Abstract
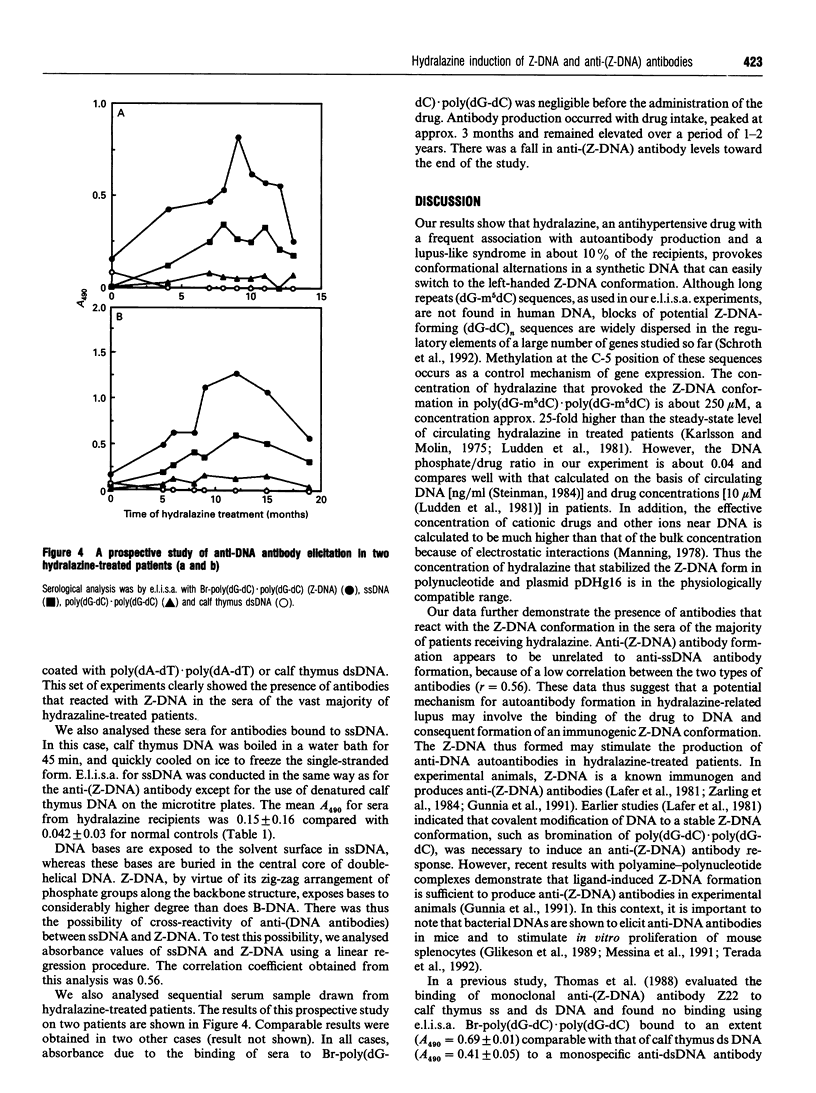
We studied the effect of hydralazine, an antihypertensive drug with lupus-inducing side effects, on the conformation of poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC) and a plasmid with a 23 bp insert of (dG-dC)n.(dG-dC)n sequences. Using an e.l.i.s.a. with a monoclonal anti-(Z-DNA) antibody Z22, we found that hydralazine provoked the Z-DNA conformation in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC) at 250-500 microM concentration. The supercoiled form of hydralazine-treated plasmid bound to Z22 in a gel-retardation assay. To examine further whether Z-DNA could act as an inciting agent in anti-nuclear antibody production in patients, we analysed 65 sera from 25 hypertensive patients taking hydralazine and found anti-(Z-DNA) antibodies in 82% of these sera. Sera from age-matched normal controls showed no binding to Z-DNA. Data on sera drawn sequentially from four hypertensive patients showed that antibodies were present after the drug treatment. These data demonstrate the presence of a high incidence of anti-(Z-DNA) antibodies in patients treated with hydralazine and suggest that a possible mechanism for the production of autoantibodies in drug-related lupus might involve the induction and stabilization of Z-DNA by drugs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergen H. R., 3rd, Losman M. J., O'Connor T., Zacharias W., Larson J. E., Accavitti M. A., Wells R. D., Koopman W. J. Specificity of monoclonal anti-Z-DNA antibodies from unimmunized MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):743–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L. Drug-induced anti-histone autoantibodies display two patterns of reactivity with substructures of chromatin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):680–690. doi: 10.1172/JCI115353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubroff L. M., Reid R. J., Jr Hydralazine-pyrimidine interactions may explain hydralazine-induced lupus erythematosus. Science. 1980 Apr 25;208(4442):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.7367866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., WHITE T. A. HUMAN ACETYLATION POLYMORPHISM. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldredge N. T., van Robertson W. B., Jiller J. J., 3rd The interaction of lupus-inducing drugs with deoxyribonucleic acid. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Nov;3(2):262–271. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkeson G. S., Grudier J. P., Karounos D. G., Pisetsky D. S. Induction of anti-double stranded DNA antibodies in normal mice by immunization with bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1482–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnia U. B., Thomas T., Thomas T. J. The effects of polyamines on the immunogenicity of polynucleotides. Immunol Invest. 1991 Jul;20(4):337–350. doi: 10.3109/08820139109057760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Kakunaga T. Potential Z-DNA forming sequences are highly dispersed in the human genome. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):396–398. doi: 10.1038/298396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon C. E., Portanova J. P. Drug-induced lupus: clinical and serological studies. Clin Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;8(1):121–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess E. Drug-related lupus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1460–1462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Molin L. Polymorphic acetylation of procaine amide in healthy subjects. Acta Med Scand. 1975 Apr;197(4):299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1975.tb04921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick M. W., Klysik J., Singleton C. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Hanau L. H., Erlanger B. F., Wells R. D. Intervening sequences in human fetal globin genes adopt left-handed Z helices. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7268–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Möller A., Nordheim A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies specific for left-handed Z-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Valle R. P., Möller A., Nordheim A., Schur P. H., Rich A., Stollar B. D. Z-DNA-specific antibodies in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):314–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI110771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Szabo P., Posnett D. N. The genomic structure of human V beta 6 T cell antigen receptor genes. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1537–1547. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwin A., Adams L. E., Zimmer H., Foad B., Loggie J. H., Hess E. V. Prospective study of immunologic effects of hydralazine in hypertensive patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Apr;29(4):447–456. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden T. M., McNay J. L., Jr, Shepherd A. M., Lin M. S. Variability of plasma hydralazine concentrations in male hypertensive patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Aug;24(8):987–993. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORROW J. D., SCHROEDER H. A., PERRY H. M., Jr Studies on the control of hypertension by hyphex. II. Toxic reactions and side effects. Circulation. 1953 Dec;8(6):829–839. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.8.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. P., Gilkeson G. S., Pisetsky D. S. Stimulation of in vitro murine lymphocyte proliferation by bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1759–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mongey A. B., Donovan-Brand R., Thomas T. J., Adams L. E., Hess E. V. Serologic evaluation of patients receiving procainamide. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;35(2):219–223. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry H. M., Jr, Tan E. M., Carmody S., Sakamoto A. Relationship of acetyl transferase activity to antinuclear antibodies and toxic symptoms in hypertensive patients treated with hydralazine. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):114–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M. Salt-induced co-operative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly (dG-dC). J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):375–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D., Michalak M., Daisley S. L., Glick R. A method for the purification of E. coli plasmid DNA by homogeneous lysis and polyethylene glycol precipitation. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 Aug;9(3):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00775367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M. Aromatic amines and the pathogenesis of lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1983 Dec;75(6):1037–1042. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90885-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Bell S. A., Burlingame R. W. Autoantibodies associated with lupus induced by diverse drugs target a similar epitope in the (H2A-H2B)-DNA complex. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):165–173. doi: 10.1172/JCI115832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Dna isolated from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus is rich in guanine-cytosine content. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1341–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Chou P. J., Ho P. S. Mapping Z-DNA in the human genome. Computer-aided mapping reveals a nonrandom distribution of potential Z-DNA-forming sequences in human genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11846–11855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley J. T., Lee J. S., Decoteau W. E. Left-handed "Z" DNA antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1984 Oct;11(5):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha B. K., Patterson M. A. Free radical metabolism of hydralazine. Binding and degradation of nucleic acids. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 15;32(22):3279–3284. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer-Green G., Kelley L., Adams L. E., Donovan-Brand R., Hess E. V. Polynucleotide antibodies in connective tissue disease: viral markers or disease mediators? J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Feb;107(2):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R. Circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Isolation and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):832–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI111278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Rubin R. L. Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs): diagnostically specific immune markers and clues toward the understanding of systemic autoimmunity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 May;47(2):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada K., Hirose S., Okuhara E. Production of antibodies specific for double stranded antigen DNA cloned from immune complexes in plasma of a SLE patient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):797–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90553-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Gunnia U. B., Thomas T. Polyamine-induced B-DNA to Z-DNA conformational transition of a plasmid DNA with (dG-dC)n insert. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6137–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Meryhew N. L., Messner R. P. DNA sequence and conformation specificity of lupus autoantibodies. Preferential binding to the left-handed Z-DNA form of synthetic polynucleotides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):367–377. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Messner R. P. Effects of lupus-inducing drugs on the B to Z transition of synthetic DNA. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):638–645. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Thomas T. Conformational transitions of polynucleotides in the presence of rhodium complexes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1990 Jun;7(6):1221–1235. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1990.10508561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden P. D. Potential Z-DNA-forming elements in serum DNA from human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1095–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Read R., Thomas M., Rutman A., Harrison K., Lund V., Cookson B., Goldman W., Lambert H., Cole P. Effects of Bordetella pertussis infection on human respiratory epithelium in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):337–345. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.337-345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacest R., Koch-Weser J. Relation of hydralazine plasma concentration to dosage and hypotensive action. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 May-Jun;13(3):420–425. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972133420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias W., Jaworski A., Larson J. E., Wells R. D. The B- to Z-DNA equilibrium in vivo is perturbed by biological processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7069–7073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias W., Koopman W. J. Lupus-inducing drugs alter the structure of supercoiled circular DNA domains. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Mar;33(3):366–374. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., McIntosh L. P., Thomae R., Jovin T. M. Immunoglobulin recognition of synthetic and natural left-handed Z DNA conformations and sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):369–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Flora S., Zanacchi P., Bennicelli C., Camoirano A., Cavanna M., Sciabà L., Cajelli E., Faggin P., Brambilla G. In vivo and in vitro genotoxicity of three antihypertensive hydrazine derivatives (hydralazine, dihydralazine, and endralazine). Environ Mutagen. 1982;4(5):605–619. doi: 10.1002/em.2860040512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]