Abstract
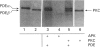
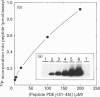
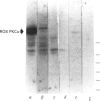
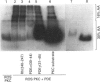
The cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) of retinal rods plays a key role in phototransduction and consists of two catalytic subunits (PDE alpha and PDE beta) and two identical inhibitory subunits (PDE gamma). Here we report that PDE alpha and PDE gamma are phosphorylated by protein kinase(s) C (PKC) from brain and rod outer segments (ROS). These same two types of PKC also phosphorylate PDE alpha in trypsin-activated PDE (without PDE gamma). In contrast, cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit phosphorylates both PDE alpha and PDE beta, but not PDE gamma. This kinase does not phosphorylate trypsin-activated PDE. The synthetic peptides AKVISNLLGPREAAV (PDE alpha 30-44) and KQRQTRQFKSKPPKK (PDE gamma 31-45) inhibited phosphorylation of PDE by PKC from ROS. These data suggest that sites (at least one for each subunit) for phosphorylation of PDE by PKC are localized in these corresponding regions of PDE alpha and PDE gamma. Isoenzyme-specific PKC antibodies against peptides unique to the alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon and zeta isoforms of protein kinase C were used to show that a major form of PKC in ROS is PKC alpha. However, other minor forms were also present.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anant J. S., Ong O. C., Xie H. Y., Clarke S., O'Brien P. J., Fung B. K. In vivo differential prenylation of retinal cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase catalytic subunits. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):687–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehr W., Devlin M. J., Applebury M. L. Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11669–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder B. M., Brewer E., Bownds M. D. Stimulation of protein phosphorylations in frog rod outer segments by protein kinase activators. Suppression of light-induced changes in membrane current and cGMP by protein kinase C activators. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8857–8864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Rubin L. J., Ghalayini A. J., Tarver A. P., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Anderson R. E. myo-Inositol polyphosphate may be a messenger for visual excitation in Limulus photoreceptors. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):160–163. doi: 10.1038/311160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catty P., Deterre P. Activation and solubilization of the retinal cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase by limited proteolysis. Role of the C-terminal domain of the beta-subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):263–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das N. D., Yoshioka T., Samuelson D., Cohen R. J., Shichi H. Immunochemical evidence for the light-regulated modulation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate in rat photoreceptor cells. Cell Struct Funct. 1987 Oct;12(5):471–481. doi: 10.1247/csf.12.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deterre P., Bigay J., Forquet F., Robert M., Chabre M. cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods is regulated by two inhibitory subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowles C., Akhtar M., Cohen P. Interplay of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in vision: protein phosphatases of bovine rod outer segments. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9385–9391. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehm B. D., Mc Connell D. G. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phospholipase C in bovine rod outer segments. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5447–5452. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghalayini A., Anderson R. E. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate: light-mediated breakdown in the vertebrate retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):503–506. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91582-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. J. An apparatus for simultaneous manual solid-phase synthesis of multiple peptide analogs. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90235-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. S., Charbonneau H., Beavo J. A. Purification of calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:543–557. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Amakawa T. Light-mediated breakdown of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate in isolated rod outer segments of frog photoreceptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):954–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Lin G. Y., Matsumoto H., Yamazaki A. Phosphatidylinositol-stimulated phosphorylation of an inhibitory subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase in vertebrate rod photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4333–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi F., Sumi M., Amakawa T. Phosphatidylinositol stimulates phosphorylation of protein components I and II in rod outer segments of frog photoreceptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermolin J., Karell M. A., Hamm H. E., Bownds M. D. Calcium and cyclic GMP regulation of light-sensitive protein phosphorylation in frog photoreceptor membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):633–655. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Huang F. L., Nakabayashi H., Yoshida Y. Biochemical characterization of rat brain protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14839–14845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Purification and characterization of the gamma regulatory subunit of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from retinal rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11094–11099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin by protein kinase C in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4749–4757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Purification of protein kinase C from bovine rod outer segments. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(6):579–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid R. L., Manganiello V. C. Assay of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase using radiolabeled and fluorescent substrates. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:457–470. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. VI. Isolation and partial purification of a protein kinase activated by guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 25;245(10):2493–2498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin V. M., Gubanov V. V., Khramtsov N. V., Vasilevskaia I. A., Atabekova N. V., Muradov Kh G., Shuvaeva T. M., Surina E. A., Zagranichnyi V. E., Li T. Fosfodiésteraza tsiklicheskogo GMP iz setchatki byka. Aninokislotnaia posledovatel'nost' beta-sub''edinitsy i nukleotidnaia posledovatel'nost' sootvetstvuiushchei kDNK. Bioorg Khim. 1990 Jan;16(1):118–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin V. M., Khramtsov N. V., Vasilevskaya I. A., Atabekova N. V., Muradov K. G., Gubanov V. V., Li T., Johnston J. P., Volpp K. J., Applebury M. L. Beta-subunit of bovine rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase. Comparison with the phosphodiesterase family. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12955–12959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin V. M., Udovichenko I. P., Bondarenko V. A., Yurovskaya A. A., Telnykh E. V., Skiba N. P. Site-directed mutagenesis of the inhibitory subunit of retinal rod cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. Biomed Sci. 1990 Mar;1(3):305–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lookhart G. L., Jones B. L., Cooper D. B., Hall S. B. A method for hydrolyzing and determining the amino acid compositions of picomole quantities of proteins in less than 3 hours. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1982 Dec;7(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(82)90032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makowske M., Ballester R., Cayre Y., Rosen O. M. Immunochemical evidence that three protein kinase C isozymes increase in abundance during HL-60 differentiation induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3402–3410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Baraban J. M., Keirns J. J., Boyce J. J., Bitensky M. W. Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. L., Fox D. A., Litman B. J. Amplification of phosphodiesterase activation is greatly reduced by rhodopsin phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):4983–4988. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. F., Cunnick J. M., Oppert B., Takemoto D. J. Interaction of the gamma-subunit of retinal rod outer segment phosphodiesterase with transducin. Use of synthetic peptides as functional probes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11671–11681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. C., Williams D. S. Involvement of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17725–17728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogita K., Koide H., Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The heterogeneity of protein kinase C in signal transduction cascade. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:218–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong O. C., Ota I. M., Clarke S., Fung B. K. The membrane binding domain of rod cGMP phosphodiesterase is posttranslationally modified by methyl esterification at a C-terminal cysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppert B., Cunnick J. M., Hurt D., Takemoto D. J. Identification of the retinal cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase inhibitory gamma-subunit interaction sites on the catalytic alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16607–16613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Lipkin V. M., Kumarev V. P., Gubanov V. V., Khramtsov N. V., Akhmedov N. B., Zagranichny V. E., Muradov K. G. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase from cattle retina. Amino acid sequence of the gamma-subunit and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):288–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80830-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Hargrave P. A., McDowell J. H., Ingebritsen T. S. The catalytic subunit of phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates phosphoopsin. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):415–419. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papermaster D. S., Dreyer W. J. Rhodopsin content in the outer segment membranes of bovine and frog retinal rods. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2438–2444. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polans A. S., Hermolin J., Bownds M. D. Light-induced dephosphorylation of two proteins in frog rod outer segments: influence of cyclic nucleotides and calcium. J Gen Physiol. 1979 Nov;74(5):595–613. doi: 10.1085/jgp.74.5.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Visual excitation and recovery. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10711–10714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter M. A modified ELISA technique for anti-hapten antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 27;53(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. J., Applebury M. L. Methylation of proteins in photoreceptor rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10599–10605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szuts E. Z., Wood S. F., Reid M. S., Fein A. Light stimulates the rapid formation of inositol trisphosphate in squid retinas. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bj2400929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto D. J., Hurt D., Oppert B., Cunnick J. Domain mapping of the retinal cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase gamma-subunit. Function of the domains encoded by the three exons of the gamma-subunit gene. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):637–643. doi: 10.1042/bj2810637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P., Findlay J. B. Phosphorylation of ovine rhodopsin. Identification of the phosphorylated sites. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 15;220(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2200773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolbring G., Cook N. J. Rapid purification and characterization of protein kinase C from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Hart C. E., Mazzei G. J., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F. Distribution of protein kinase C immunoreactivity in rat retina. Histochem J. 1988 Feb;20(2):63–68. doi: 10.1007/BF01746605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zozulya S. A., Gurevich V. V., Zvyaga T. A., Shirokova E. P., Dumler I. L., Garnovskaya M. N., Natochin MYu, Shmukler B. E., Badalov P. R. Functional expression in vitro of bovine visual rhodopsin. Protein Eng. 1990 Apr;3(5):453–458. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]