Abstract
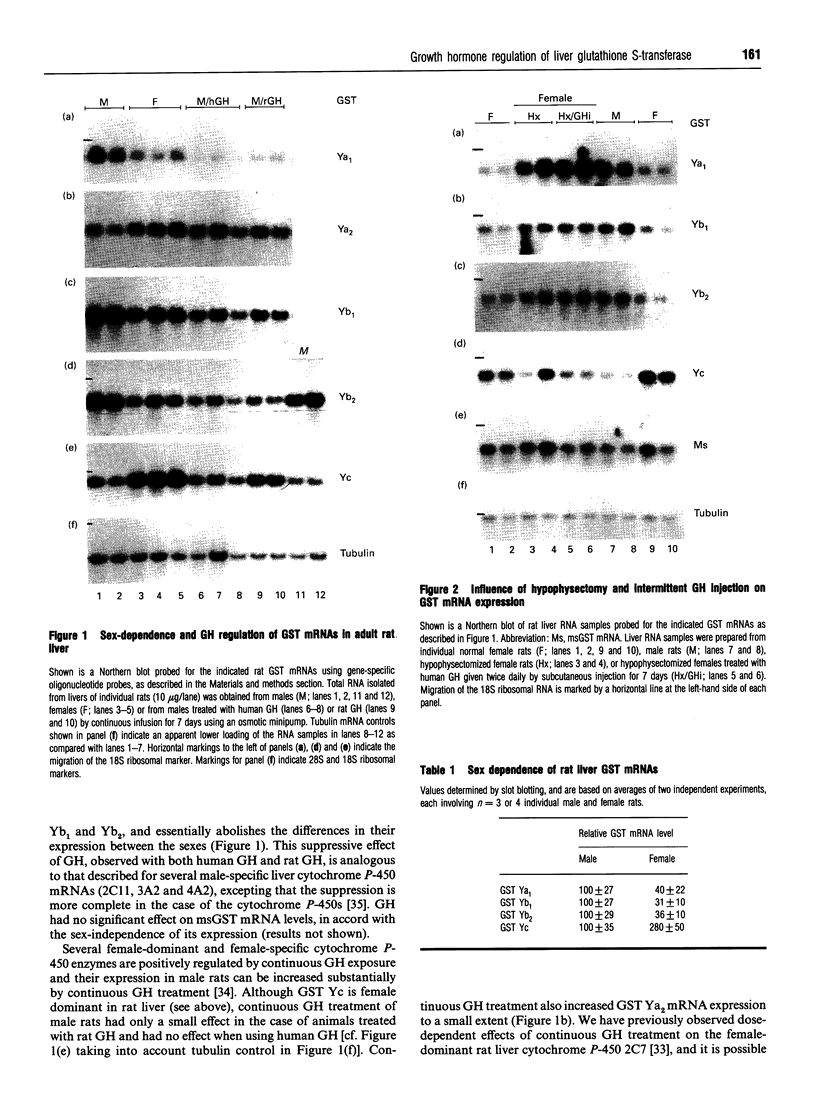
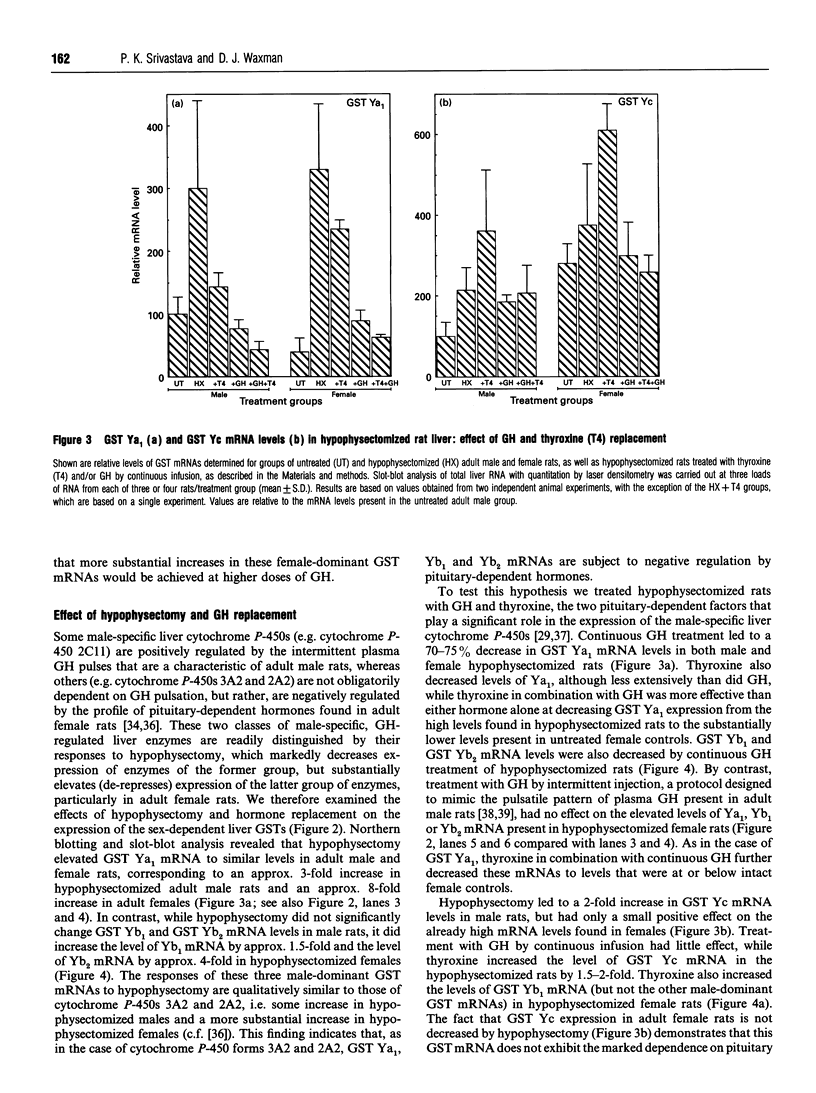
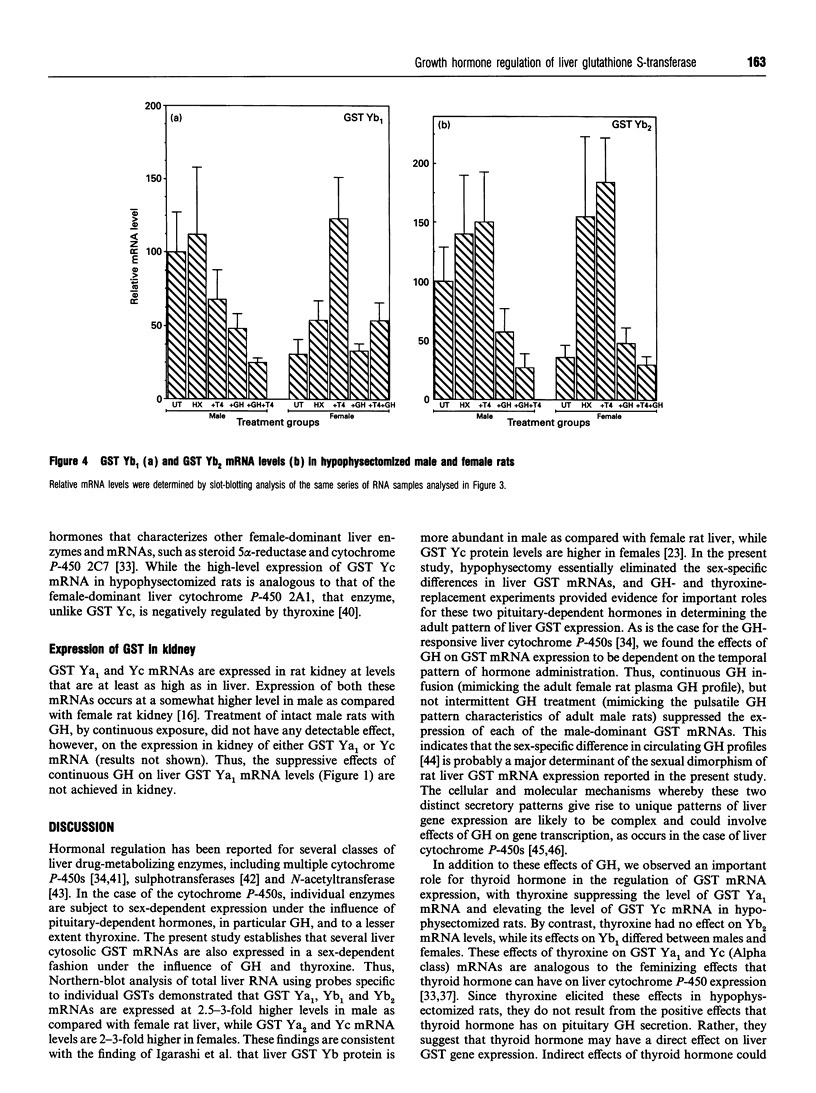
The sex-dependent expression and growth hormone (GH) regulation of rat liver glutathione S-transferase (GST) was examined using oligonucleotide probes that distinguish between closely related class Alpha (Ya1, Ya2, Yc) and class Mu (Yb1, Yb2, Yb3) GST mRNAs [Waxman, Sundseth, Srivastava and Lapenson (1992) Cancer Res. 52, 5797-5802]. Northern-blot analysis revealed that the steady-state levels of GST Ya1, Yb1 and Yb2 mRNAs are 2.5-3-fold higher in male as compared with female rat liver. In contrast, GST Yc and Ya2 mRNAs were expressed at a 2-3-fold higher level in female rat liver. Microsomal GST mRNA did not exhibit significant sex-dependent differences in rat liver. Treatment of male rats with GH by continuous infusion suppressed expression of the male-dominant GST Ya1, Yb1 and Yb2 mRNAs to levels at or below those found in female rat liver. This suppressive effect of GH was liver-specific, insofar as GH treatment did not alter kidney GST Ya1 mRNA levels. Hypophysectomy increased expression of the male-dominant GSTs, particularly in female rats (e.g. 8-fold elevation of GST Ya1 mRNA). GST Yc mRNA was increased approx. 2-fold in hypophysectomized males, indicating that this mRNA is subject to negative regulation by one or more pituitary-dependent factors. Continuous GH treatment of the hypophysectomized rats suppressed the expression of mRNA of GSTs Ya1, Yb1 and Yb2 when given as a continuous infusion, but not when given by an intermittent (twice daily) GH-injection schedule. Combination of continuous exposure to GH with thyroxine treatment resulted in a more complete suppression of GSTs Ya1, Yb1 and Yb2. In contrast, thyroxine increased the expression of GST Yc in hypophysectomized rats. These studies establish that several Alpha and Mu class GSTs are expressed in a sex-dependent fashion in adult rat liver, where they are regulated by multiple pituitary-dependent hormones through pretranslational mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovitz M., Listowsky I. Developmental regulation of glutathione S-transferases. Xenobiotica. 1988 Nov;18(11):1249–1254. doi: 10.3109/00498258809042248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton M. G., Colvin O. M., Hilton J. Specificity of isozymes of murine hepatic glutathione S-transferase for the conjugation of glutathione with L-phenylalanine mustard. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2410–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chengelis C. P. Age- and sex-related changes in epoxide hydrolase, UDP-glucuronosyl transferase, glutathione S-transferase, and PAPS sulphotransferase in Sprague-Dawley rats. Xenobiotica. 1988 Nov;18(11):1225–1237. doi: 10.3109/00498258809042246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaccio P. J., Tew K. D., LaCreta F. P. The spontaneous and glutathione S-transferase-mediated reaction of chlorambucil with glutathione. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(8):279–285. doi: 10.3727/095535490820874263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulder C. G., Hirrell P. A., Hume R., Strange R. C. Studies of the development of basic, neutral and acidic isoenzymes of glutathione S-transferase in human liver, adrenal, kidney and spleen. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):221–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2410221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. M., Hait W. N., Matlin S. A., Benz C. C. Modulation of resistance to alkylating agents in cancer cell by gossypol enantiomers. Cancer Lett. 1991 Jan;56(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(91)90198-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita S., Kitagawa H., Ishizawa H., Suzuki T., Kitani K. Age-associated alterations in hepatic glutathione-S-transferase activities. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 1;34(21):3891–3894. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. D., Kerr L. A., Harrison D. J., Cronshaw A. D., Ross A. G., Neal G. E. Preferential over-expression of the class alpha rat Ya2 glutathione S-transferase subunit in livers bearing aflatoxin-induced pre-neoplastic nodules. Comparison of the primary structures of Ya1 and Ya2 with cloned class alpha glutathione S-transferase cDNA sequences. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):295–302. doi: 10.1042/bj2680295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi T., Irokawa N., Ono S., Ohmori S., Ueno K., Kitagawa H., Satoh T. Difference in the effects of phenobarbital and 3-methylcholanthrene treatment on subunit composition of hepatic glutathione S-transferase in male and female rats. Xenobiotica. 1987 Feb;17(2):127–137. doi: 10.3109/00498258709043923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi T., Satoh T. Sex and species differences in glutathione S-transferase activities. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 1989;7(2-3):191–212. doi: 10.1515/dmdi.1989.7.2-3.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Edén S., Isaksson O. Sexual dimorphism in the control of growth hormone secretion. Endocr Rev. 1985 Spring;6(2):128–150. doi: 10.1210/edrv-6-2-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson J. O., Frohman L. A. Differential effects of neonatal and adult androgen exposure on the growth hormone secretory pattern in male rats. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato R., Yamazoe Y., Shimada M., Murayama N., Kamataki T. Effect of growth hormone and ectopic transplantation of pituitary gland on sex-specific forms of cytochrome P-450 and testosterone and drug oxidations in rat liver. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):895–902. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamartiniere C. A. The hypothalamic--hypophyseal--gonadal regulation of hepatic glutathione S-transferases in the rat. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):211–217. doi: 10.1042/bj1980211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc G. A., Sundseth S. S., Weber G. F., Waxman D. J. Platinum anticancer drugs modulate P-450 mRNA levels and differentially alter hepatic drug and steroid hormone metabolism in male and female rats. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):540–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc G. A., Waxman D. J. Feminization of rat hepatic P-450 expression by cisplatin. Evidence for perturbations in the hormonal regulation of steroid-metabolizing enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15732–15739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Mayer R. D. Inhibition of testicular cytochrome P-450-dependent steroid biosynthesis by cis-platinum. Reversal by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6063–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Sluss P. M., Iscan M. cis-platinum-mediated decrease in serum testosterone is associated with depression of luteinizing hormone receptors and cytochrome P-450scc in rat testis. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2398–2406. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankowitz L., Castro V. M., Mannervik B., Rydström J., DePierre J. W. Increase in the amount of glutathione transferase 4-4 in the rat adrenal gland after hypophysectomy and down-regulation by subsequent treatment with adrenocorticotrophic hormone. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):147–154. doi: 10.1042/bj2650147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Alin P., Guthenberg C., Jensson H., Tahir M. K., Warholm M., Jörnvall H. Identification of three classes of cytosolic glutathione transferase common to several mammalian species: correlation between structural data and enzymatic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7202–7206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Danielson U. H. Glutathione transferases--structure and catalytic activity. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(3):283–337. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Coles B., Pemble S. E., Gilmore K. S., Fraser G. M., Ketterer B. Theta, a new class of glutathione transferases purified from rat and man. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2740409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. T., MacGeoch C., Gustafsson J. A. Hormonal and developmental regulation of expression of the hepatic microsomal steroid 16 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 apoprotein in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11895–11898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. S., Cowan K. H. Glutathione S-transferases and drug resistance. Cancer Cells. 1990 Jan;2(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradelo J. C., Waxman M. J., Throne B. J., Beller T. A., Kopecky W. J. Endobronchial irradiation with 192Ir in the treatment of malignant endobronchial obstruction. Chest. 1992 Oct;102(4):1072–1074. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.4.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Reinhart J., Sisk S. C., Anderson K. S., Adler P. N. Tissue-specific induction of murine glutathione transferase mRNAs by butylated hydroxyanisole. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13324–13332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemble S. E., Taylor J. B. An evolutionary perspective on glutathione transferases inferred from class-theta glutathione transferase cDNA sequences. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 1;287(Pt 3):957–963. doi: 10.1042/bj2870957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Lu A. Y. Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure, regulation, and biological function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:743–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Telakowski-Hopkins C. A., Ding G. J., Argenbright L., Lu A. Y. Rat liver glutathione S-transferases. Complete nucleotide sequence of a glutathione S-transferase mRNA and the regulation of the Ya, Yb, and Yc mRNAs by 3-methylcholanthrene and phenobarbital. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5182–5188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram P. A., Waxman D. J. Hepatic P450 expression in hypothyroid rats: differential responsiveness of male-specific P450 forms 2a (IIIA2), 2c (IIC11), and RLM2 (IIA2) to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):13–20. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram P. A., Waxman D. J. Pretranslational control by thyroid hormone of rat liver steroid 5 alpha-reductase and comparison to the thyroid dependence of two growth hormone-regulated CYP2C mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19223–19229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabry I., Reiter R. J. Neither prolactin nor growth hormone restore the nocturnal rise in pineal N-acetyltransferase activity or melatonin content in hypophysectomized rats. Experientia. 1988 Jun 15;44(6):509–511. doi: 10.1007/BF01958931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal S. S., Saxena M., Awasthi S., Ahmad H., Sharma R., Awasthi Y. C. Gender related differences in the expression and characteristics of glutathione S-transferases of human colon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 15;1171(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90135-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Evans C. G., Doane-Setzer P., Castro V. M., Tahir M. K., Mannervik B. Denitrosation of 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea by class mu glutathione transferases and its role in cellular resistance in rat brain tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2621–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staffas L., Mankowitz L., Söderström M., Blanck A., Porsch-Hällström I., Sundberg C., Mannervik B., Olin B., Rydström J., DePierre J. W. Further characterization of hormonal regulation of glutathione transferase in rat liver and adrenal glands. Sex differences and demonstration that growth hormone regulates the hepatic levels. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):65–72. doi: 10.1042/bj2860065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundseth S. S., Alberta J. A., Waxman D. J. Sex-specific, growth hormone-regulated transcription of the cytochrome P450 2C11 and 2C12 genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3907–3914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundseth S. S., Waxman D. J. Sex-dependent expression and clofibrate inducibility of cytochrome P450 4A fatty acid omega-hydroxylases. Male specificity of liver and kidney CYP4A2 mRNA and tissue-specific regulation by growth hormone and testosterone. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3915–3921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tee L. B., Gilmore K. S., Meyer D. J., Ketterer B., Vandenberghe Y., Yeoh G. C. Expression of glutathione S-transferase during rat liver development. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):209–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2820209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew K. D., Bomber A. M., Hoffman S. J. Ethacrynic acid and piriprost as enhancers of cytotoxicity in drug resistant and sensitive cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3622–3625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Glutathione S-transferases: role in alkylating agent resistance and possible target for modulation chemotherapy--a review. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6449–6454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., LeBlanc G. A., Morrissey J. J., Staunton J., Lapenson D. P. Adult male-specific and neonatally programmed rat hepatic P-450 forms RLM2 and 2a are not dependent on pulsatile plasma growth hormone for expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11396–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Morrissey J. J., LeBlanc G. A. Female-predominant rat hepatic P-450 forms j (IIE1) and 3 (IIA1) are under hormonal regulatory controls distinct from those of the sex-specific P-450 forms. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):2954–2966. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-6-2954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Ram P. A., Notani G., LeBlanc G. A., Alberta J. A., Morrissey J. J., Sundseth S. S. Pituitary regulation of the male-specific steroid 6 beta-hydroxylase P-450 2a (gene product IIIA2) in adult rat liver. Suppressive influence of growth hormone and thyroxine acting at a pretranslational leve;. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):447–454. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J. Rat hepatic P450IIA and P450IIC subfamily expression using catalytic, immunochemical, and molecular probes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:249–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06095-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Sundseth S. S., Srivastava P. K., Lapenson D. P. Gene-specific oligonucleotide probes for alpha, mu, pi, and microsomal rat glutathione S-transferases: analysis of liver transferase expression and its modulation by hepatic enzyme inducers and platinum anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 15;52(20):5797–5802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Gong D., Murayama N., Abu-Zeid M., Kato R. Regulation of hepatic cortisol sulfotransferase in rats by pituitary growth hormone. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 May;35(5):707–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe Y., Ling X., Murayama N., Gong D., Nagata K., Kato R. Modulation of hepatic level of microsomal testosterone 7 alpha-hydroxylase, P-450a (P450IIA), by thyroid hormone and growth hormone in rat liver. J Biochem. 1990 Oct;108(4):599–603. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaphiropoulos P. G., Mode A., Norstedt G., Gustafsson J. A. Regulation of sexual differentiation in drug and steroid metabolism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]