Abstract
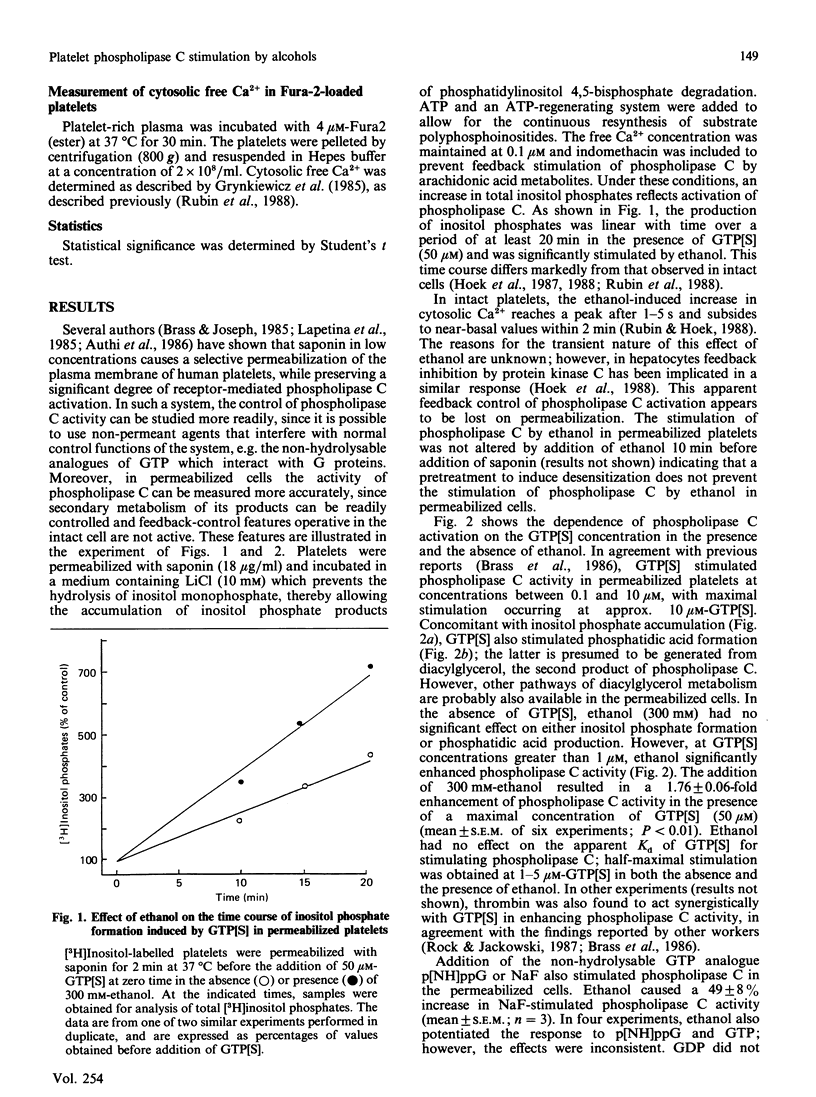
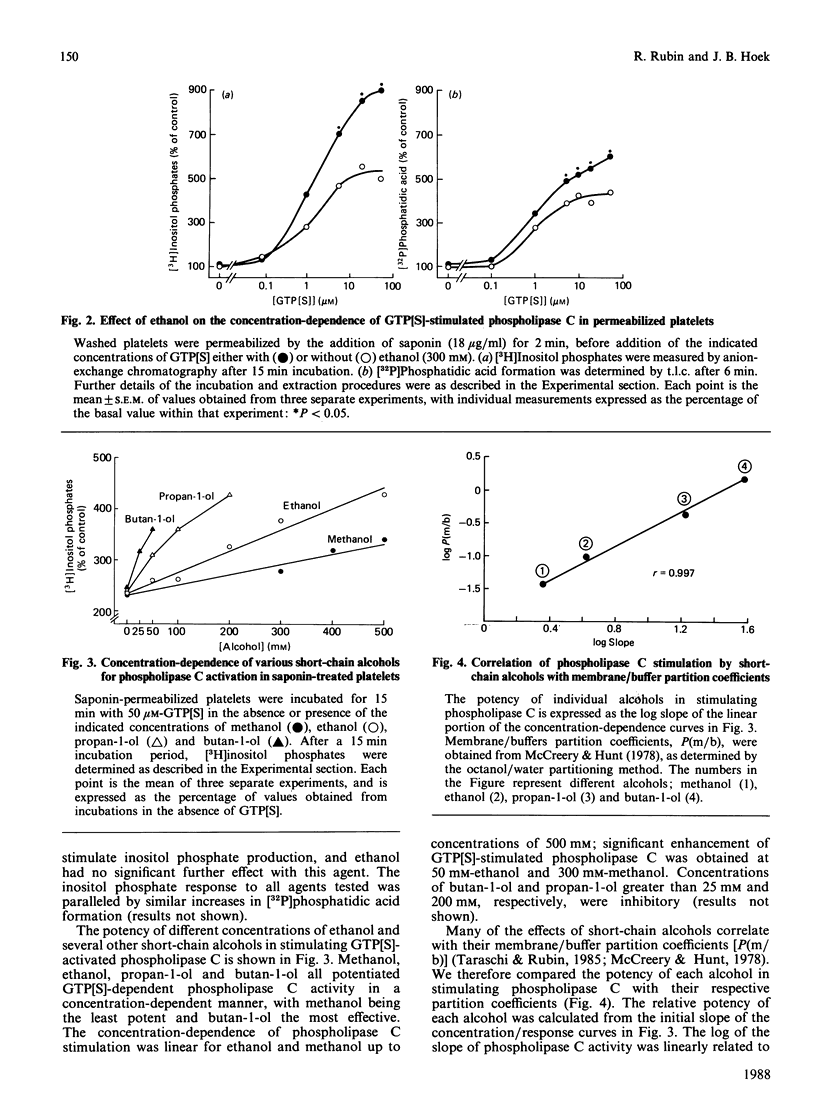
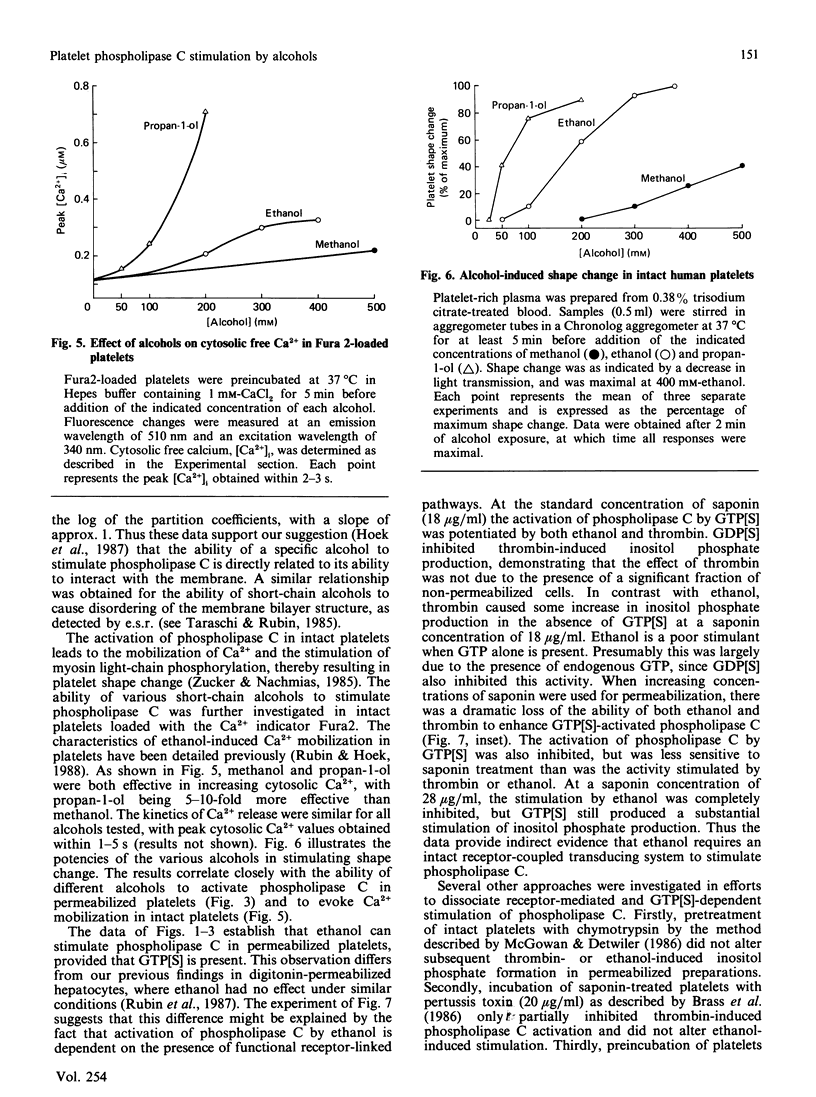
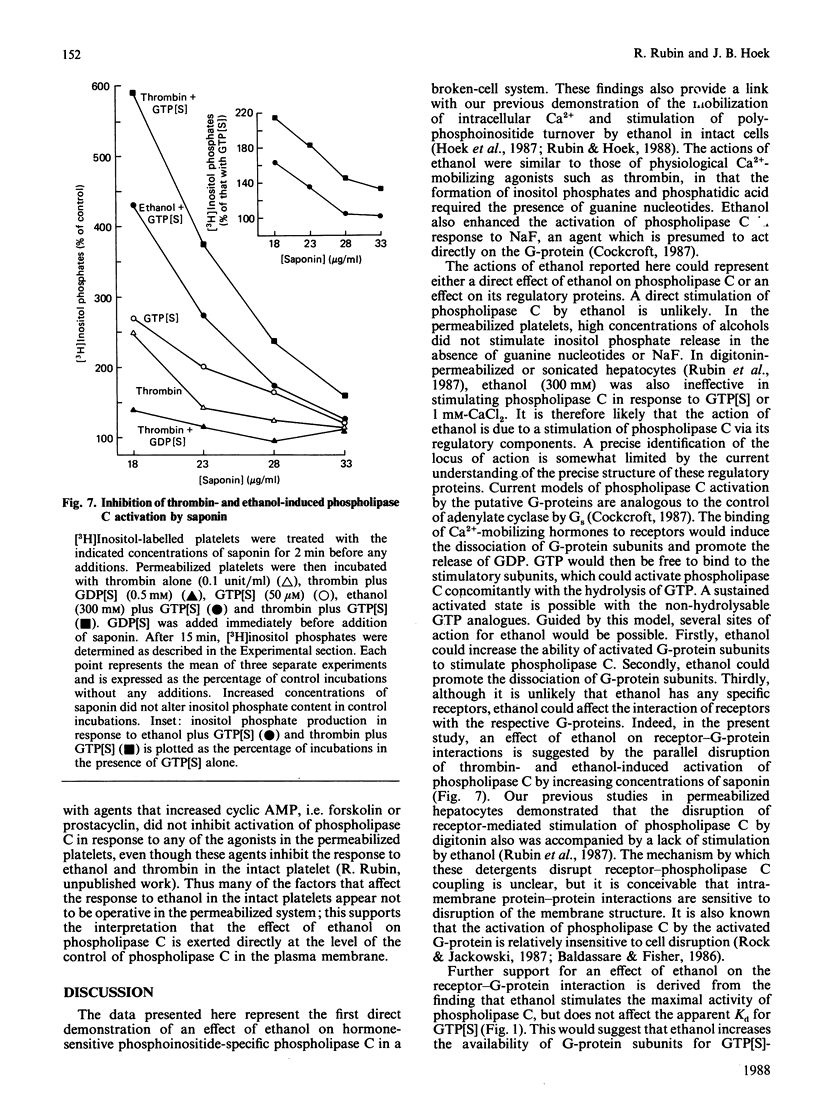
In previous studies we have demonstrated that ethanol activates hormone-sensitive phospholipase C in intact human platelets, resulting in the mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ and platelet shape change. The present study aims to localize further this effect of ethanol by examining its interaction with the regulation of phospholipase C in a permeabilized cell system. In platelets permeabilized with a minimal concentration (18 micrograms/ml) of saponin, ethanol by itself did not activate phospholipase C. However, ethanol potentiated the activation of phospholipase C in response to the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GTP[S] (guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate), an effect similar to that observed with thrombin. Ethanol also potentiated the response to fluoride, which acts directly on G-proteins. Other short-chain alcohols also stimulated phospholipase C in a synergistic manner with GTP[S]. The ability of specific alcohols to stimulate phospholipase C was directly related to their respective lipid-solubilities, as determined by their partition coefficients. Moreover, the potencies of each alcohol correlated with their ability to elicit Ca2+ mobilization and shape change in intact platelets. These effects of ethanol were eliminated by a disruption of receptor-phospholipase C coupling induced by the addition of higher concentrations of saponin. These data indicate that the activation of phospholipase C by ethanol may occur by affecting protein-protein interactions in the signal-transduction complex involving GTP-binding regulatory proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Authi K. S., Evenden B. J., Crawford N. Metabolic and functional consequences of introducing inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate into saponin-permeabilized human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):707–718. doi: 10.1042/bj2330707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Fisher G. J. Regulation of membrane-associated and cytosolic phospholipase C activities in human platelets by guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11942–11944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Differential effects of phorbol ester on phenylephrine and vasopressin-induced Ca2+ mobilization in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3281–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):487–493. doi: 10.1038/300487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Rubin R., Thomas A. P. Ethanol-induced phospholipase C activation is inhibited by phorbol esters in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):865–871. doi: 10.1042/bj2510865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Thomas A. P., Rubin R., Rubin E. Ethanol-induced mobilization of calcium by activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C in intact hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):682–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Wirtz K. W., Schotman P., Gispen W. H. Pituitary hormones influence polyphosphoinositide metabolism in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80897-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Effect of pertussis toxin on the phosphodiesteratic cleavage of the polyphosphoinositides by guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate and thrombin in permeabilized human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 19;884(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Silió J., Ruggiero M. Thrombin induces serotonin secretion and aggregation independently of inositol phospholipids hydrolysis and protein phosphorylation in human platelets permeabilized with saponin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7078–7083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthin G. R., Tabakoff B. Activation of adenylate cyclase by alcohols requires the nucleotide-binding protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Mar;228(3):579–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon R. C., McComb J. A., Schreurs J., Goldstein D. B. A relationship between alcohol intoxication and the disordering of brain membranes by a series of short-chain alcohols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):669–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreery M. J., Hunt W. A. Physico-chemical correlates of alcohol intoxication. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Jul;17(7):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan E. B., Detwiler T. C. Modified platelet responses to thrombin. Evidence for two types of receptors or coupling mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W. The nature of the site of general anesthesia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1985;27:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. O., Jackowski S. Thrombin- and nucleotide-activated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phospholipase C in human platelet membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5492–5498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Ponnappa B. C., Thomas A. P., Hoek J. B. Ethanol stimulates shape change in human platelets by activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):480–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R., Thomas A. P., Hoek J. B. Ethanol does not stimulate guanine nucleotide-induced activation of phospholipase C in permeabilized hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jul;256(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Neomycin inhibits inositol phosphate formation in human platelets stimulated by thrombin but not other agonists. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzdak P. D., Schwartz R. D., Skolnick P., Paul S. M. Ethanol stimulates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-mediated chloride transport in rat brain synaptoneurosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Rubin E. Effects of ethanol on the chemical and structural properties of biologic membranes. Lab Invest. 1985 Feb;52(2):120–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Marks J. S., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Quantitation and early kinetics of inositol lipid changes induced by vasopressin in isolated and cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5716–5725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. A non-disruptive technique for loading calcium buffers and indicators into cells. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):527–528. doi: 10.1038/290527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Nachmias V. T. Platelet activation. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):2–18. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


