Abstract
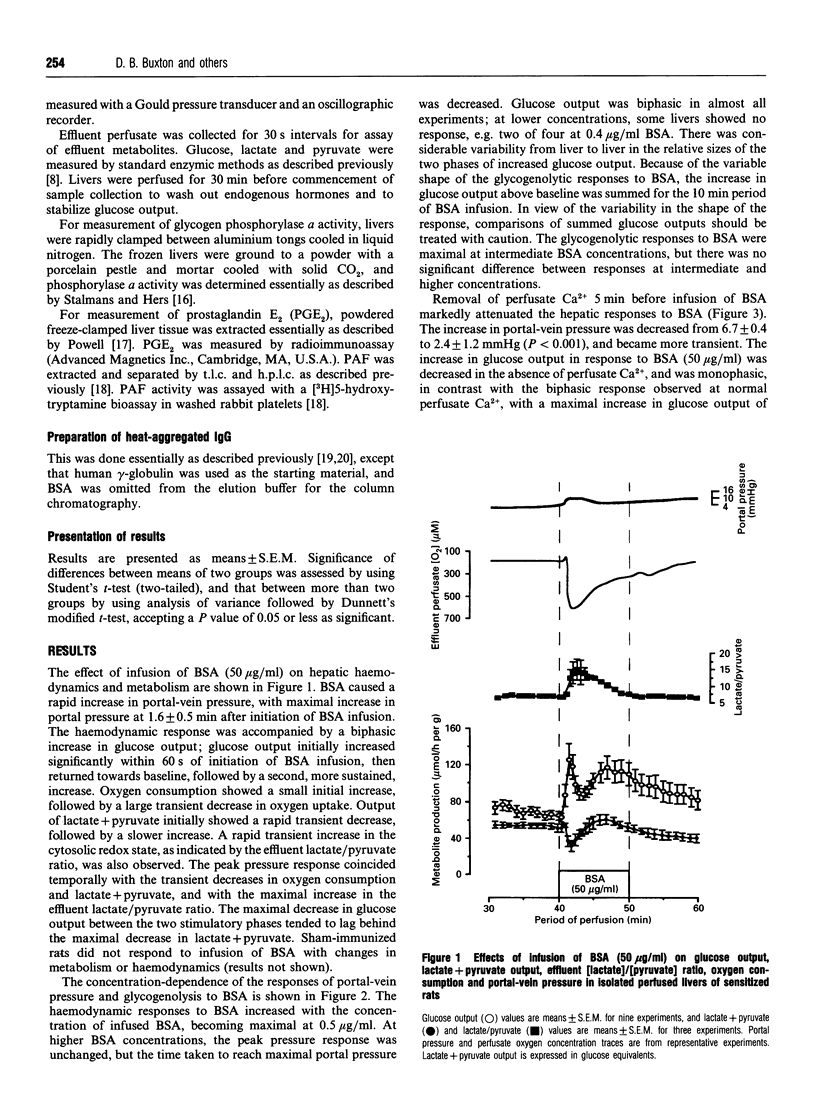
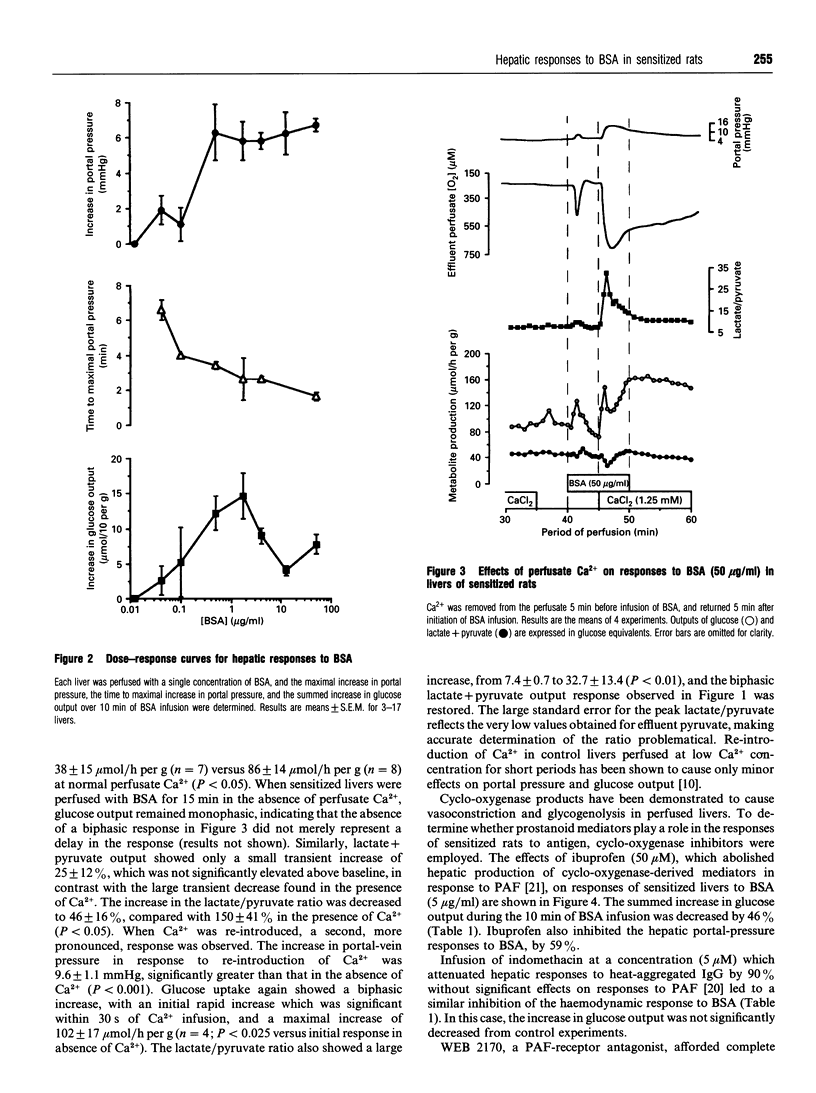
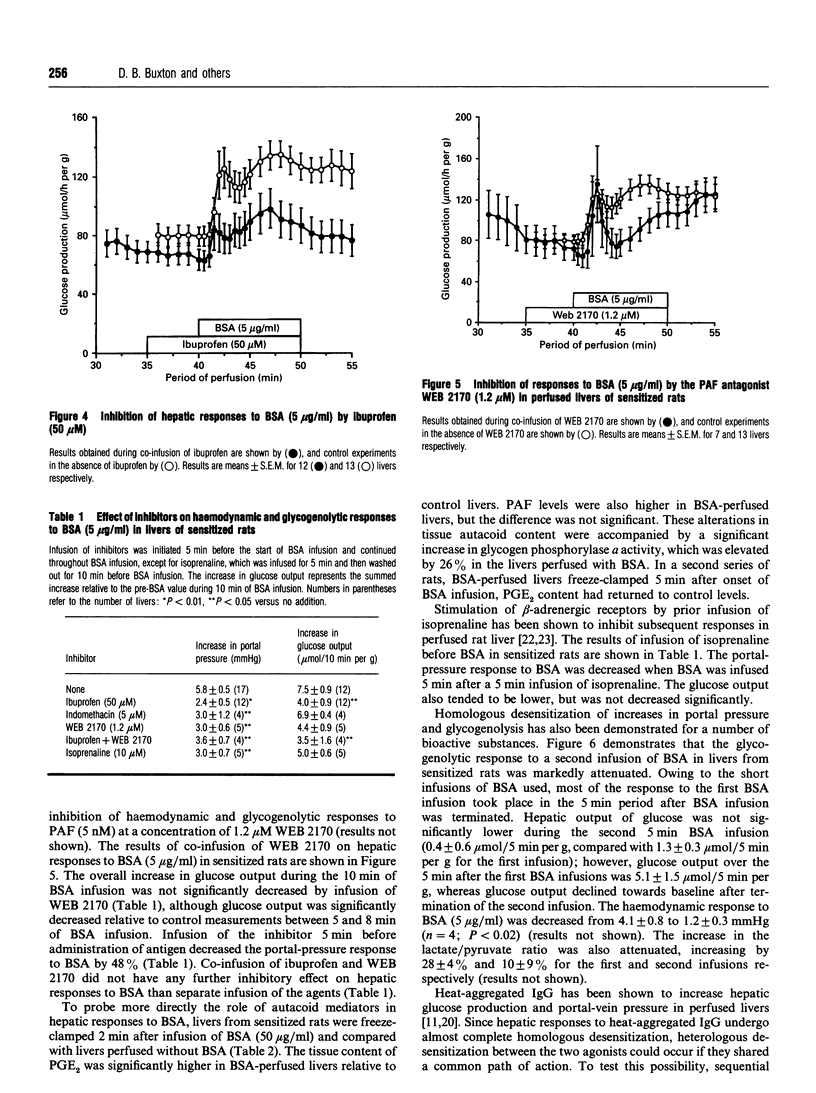
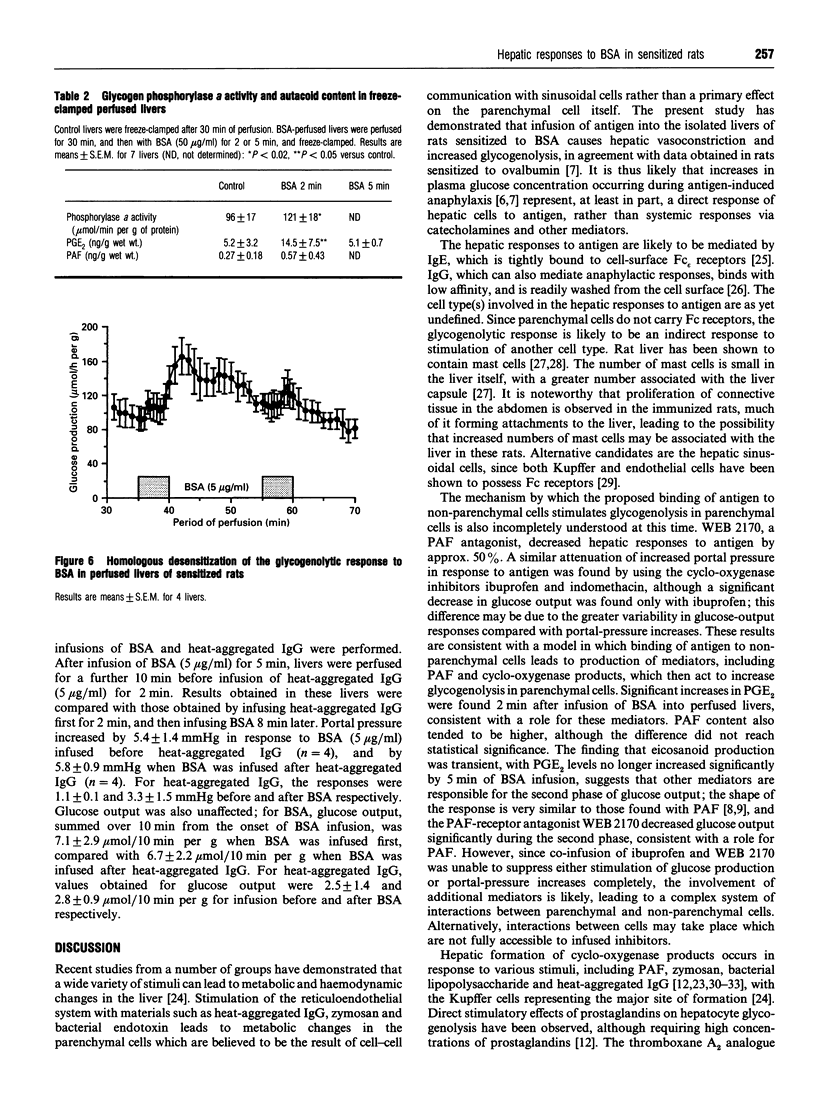
Infusion of BSA into isolated perfused livers of rats sensitized by intraperitoneal injection of BSA led to rapid increases in portal-vein pressure, glucose output and the lactate/pyruvate ratio in the effluent perfusate, with concomitant decreases in oxygen consumption and lactate+pyruvate efflux. The responses were attenuated at low (approximately 7 microM) perfusate Ca2+, but were restored on re-addition of normal Ca2+ concentration. Co-infusion of the cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor ibuprofen (50 microM) or of the platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist WEB 2170 (1.2 microM) inhibited haemodynamic responses to BSA (5 micrograms/ml) by 48% and 59% respectively. Responses to BSA were also attenuated by prior infusion of the beta-adrenergic agonist isoprenaline. Glycogen phosphorylase a activity was increased by 26% in livers freeze-clamped 2 min after onset of BSA infusion; tissue prostaglandin E2 content was increased at 2 min, but returned to control levels at 5 min. Homologous desensitization of hepatic responses to BSA was observed, but heterologous desensitization with heat-aggregated IgG did not take place. It is concluded that livers from rats sensitized to antigen respond directly to subsequent antigen administration by vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis, and that autacoid mediators are involved in these responses.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermelin M., Decker K. Ca2+ flux as an initial event in phagocytosis by rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birmelin M., Decker K. Synthesis of prostanoids and cyclic nucleotides by phagocytosing rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Fisher R. A., Briseno D. L., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Glycogenolytic and haemodynamic responses to heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G and prostaglandin E2 in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):493–498. doi: 10.1042/bj2430493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Fisher R. A., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Platelet-activating factor-mediated vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):644–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and platelet-activating factor production by heat-aggregated immunoglobulin G in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13758–13761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Shukla S. D., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Stimulation of hepatic glycogenolysis by acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1468–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteleijn E., Kuiper J., Van Rooij H. C., Kamps J. A., Koster J. F., Van Berkel T. J. Endotoxin stimulates glycogenolysis in the liver by means of intercellular communication. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):6953–6955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteleijn E., Kuiper J., van Rooij H. C., Kamps J. A., Koster J. F., van Berkel T. J. Hormonal control of glycogenolysis in parenchymal liver cells by Kupffer and endothelial liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2699–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):245–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieter P., Schulze-Specking A., Decker K. Differential inhibition of prostaglandin and superoxide production by dexamethasone in primary cultures of rat Kupffer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Biftu T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) mediation of rat anaphylactic responses to soluble immune complexes. Studies with PAF receptor antagonist L-652,731. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4659–4668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egido J., Sancho J., Rivera F., Sanchez-Crespo M. Handling of soluble IgA aggregates by the mononuclear phagocytic system in mice. A comparison with IgG aggregates. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Kumar R., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Effects of beta-adrenergic stimulation on 1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine-mediated vasoconstriction and glycogenolysis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8817–8823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and vasoconstriction in the perfused rat liver by the thromboxane A2 analogue U-46619. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4631–4638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Shukla S. D., Debuysere M. S., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. The effect of acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine on glycogenolysis and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8685–8688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V. Mechanisms and quantitative assessment of drug effects on cardiac output with a new model of the circulation. Pharmacol Rev. 1981 Dec;33(4):213–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines K. L., Fisher R. A. Regulation of hepatic glycogenolysis and vasoconstriction during antigen-induced anaphylaxis. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):G868–G877. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.5.G868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai M., Gardemann A., Püschel G., Jungermann K. Potential role for prostaglandin F2 alpha, D2, E2 and thromboxane A2 in mediating the metabolic and hemodynamic actions of sympathetic nerves in perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper J., De Rijke Y. B., Zijlstra F. J., Van Waas M. P., Van Berkel T. J. The induction of glycogenolysis in the perfused liver by platelet activating factor is mediated by prostaglandin D2 from Kupffer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1288–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe D. S., Olson M. S. Alteration of hepatic tissue spaces by platelet-activating factor and phenylephrine. Hepatology. 1989 Feb;9(2):278–284. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe D. S., Olson M. S. Platelet-activating factor-stimulated hepatic glycogenolysis is not mediated through cyclooxygenase-derived metabolites of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12130–12133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARX L., HIROTA M., PRINTUP C. A., WARNICK M. A., MARX W. Effects of exposure of 5oC and advancing age on tissue mast cells and heparin in male rats. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:180–182. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlovic F., Corvera S., García-Sáinz J. A. Possible involvement of cyclooxygenase products in the actions of platelet-activating factor and of lipoxygenase products in the vascular effects of epinephrine in perfused rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. The IgE-mast cell system as a paradigm for the study of antibody mechanisms. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:186–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. S. Rapid extraction of arachidonic acid metabolites from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:467–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulford K., Souhami R. L. The surface properties and antigen-presenting function of hepatic non-parenchymal cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Dec;46(3):581–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Hurwitz E. Binding of affinity cross-linked oligomers of IgG to cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1338–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer J. J. Myocardial substrate utilization in anaphylactic shock. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jan;151(1):28–31. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhelper M. E., Fisher R. A., Revtyak G. E., Hanahan D. J., Olson M. S. Beta 2-adrenergic agonist regulation of immune aggregate- and platelet-activating factor-stimulated hepatic metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):10976–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel F., Waebens M., Van Hecke P., Decanniere C., Stalmans W. Modulation of maximal glycogenolysis in perfused rat liver by adenosine and ATP. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):597–602. doi: 10.1042/bj2770597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou W. G., Chao W., Levine B. A., Olson M. S. Evidence for platelet-activating factor as a late-phase mediator of chronic pancreatitis in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1501–1508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


