Abstract
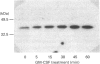
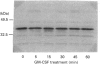
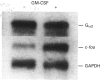
Preincubation of human neutrophils with the human cytokine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) results in an increase in the amount of alpha-subunit of Gi2 (Gi alpha 2) associated with the plasma membrane and a corresponding decrease in the amount associated with the granule fractions. Similar results are obtained with interleukin-8. GM-CSF has no effect on the distribution of Gi alpha 3. The effect of GM-CSF on Gi alpha 2 is time-dependent, and, although a significant effect can be observed after incubation for 5 min with GM-CSF, the enhancement increases with increasing time. Genistein, a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and 1,2-bis-(O-aminophenoxyl)ethane-NNN'N'-tetra-acetic acid (BAPTA), an intracellular Ca2+ chelator, decrease the stimulatory effect of GM-CSF. On the other hand, the protein-synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide does not affect the action of GM-CSF. Also, although preincubation of human neutrophils with GM-CSF increases the levels of Gi alpha 2 in the plasma membrane it does not alter the total amount of cellular Gi alpha 2. In addition, the level of Gi alpha 2 mRNA, unlike that of the proto-oncogene c-fos, is not increased in cells treated with GM-CSF. This indicates that the observed increase in the amount of Gi alpha 2 associated with the plasma membrane is not due to the synthesis of new Gi alpha 2. These data provide insight into the mechanism by which GM-CSF may prime human neutrophils for increased responsiveness to subsequent stimulation by G-protein-dependent agonists.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey S. J., Rosoff P. M. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor primes neutrophils by activating a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein not associated with phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14165–14171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Zingg J., Maly F. E., de Weck A. L. Leukotriene production in human neutrophils primed by recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and stimulated with the complement component C5A and FMLP as second signals. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1281–1295. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Wang E., Casnellie J. E., Shiraishi T., Sha'afi R. I. Tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1478–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90841-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Gomez-Cambronero T. M., Waterman W. H., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced protein tyrosine phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein kinase in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and the neutrophil: mechanisms of action. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;314:35–71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6024-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Yamazaki M., Metwally F., Molski T. F., Bonak V. A., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. R., Casnellie J. E. Chemotactic factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane associated proteins in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):794–801. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Cannistra S. A., Furukawa Y., Torimoto Y., Griffin J. D. Signal transduction of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors involves tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of cytoplasmic proteins. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):706–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnekin D., Farrar W. L. Signal transduction of human interleukin 3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor through serine and tyrosine phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):317–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2710317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Beauseigle D., Gilbert C., Naccache P. H. Priming of the human neutrophil respiratory burst by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha involves regulation at a post-cell surface receptor level. Enhancement of the effect of agents which directly activate G proteins. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3047–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Kreis C., DiPersio J. F., Borgeat P., Naccache P. H. Involvement of guanine nucleotide binding proteins in neutrophil activation and priming by GM-CSF. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Faucher N., Borgeat P., Gasson J. C., DiPersio J. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor modulates the excitation-response coupling sequence in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3541–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Gilbert C., Caon A. C., Gaudry M., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Umezawa K., McColl S. R. Selective inhibition of human neutrophil functional responsiveness by erbstatin, an inhibitor of tyrosine protein kinase. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2098–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A. Hemopoietic cell growth factors and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:45–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelz C., Matsumoto T., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Characterization of the membrane-associated GTPase activity: effects of chemotactic factors and toxins. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):197–206. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J., Andersson T., Olsson I. Effect of tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil degranulation. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3199–3205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. M., Malech H. L. Subcellular localization of Gi alpha in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10958–10964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Molski T. F. Activation of the neutrophil. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:1–64. doi: 10.1159/000318681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Justen J. M., Sam L. M. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces granule exocytosis from human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Inflammation. 1990 Feb;14(1):83–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00914032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socinski M. A., Cannistra S. A., Sullivan R., Elias A., Antman K., Schnipper L., Griffin J. D. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces the expression of the CD11b surface adhesion molecule on human granulocytes in vivo. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):691–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Griffin J. D., Simons E. R., Schafer A. I., Meshulam T., Fredette J. P., Maas A. K., Gadenne A. S., Leavitt J. L., Melnick D. A. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors on signal transduction pathways in human granulocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3422–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Kwan L., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Human GM-CSF primes neutrophils for enhanced oxidative metabolism in response to the major physiological chemoattractants. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]