Abstract
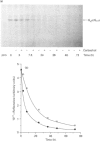
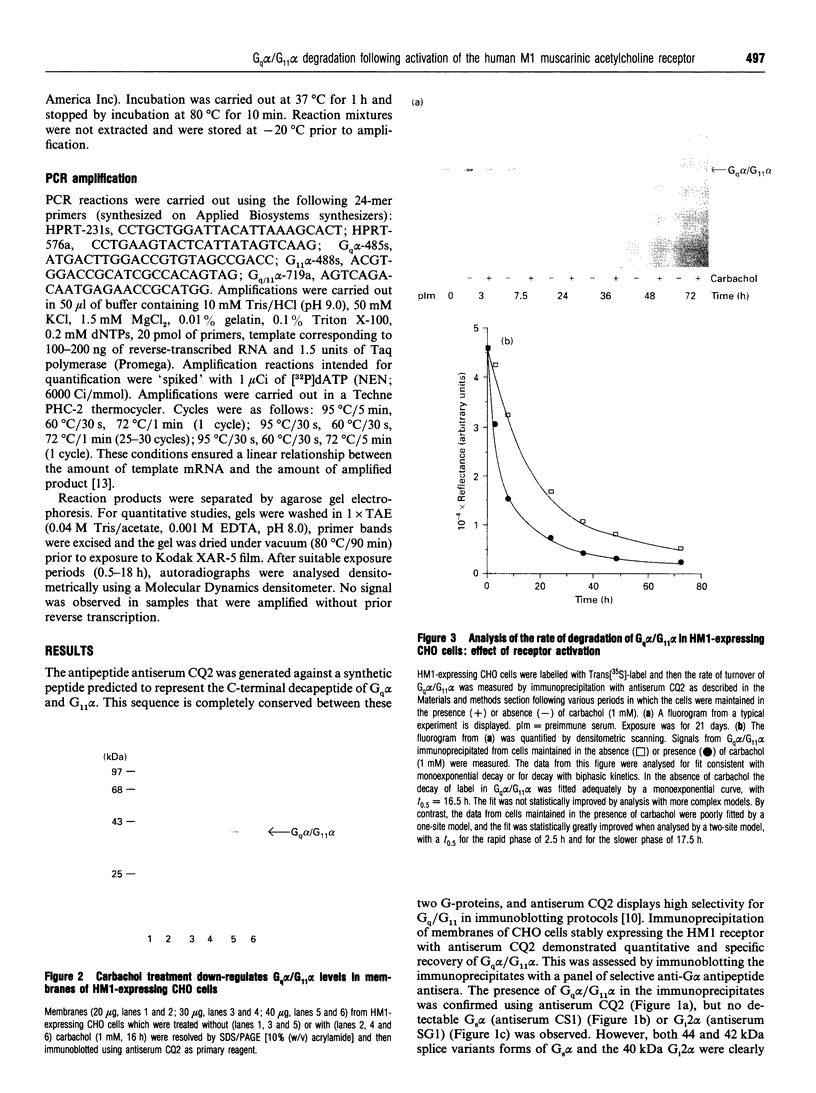
Treatment of CHO cells stably expressing the human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine (HM1) receptor with the cholinergic agonist carbachol results in a reduction in cellular levels of Gq alpha/G11 alpha. Half-maximal effects are produced by 3 h, and a new steady state of some 50% of the resting levels of Gq alpha/G11 alpha is subsequently established [Mullaney, Dodd, Buckley and Milligan, (1993) Biochem. J. 289, 125-131]. To analyse the mechanism of this effect, we examined the rate of turnover of Gq alpha/G11 alpha in these HM1-expressing cells in the presence and absence of carbachol (1 mM). In untreated cells the measured removal of 35S-labelled Gq alpha/G11 alpha was adequately described by a monoexponential curve with a half-time (t0.5) of 18.0 +/- 2.2 h. When the cells were treated with carbachol a more complex pattern of Gq alpha/G11 alpha degradation was observed. Upon addition of the agonist, the rate of degradation initially increased markedly (t0.5 = 2.9 +/- 0.2 h). The maintained presence of the agonist was unable, however, to sustain the enhanced rate of degradation. Beyond 8 h of treatment with carbachol, degradation of Gq alpha/G11 alpha returned to a rate close to that observed in untreated cells (t0.5 = 18.5 +/- 1.3 h). Parallel experiments indicated that the effect of carbachol was specific for Gq alpha/G11 alpha, as the t0.5 of Gi2 alpha (approx. 30 h) was not affected by the agonist. Analysis of Gq alpha/G11 alpha mRNA levels by reverse transcriptase/PCR indicated that there was no difference in cells maintained in the absence and presence of carbachol. Such data demonstrate that agonist-induced establishment of a new steady-state level of Gq alpha/G11 alpha results from an initial receptor-mediated enhancement of protein turnover followed by a desensitization of the receptor response.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adie E. J., Mullaney I., McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Concurrent down-regulation of IP prostanoid receptors and the alpha-subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gs) during prolonged exposure of neuroblastoma x glioma cells to prostanoid agonists. Quantification and functional implications. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 15;285(Pt 2):529–536. doi: 10.1042/bj2850529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Buckley N. J., Young A. C., Brann M. R. Identification of a family of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):527–532. doi: 10.1126/science.3037705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabet P., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Metabolism of two Go alpha isoforms in neuronal cells during differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12825–12828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. J., Bonner T. I., Buckley C. M., Brann M. R. Antagonist binding properties of five cloned muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. H., Bourne H. R. Cholera toxin induces cAMP-independent degradation of Gs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5352–5357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Port J. D., Malbon C. C. Cross-regulation between G-protein-mediated pathways. Activation of the inhibitory pathway of adenylylcylclase increases the expression of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11915–11922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadcock J. R., Ros M., Watkins D. C., Malbon C. C. Cross-regulation between G-protein-mediated pathways. Stimulation of adenylyl cyclase increases expression of the inhibitory G-protein, Gi alpha 2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14784–14790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K. G., Milligan G. Biphasic regulation of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells is due to the activation and subsequent loss of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory GTP binding protein (GS). Cell Signal. 1990;2(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Prostaglandin E1-mediated, cyclic AMP-independent, down-regulation of Gs alpha in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17084–17093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Green A. Agonist control of G-protein levels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jun;12(6):207–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G. Persistent activation of the alpha subunit of Gs promotes its removal from the plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):837–841. doi: 10.1042/bj2600837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Unson C. G., Wakelam M. J. Cholera toxin treatment produces down-regulation of the alpha-subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gs). Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):643–649. doi: 10.1042/bj2620643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Griffiths S. L., Saggerson E. D., Houslay M. D., Knowler J. T., Milligan G. Guanine-nucleotide-binding proteins expressed in rat white adipose tissue. Identification of both mRNAs and proteins corresponding to Gi1, Gi2 and Gi3. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):403–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2620403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell F. M., Mullaney I., Godfrey P. P., Arkinstall S. J., Wakelam M. J., Milligan G. Widespread distribution of Gq alpha/G11 alpha detected immunologically by an antipeptide antiserum directed against the predicted C-terminal decapeptide. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullaney I., Dodd M. W., Buckley N., Milligan G. Agonist activation of transfected human M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in CHO cells results in down-regulation of both the receptor and the alpha subunit of the G-protein Gq. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2890125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Kahn C. R. Insulin inhibits pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of G-proteins. Evidence for a novel interaction between insulin receptors and G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15546–15552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbert S., Michel T., Lee R., Neer E. J. Differential degradation rates of the G protein alpha o in cultured cardiac and pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3102–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]