenque R., Heinrich P. C. Acute-phase response of human hepatocytes: regulation of acute-phase protein synthesis by interleukin-6. Hepatology. 1990 Nov;12(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Mao S. J., Larsen W. J. Identification of a factor in fetal bovine serum that stabilizes the cumulus extracellular matrix. A role for a member of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor family. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12380–12386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daveau M., Christian-Davrinche, Julen N., Hiron M., Arnaud P., Lebreton J. P. The synthesis of human alpha-2-HS glycoprotein is down-regulated by cytokines in hepatoma HepG2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daveau M., Davrinche C., Djelassi N., Lemetayer J., Julen N., Hiron M., Arnaud P., Lebreton J. P. Partial hepatectomy and mediators of inflammation decrease the expression of liver alpha 2-HS glycoprotein gene in rats. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 29;273(1-2):79–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81055-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. Structure of the human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene: sequence homology with other human acute phase protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3941–3952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diarra-Mehrpour M., Bourguignon J., Sesboü R., Matteï M. G., Passage E., Salier J. P., Martin J. P. Human plasma inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor is encoded by four genes on three chromosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enghild J. J., Salvesen G., Hefta S. A., Thøgersen I. B., Rutherfurd S., Pizzo S. V. Chondroitin 4-sulfate covalently cross-links the chains of the human blood protein pre-alpha-inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):747–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enghild J. J., Thøgersen I. B., Pizzo S. V., Salvesen G. Analysis of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor and a novel trypsin inhibitor, pre-alpha-trypsin inhibitor, from human plasma. Polypeptide chain stoichiometry and assembly by glycan. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15975–15981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., Rzewnicki D., Samols D., Jiang S. L., Kushner I. Effect of combinations of cytokines and hormones on synthesis of serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein in Hep 3B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1261–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Hochstrasser K., Fritz H., Enghild J. J., Pizzo S. V., Salvesen G. Structure of inter-alpha-inhibitor (inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor) and pre-alpha-inhibitor: current state and proposition of a new terminology. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 May;371 (Suppl):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Schreitmüller T., Hochstrasser K., Wachter E. Complementary DNA and derived amino acid sequence of the precursor of one of the three protein components of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor complex. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80798-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard W., Schreitmüller T., Hochstrasser K., Wachter E. Two out of the three kinds of subunits of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor are structurally related. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):571–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb A. O., López C., Tejler L., Mendez E. Isolation of human complex-forming glycoprotein, heterogeneous in charge (protein HC), and its IgA complex from plasma. Physiochemical and immunochemical properties, normal plasma concentration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14698–14707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich P. C., Castell J. V., Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):621–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2650621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Enomoto H., Takagi K., Kawai T., Yamanaka T. Human alpha 1-microglobulin in various hepatic disorders. Digestion. 1983;27(2):75–80. doi: 10.1159/000198933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen T. E., Faarvang K. L., Ploug M. Carbohydrate as covalent crosslink in human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor: a novel plasma protein structure. FEBS Lett. 1988 Mar 28;230(1-2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80670-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Polazzi J. O., Kotick M. P. The mRNA for a proteinase inhibitor related to the HI-30 domain of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor also encodes alpha-1-microglobulin (protein HC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7839–7850. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Bowman B. H., Yang F. M. Human alpha 2-HS-glycoprotein: the A and B chains with a connecting sequence are encoded by a single mRNA transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackiewicz A., Speroff T., Ganapathi M. K., Kushner I. Effects of cytokine combinations on acute phase protein production in two human hepatoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3032–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum L., Hansen-Nord G., Byrjalsen I. Human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor and immunologically related inhibitors investigated by quantitative immunoelectrophoresis. II. Pathological conditions. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Jan 30;162(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum L. Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor and pre-alpha-trypsin inhibitor in health and disease. Determination by immunoelectrophoresis and immunoblotting. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Dec;371(12):1153–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
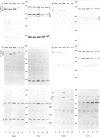
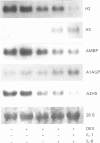
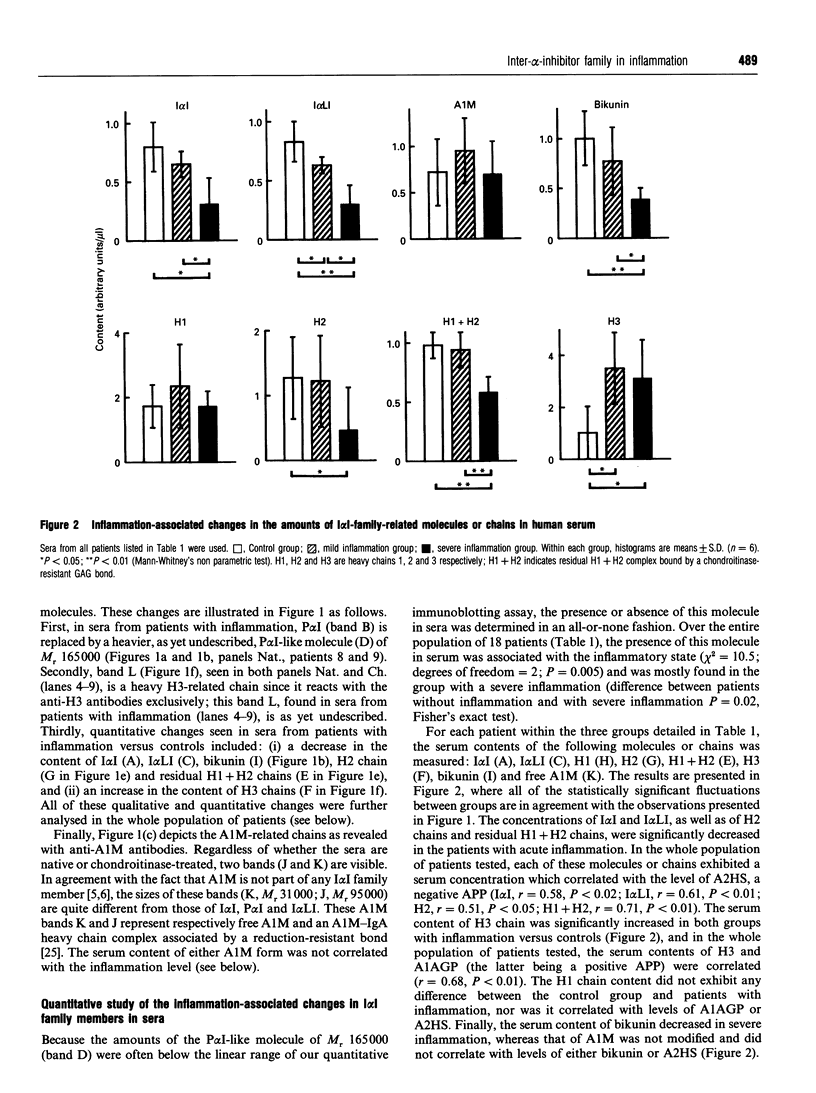
- Rouet P., Daveau M., Salier J. P. Electrophoretic pattern of the inter-alpha-inhibitor family proteins in human serum, characterized by chain-specific antibodies. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1992 Oct;373(10):1019–1024. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Diarra-Mehrpour M., Sesboue R., Bourguignon J., Benarous R., Ohkubo I., Kurachi S., Kurachi K., Martin J. P. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding the heavy chain of human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor (I alpha TI): unambiguous evidence for multipolypeptide chain structure of I alpha TI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8272–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P. Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor: emergence of a family within the Kunitz-type protease inhibitor superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):435–439. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90282-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Sesboü R., Vercaigne D., Bourguignon J., Martin J. P. Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor (ITI): use of new antisera for qualitative studies and discrete quantitation of ITI and its derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salier J. P., Verga V., Doly J., Diarra-Mehrpour M., Erickson R. P. The genes for the inter-alpha-inhibitor family share a homologous organization in human and mouse. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(4):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00355432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreitmüller T., Hochstrasser K., Reisinger P. W., Wachter E., Gebhard W. cDNA cloning of human inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor discloses three different proteins. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Aug;368(8):963–970. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesboü R., Basuyau J. P., Salier J. P. Quantitative study of human blood alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-macroglobulin and inter-alpha-trypsin-inhibitor with respect to plasma renin activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Nov 30;135(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson M., Doskow J., Lindsey S. RNA blots: staining procedures and optimization of conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):679–679. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]