Abstract
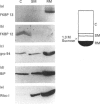
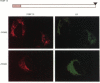
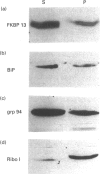
The function of the immunophilins, FKBP 12 and FKBP 13, which are binding proteins for the immunosuppressant drug FK506 and rapamycin, remains poorly defined, although it has been suggested that immunophilins and immunophilin-like proteins may play a role in protein sorting/folding and intracellular calcium ion regulation. As a first step towards understanding the function of FKBP 13, we studied its subcellular localization by immunoblotting of well-defined subcellular fractions from a canine pancreatic homogenate and immunocytochemical analysis of an overexpressed cloned cDNA for FKBP 13. Whereas FKBP 12 fractionated entirely into the cytosol, virtually all FKBP 13 was found in the rough microsomal fraction which consisted of highly purified rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER), along with several well-characterized ER markers [the immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein (BiP), grp 94 and ribophorin I]. Moreover, FKBP 13 co-banded with the ER markers on isopycnic sucrose gradients. By immunofluorescence, the overexpressed cDNA for FKBP 13 in Hela cells gave an ER-staining pattern highly similar to that of known ER proteins. Addition of the ligand FK506 did not appear to alter the distribution of FKBP 13. Separation of the ER luminal contents and membrane revealed FKBP 13 to be a luminal ER protein. Since the lumen of the ER is where the folding of membrane and secreted proteins occurs, as well as a major site of intracellular calcium storage, it seems possible that FKBP 13 may be involved in one of these functions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber S., Krause K. H., Caroni P. s-cyclophilin is retained intracellularly via a unique COOH-terminal sequence and colocalizes with the calcium storage protein calreticulin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):113–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Somers P. K., Wandless T. J., Burakoff S. J., Schreiber S. L. Probing immunosuppressant action with a nonnatural immunophilin ligand. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):556–559. doi: 10.1126/science.1700475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Studies on free and membrane-bound ribosomes in rat liver. I. Distribution as related to total cellular RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Klee C. B., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Calcineurin phosphatase activity in T lymphocytes is inhibited by FK 506 and cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman T., Brillantes A. M., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Marks A. R. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9474–9477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y. J., Albers M. W., Lane W. S., Bierer B. E., Schreiber S. L., Burakoff S. J. Molecular cloning of a membrane-associated human FK506- and rapamycin-binding protein, FKBP-13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6677–6681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye R. E., Fruman D. A., Bierer B. E., Albers M. W., Zydowsky L. D., Ho S. I., Jin Y. J., Castells M. C., Schreiber S. L., Walsh C. T. Effects of cyclosporin A and FK506 on Fc epsilon receptor type I-initiated increases in cytokine mRNA in mouse bone marrow-derived progenitor mast cells: resistance to FK506 is associated with a deficiency in FK506-binding protein FKBP12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8542–8546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J., Nigam S. K. Intracellular calcium: molecules and pools. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Schumacher T. N., Ploegh H. L. Assembly and intracellular transport of major histocompatibility complex molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):601–609. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in canine pancreatic rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16927–16932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K. Subcellular distribution of small GTP binding proteins in pancreas: identification of small GTP binding proteins in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1296–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Towers T. Subcellular distribution of calcium-binding proteins and a calcium-ATPase in canine pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):197–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90303-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Shortridge R. D., Larrivee D. C., Ono T., Ozaki M., Pak W. L. Drosophila ninaA gene encodes an eye-specific cyclophilin (cyclosporine A binding protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5390–5394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. H., Snyder S. H., Nigam S. K. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Localization in epithelial tissue. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7444–7449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki C. K., Bonifacino J. S., Lin A. Y., Davis M. M., Klausner R. D. Regulating the retention of T-cell receptor alpha chain variants within the endoplasmic reticulum: Ca(2+)-dependent association with BiP. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):189–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., Peterson P. A. Invariant chain--a regulator of antigen presentation. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;2(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90163-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada I., Rindress D., Cameron P. H., Ou W. J., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Louvard D., Bell A. W., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bergeron J. J. SSR alpha and associated calnexin are major calcium binding proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19599–19610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]