Abstract
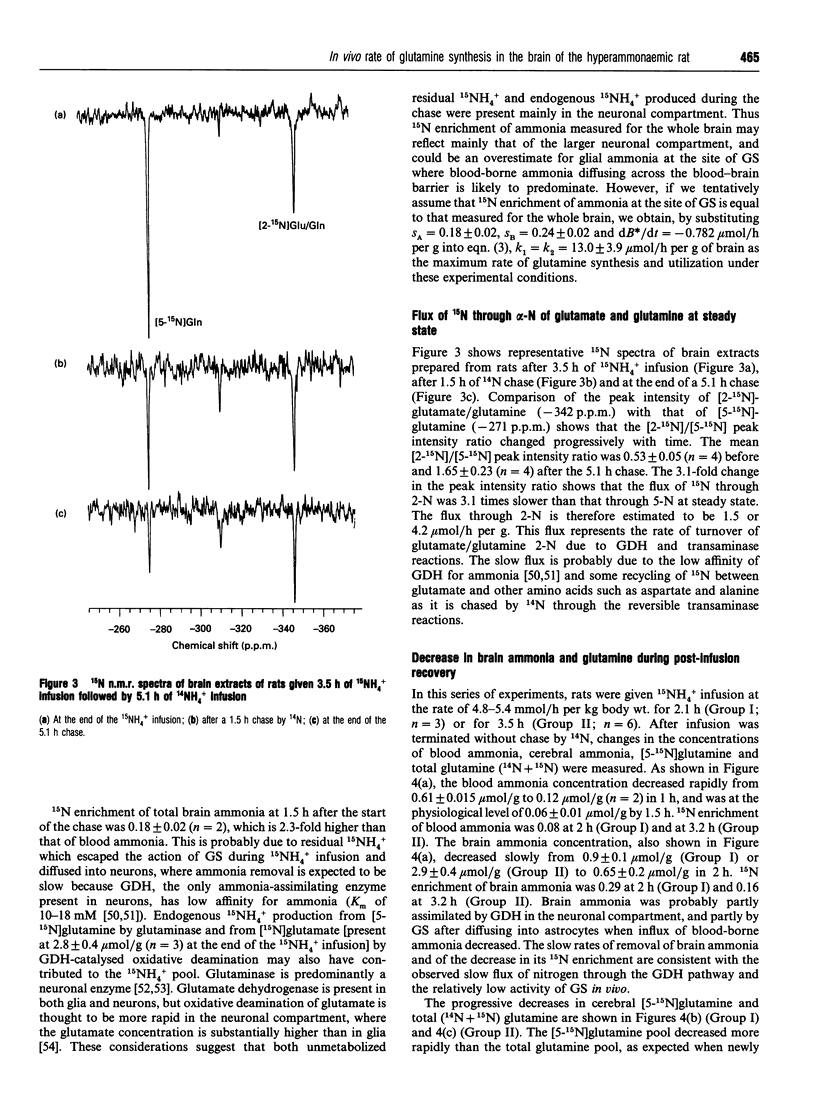
The rate of glutamine synthesis and utilization at steady state was measured in vivo in the brains of hyperammonaemic rats by 15N n.m.r. in combination with biochemical techniques. Rats were given an intravenous 15NH4+ infusion at the rate of 4.8 +/- 0.3 mmol/h per kg body wt. for 3.5 +/- 0.2 h, followed by 14NH4+ infusion at the same rate for an additional 5.1 h (chase period). During the chase period, blood ammonia (0.61 +/- 0.015 mumol/g), brain ammonia (2.9 +/- 0.3 mumol/g), glutamate (9.4 +/- 0.8 mumol/g) and glutamine (15N + 14N; 14.4 +/- 1.3 mumol/g) were at steady state. The rate of change in the cerebral [5-15N]glutamine concentration was measured in vivo by 15N n.m.r. at 20.27 MHz. To estimate 15N enrichment of precursor ammonia for glutamine synthetase (GS) in astrocytes which are interposed between cerebral capillaries and neurons, 15N enrichments of blood and brain ammonia were measured by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The in vivo rate of glutamine synthesis, which is equal to the rate of glutamine utilization at steady state, was estimated, from the observed rate of change in [5-15N]glutamine concentration and 15N enrichment of brain glutamine, to be 4.8 +/- 1.1 mumol/h per g of brain if 15N enrichment of ammonia at the site of GS in astrocytes is equal to that of blood-borne ammonia, and 13.0 +/- 3.9 mumol/h per g if it is equal to that measured for the whole brain. The observed GS activity in vivo in the brain of the hyperammonaemic rat is 2-5% of the reported optimum activity in vitro measured at enzyme-saturating concentrations of all substrates. The result suggests that substrates and/or cofactors other than ammonia kinetically limit GS activity in vivo. The g.c. chromatogram and mass spectrum of ammonia-derived N-trifluoroacetyl-dibutylglutamate (TAB-glutamate) are shown in Supplementary Publication SUP 50170 (4 pages), which has been deposited at the British Library Document Supply Centre, Boston Spa, Wetherby, West Yorkshire, U.K., from whom copies can be obtained on the terms indicated in Biochem. J.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam W. R., Craik D. J., Hall J. G., Kneen M. M., Wellard R. M. Problems in the assessment of magnesium depletion in the rat by in vivo 31P NMR. Magn Reson Med. 1988 Jul;7(3):300–310. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910070307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Metabolic compartments in vivo. Ammonia and glutamic acid metabolism in brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2562–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates T. E., Williams S. R., Kauppinen R. A., Gadian D. G. Observation of cerebral metabolites in an animal model of acute liver failure in vivo: a 1H and 31P nuclear magnetic resonance study. J Neurochem. 1989 Jul;53(1):102–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglioli G., Martin D. L. GABA synthesis in brain slices is dependent on glutamine produced in astrocytes. Neurochem Res. 1991 Feb;16(2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00965703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin A. M. Control of glutaminase activity in rat brain cortex in vitro: influence of glutamate, phosphate, ammonium, calcium and hydrogen ions. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 16;208(2):363–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90564-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth R. F., Girard G., Giguère J. F. Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portocaval anastomosis. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):486–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammer W. Glutamine synthetase in the central nervous system is not confined to astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Feb;26(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee P. Y., Dahl J. L., Fahien L. A. The purification and properties of rat brain glutamate dehydrogenase. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colon A. D., Plaitakis A., Perakis A., Berl S., Clarke D. D. Purification and characterization of a soluble and a particulate glutamate dehydrogenase from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1811–1819. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., McDonald J. M., Gelbard A. S., Gledhill R. F., Duffy T. E. The metabolic fate of 13N-labeled ammonia in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4982–4992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Mora S. N., Cruz N. F., Gelbard A. S. Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1716–1723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Plum F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Apr;67(2):440–519. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejong C. H., Kampman M. T., Deutz N. E., Soeters P. B. Cerebral cortex ammonia and glutamine metabolism during liver insufficiency-induced hyperammonemia in the rat. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):1071–1079. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Louie M., Lerner A. Glutamine synthetase from rat liver. Purification, properties, and preparation of specific antisera. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6111–6118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Silver I. A. Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(4):245–296. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst T., Ross B. D., Flores R. Cerebral MRS in infant with suspected Reye's syndrome. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):486–486. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91808-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow N. A., Kanamori K., Ross B. D., Parivar F. A 15N-n.m.r. study of cerebral, hepatic and renal nitrogen metabolism in hyperammonaemic rats. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):473–481. doi: 10.1042/bj2700473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler A., Kanamori K., Ross B. D. Real-time study of the urea cycle using 15N n.m.r. in the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 1;287(Pt 3):813–820. doi: 10.1042/bj2870813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. A., Miller A. L., Nielsen R. C., Veech R. L. The acute action of ammonia on rat brain metabolism in vivo. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1001–1008. doi: 10.1042/bj1341001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindfelt B., Plum F., Duffy T. E. Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):386–396. doi: 10.1172/JCI108651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. M., MacDonnell L., Xanalatos C. Effect of ammonium salts on brain metabolism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Aug;37(8):948–953. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.8.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessy J., DeJoseph M. R., Hawkins R. A. Hyperammonaemia depresses glucose consumption throughout the brain. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):693–696. doi: 10.1042/bj2770693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Parivar F., Ross B. D. A 15N NMR study of in vivo cerebral glutamine synthesis in hyperammonemic rats. NMR Biomed. 1993 Jan-Feb;6(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori K., Ross B. D., Farrow N. A., Parivar F. A 15N-NMR study of isolated brain in portacaval-shunted rats after acute hyperammonemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 5;1096(4):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90062-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Urade Y., Watanabe Y., Mizuno N. Production, characterization, and immunohistochemical application of monoclonal antibodies to glutaminase purified from rat brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):302–309. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00302.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis R., Ross B. D., Farrow N. A., Ackerman Z. Metabolic disorders of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy detected with H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 1992 Jan;182(1):19–27. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.1.1345760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Mouse glutamine synthetase is encoded by a single gene that can be expressed in a localized fashion. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 5;208(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimer K. R., Rice R. H., Gehrke C. W. Complete mass spectra of N-trifluoroacetyl-n-butyl esters of amino acids. J Chromatogr. 1977 Aug 21;141(2):121–144. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)99131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mans A. M., Biebuyck J. F., Hawkins R. A. Ammonia selectively stimulates neutral amino acid transport across blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C74–C77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearow K. M., Mill J. F., Freese E. Neuron-glial interactions involved in the regulation of glutamine synthetase. Glia. 1990;3(5):385–392. doi: 10.1002/glia.440030510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mill J. F., Mearow K. M., Purohit H. J., Haleem-Smith H., King R., Freese E. Cloning and functional characterization of the rat glutamine synthetase gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Feb;9(3):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90003-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D. A light and electron microscopic study of experimental portal-systemic (ammonia) encephalopathy. Progression and reversal of the disorder. Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;36(6):618–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Martinez-Hernandez A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Feb 2;161(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90071-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottersen O. P., Zhang N., Walberg F. Metabolic compartmentation of glutamate and glutamine: morphological evidence obtained by quantitative immunocytochemistry in rat cerebellum. Neuroscience. 1992;46(3):519–534. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90141-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen R. E., Odden E., Fonnum F. Importance of glutamine for gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in rat neostriatum in vivo. J Neurochem. 1988 Oct;51(4):1294–1299. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINER J. M. The study of metabolic turnover rates by means of isotopic tracers. I. Fundamental relations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Sep;46(1):53–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B., Kreis R., Ernst T. Clinical tools for the 90s: magnetic resonance spectroscopy and metabolite imaging. Eur J Radiol. 1992 Mar-Apr;14(2):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0720-048x(92)90226-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman D. L., Novotny E. J., Shulman G. I., Howseman A. M., Petroff O. A., Mason G., Nixon T., Hanstock C. C., Prichard J. W., Shulman R. G. 1H-[13C] NMR measurements of [4-13C]glutamate turnover in human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9603–9606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALGANICOFF L., DEROBERTIS E. SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF THE ENZYMES OF THE GLUTAMIC ACID, GLUTAMINE AND GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID CYCLES IN RAT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1965 Apr;12:287–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERLOCK S., SUMMERSKILL W. H., WHITE L. P., PHEAR E. A. Portal-systemic encephalopathy; neurological complications of liver disease. Lancet. 1954 Sep 4;267(6836):454–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Leu F. Y., Meister A. Rat liver glutamine synthetase. Preparation, properties, and mechanism of inhibition by carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5312–5321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Regulation of rat liver glutamine synthetase: activation by alpha-ketoglutarate and inhibition by glycine, alanine, and carbamyl phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):781–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanki C. M., Sugden D., Thomas A. J., Bradford H. F. In vivo release from cerebral cortex of [14C]glutamate synthesized from [U-14C]glutamine. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):611–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veech R. L., Harris R. L., Veloso D., Veech E. H. Freeze-blowing: a new technique for the study of brain in vivo. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waniewski R. A. Physiological levels of ammonia regulate glutamine synthesis from extracellular glutamate in astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. K., Bradford H. F. Relative activities of glutamine synthetase and glutaminase in mammalian synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):339–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Denman R. B., Roby W. G. Glutamine synthetase from ovine brain is a manganese(II) enzyme. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 7;21(25):6389–6396. doi: 10.1021/bi00268a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. C., Schousboe A., Hertz L. Influence of pathological concentrations of ammonia on metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1984 Feb;42(2):594–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. C., Schousboe A., Hertz L. Metabolic fate of 14C-labeled glutamate in astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):954–960. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudkoff M., Nissim I., Hummeler K., Medow M., Pleasure D. Utilization of [15N]glutamate by cultured astrocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):185–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2340185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Zande L., Labruyère W. T., Arnberg A. C., Wilson R. H., van den Bogaert A. J., Das A. T., van Oorschot D. A., Frijters C., Charles R., Moorman A. F. Isolation and characterization of the rat glutamine synthetase-encoding gene. Gene. 1990 Mar 15;87(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


