Abstract
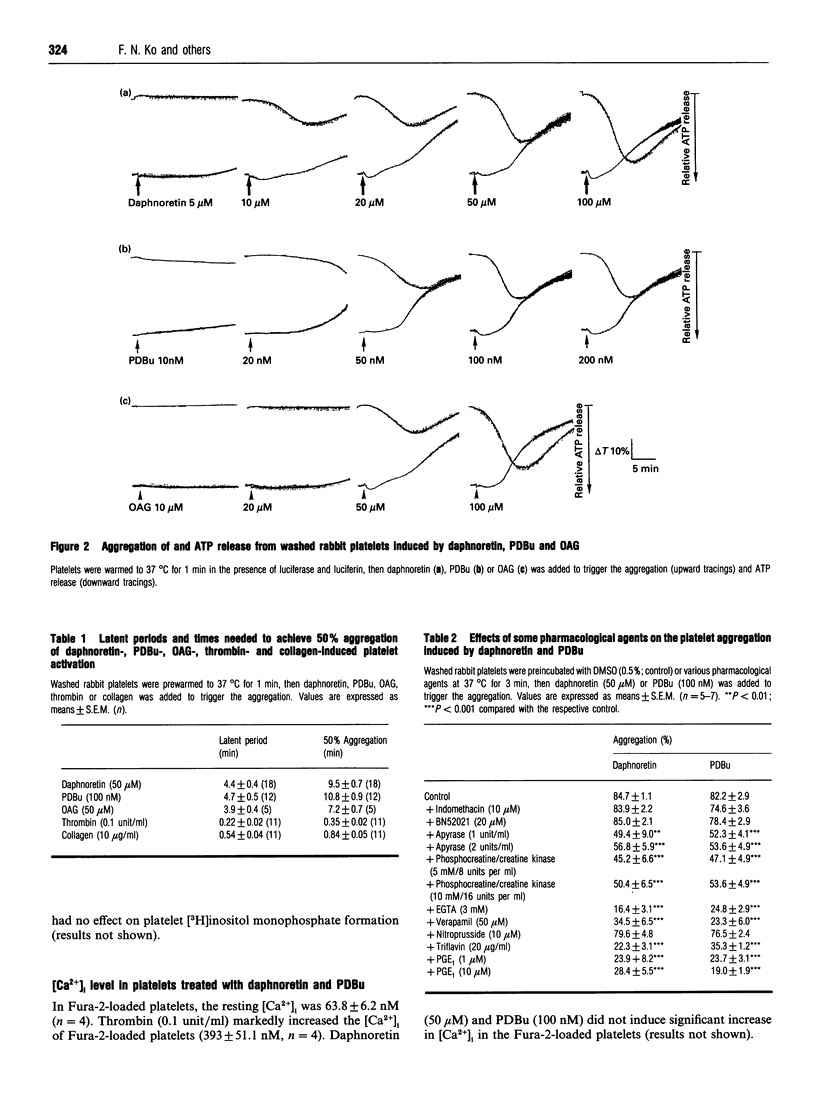
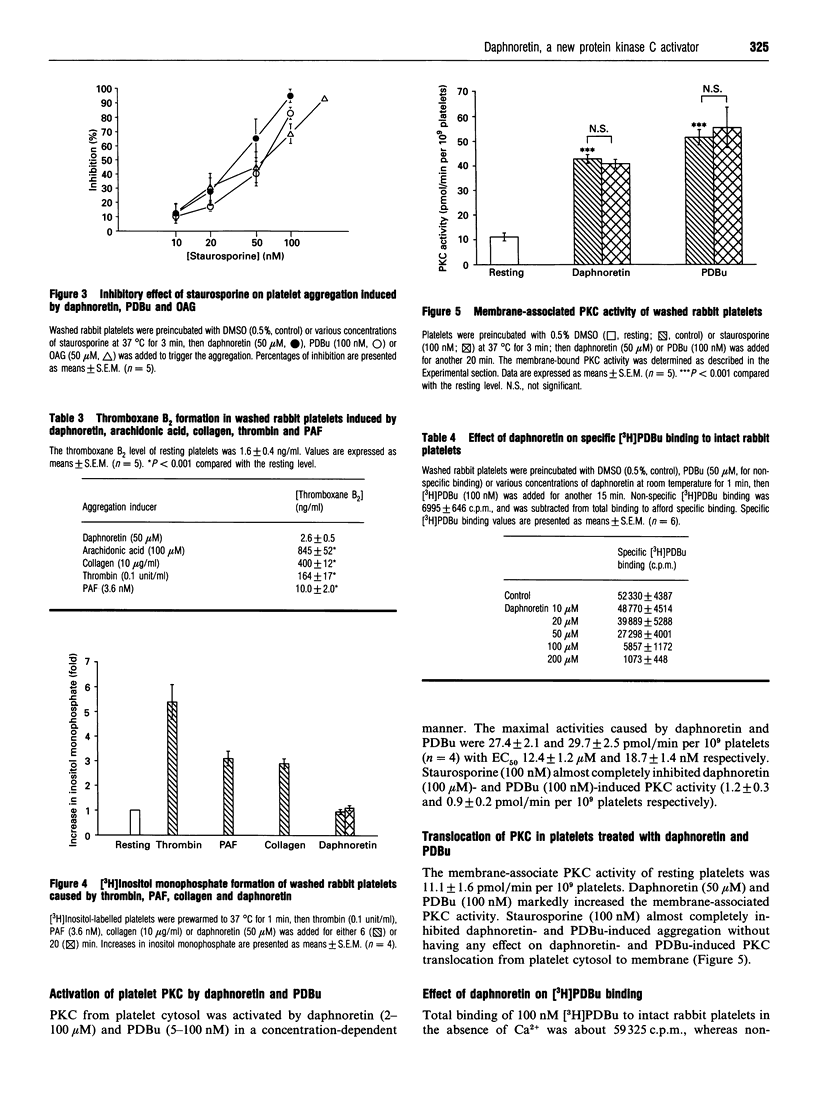
Daphnoretin, a biologically active principle isolated from Wikstroemia indica C.A. Mey., caused platelet aggregation in washed rabbit platelets, platelet-rich plasma and whole blood. The aggregation of and ATP release from platelets induced by daphnoretin were similar to phorbol ester- and diacylglycerol-induced aggregation and release. The EC50 values of daphnoretin-, phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu)- and 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol (OAG)-induced platelet aggregation in washed rabbit platelets were 17.2 +/- 2.8 microM, 20.6 +/- 2.1 nM and 38.6 +/- 1.7 microM respectively. Platelet aggregation induced by daphnoretin and PDBu was not inhibited by indomethacin, BN52021 or sodium nitroprusside. ADP-scavenging systems, apyrase and phosphocreatine/creatine kinase, showed weak inhibition of the aggregation, and EGTA, triflavin, verapamil and prostaglandin E1 markedly inhibited the aggregation. Staurosporine, a potent protein kinase C inhibitor, suppressed daphnoretin-, PDBu- and OAG-induced aggregation and ATP release in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC50 values of staurosporine on daphnoretin (50 microM)-, PDBu (100 nM)- and OAG (50 microM)-induced aggregation were 37.7 +/- 8.3, 52.2 +/- 6.3 and 42.8 +/- 8.9 nM respectively. Daphnoretin did not cause significant thromboxane B2 formation in rabbit platelets. Neither daphnoretin nor PDBu caused [3H]inositol monophosphate formation or an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration in myo-[3H]inositol-labelled and Fura-2-loaded platelets. Platelet cytosolic protein kinase C was activated by daphnoretin and PDBu in a concentration-dependent manner with an EC50 of 12.4 +/- 1.2 microM and 18.7 +/- 1.4 nM respectively. Membrane-associated protein kinase C activity was increased by either daphnoretin or PDBu. [3H]PDBu binding to washed rabbit platelets was inhibited by daphnoretin in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 45.2 +/- 5.2 microM. These results indicate that daphnoretin is a protein kinase C activator in rabbit platelets.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball G., Brereton G. G., Fulwood M., Ireland D. M., Yates P. Effet of prostaglandin E1 alone and in combination with theophylline or aspirin on collagen-induced platelet aggregation and on platelet nucleotides including adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):709–718. doi: 10.1042/bj1200709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech P., Cohen L. E., Szklarek D., Lehrer R. I. High- and low-affinity receptors regulate platelet responses to phorbol diesters and teleocidin. Thromb Res. 1987 Mar 15;45(6):827–837. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(87)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech P., Rosove M. H., Harwig S. S., Lehrer R. I. Effects of phorbol diesters and teleocidin on normal human platelets. Thromb Res. 1986 May 1;42(3):383–396. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90267-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daigen A., Akiyama K., Otsuki S. Long-lasting change in the membrane-associated protein kinase C activity in the hippocampal kindled rat. Brain Res. 1991 Apr 5;545(1-2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling J. G., Vandenbark G. R., Kuhn L. J., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerols mimic phorbol diester induction of leukemic cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne P., Schachter M., Fabbro D., Miles C. M., Sever P. S. Calcium transients in human platelets monitored by aequorin, fura-2 and quin-2: effects of protein kinase C activation and inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M., Detwiler T. C. The effects of lithium on platelet phosphoinositide metabolism. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 15;236(3):895–901. doi: 10.1042/bj2360895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Sheu J. R., Teng C. M. Mechanism of action of a potent antiplatelet peptide, triflavin from Trimeresurus flavoviridis snake venom. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Oct 1;66(4):489–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., James M. L., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of a specific phorbol ester aporeceptor in mouse brain cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake R., Tanaka Y., Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of protein kinase C by non-phorbol tumor promoter, mezerein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka M., Nishikawa M., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Phorbol ester-induced activation of human platelets is associated with protein kinase C phosphorylation of myosin light chains. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):490–492. doi: 10.1038/306490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. Stimulation of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat kidney mediates increased inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):367–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerschke E. I. The platelet fibrinogen receptor. Semin Hematol. 1985 Oct;22(4):241–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platelet aggregation: Part II Some results from a new method of study. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;15(5):452–455. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.5.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J. Thrombin and ionomycin can raise platelet cytosolic Ca2+ to micromolar levels by discharge of internal Ca2+ stores: studies using fura-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Ca2+ mobilization primes protein kinase C in human platelets. Ca2+ and phorbol esters stimulate platelet aggregation and secretion synergistically through protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Inoue M., Nishizuka Y. Studies on a cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase and its proenzyme in mammalian tissues. I. Purification and characterization of an active enzyme from bovine cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7603–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P. M., Murray A. W. Modulation of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in platelets treated with a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley P. M., Murray A. W. Modulation of Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in platelets treated with a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng C. M., Ko F. N. Comparison of the platelet aggregation induced by three thrombin-like enzymes of snake venoms and thrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Apr 8;59(2):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerols do not potentiate the action of phospholipases A2 and C in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 31;121(1):386–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90734-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


