Abstract
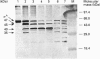
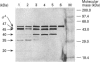
By the use of a partial proteolysis method and Western-blot analysis, the conformational properties of Bacillus subtilis sigma A factor in the transcription initiation stage were studied. From a comparison of the trypsin-digestion patterns of free sigma A and of sigma A associated with core enzyme, it was found that the production of 45 kDa sigma A tryptic-derived fragment was enhanced when sigma A was associated with the core enzyme. More importantly, a 40 kDa sigma A tryptic-derived fragment was found exclusively in this associated state. Based on the change of the digestion kinetics when producing the 45 kDa tryptic fragment and the generation of this new 40 kDa tryptic fragment from sigma A, it was apparent that a conformation change of sigma A occurred during the association of sigma A with the core enzyme. Also, similar patterns were found for the sigma A present in the holoenzyme-promoter DNA complex. These findings suggest that no further distinctive conformational change of sigma A occurs at the step of RNA polymerase holoenzyme and promoter DNA complex formation. Trypsin-digestion patterns of sigma A in different RNA polymerase holoenzyme and promoter DNA complexes were also studied. The presence of similar trypsin digestion-patterns of sigma A in those complexes strongly supports the idea that a similar sigma A conformation is used in the recognition of different sigma A-type promoters and the formation of different open complexes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binnie C., Lampe M., Losick R. Gene encoding the sigma 37 species of RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5943–5947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. Y., Doi R. H. Overproduction, purification, and characterization of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase sigma A factor. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3257–3263. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3257-3263.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. Y., Shyu Y. T., Doi R. H. The interaction between Bacillus subtilis sigma-A (sigma A) factor and RNA polymerase with promoters. Biochimie. 1992 Jul-Aug;74(7-8):601–612. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90131-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan M. L., Kalman S. S., Thomas S. M., Price C. W. Gene encoding the 37,000-dalton minor sigma factor of Bacillus subtilis RNA polymerase: isolation, nucleotide sequence, chromosomal locus, and cryptic function. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.771-778.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Moyle H., Susskind M. M. A mutant Escherichia coli sigma 70 subunit of RNA polymerase with altered promoter specificity. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitt M. A., Wang L. F., Doi R. H. A strong sequence homology exists between the major RNA polymerase sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7178–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Vaughn V., Lau E. T., VanBogelen R. A., Erickson J. W., Neidhardt F. C. Nucleotide sequence of the heat shock regulatory gene of E. coli suggests its protein product may be a transcription factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley S. A., Burgess R. R. Characterization of the Escherichia coli transcription factor sigma 70: localization of a region involved in the interaction with core RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7728–7734. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenberger O., Heumann H., Pilz I. Small-angle X-ray study of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase holoenzyme from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):22–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. L., Rabinowitz J. C. Nucleotide sequences of transcription and translation initiation regions in Bacillus phage phi 29 early genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1053–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz I., Kratky O., Rabussay D. Studies on the conformation of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in solution by small-angle x-ray measurements. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):205–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Hu J. C., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Altered promoter recognition by mutant forms of the sigma 70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):591–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Kirkegaard K., Buc H. Changes in the DNA structure of the lac UV5 promoter during formation of an open complex with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2723–2731. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland M. S., Thompson N. E., Burgess R. R. Structure and function of the sigma-70 subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Monoclonal antibodies: localization of epitopes by peptide mapping and effects on transcription. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5755–5762. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. Y., Yarbrough L. R., Wu C. W. Conformational transition of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase induced by the interaction of sigma subunit with core enzyme. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3254–3258. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh L. C., Lee J. C. Probing the yeast 5 S RNA-protein complex by fluorescence and controlled proteolytic digestion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 1;276(2):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90748-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung B. Y., Crooke E., Kornberg A. Fate of the DnaA initiator protein in replication at the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1282–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber P., Healy J., Carter H. L., 3rd, Cutting S., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Mutation changing the specificity of an RNA polymerase sigma factor. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]