Abstract
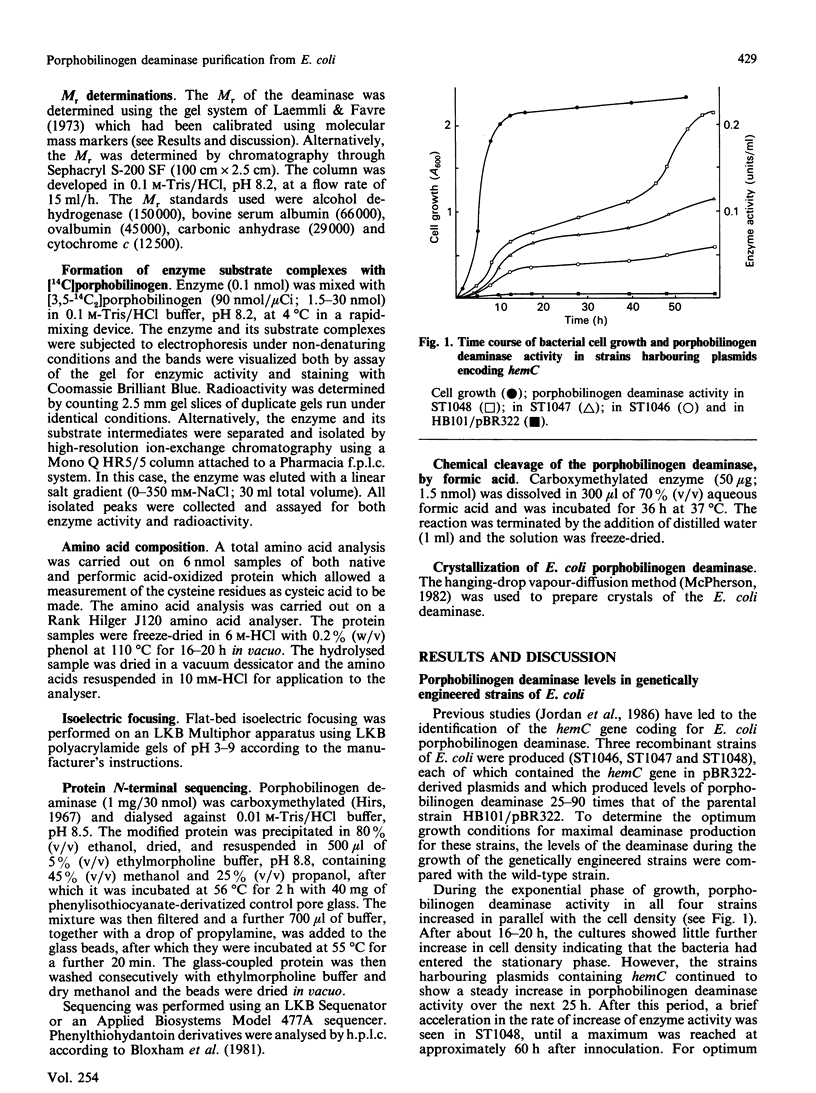
Porphobilinogen deaminase has been purified and crystallized from an overproducing recombinant strain of Escherichia coli harbouring a hemC-containing plasmid which has permitted the purification of milligram quantities of the enzyme. Determination of the Mr of the enzyme by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis (35,000) and gel filtration (32,000) agrees with the gene-derived Mr of 33,857. The enzyme has a Km of 19 +/- 7 microM, an isoelectric point of 4.5 and an N-terminal sequence NH2-MLDNVLRIAT. The substrate, porphobilinogen, binds to the active-site dipyrromethane cofactor to form three intermediate complexes: ES, ES2 and ES3. The gene-derived primary structure of the E. coli deaminase is compared with that derived from the cDNA of the human enzyme.
Full text
PDF

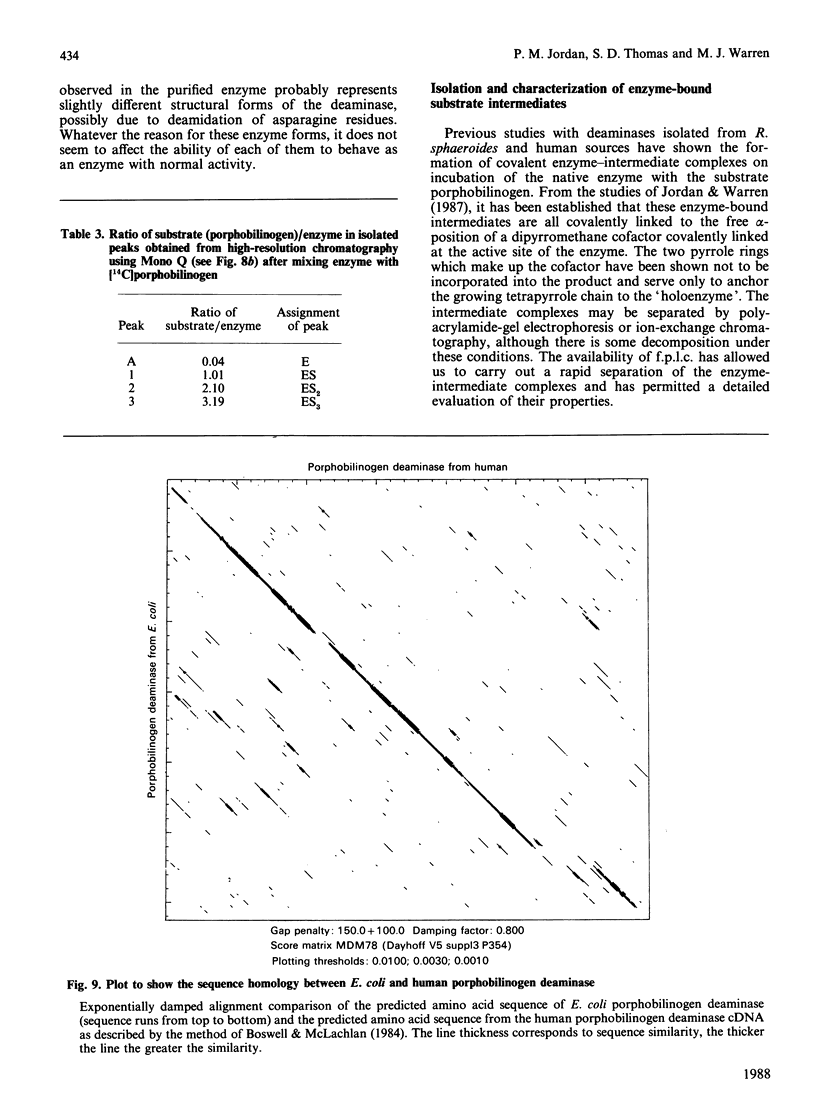

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. M., Desnick R. J. Purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthase from human erythrocytes. Identification of stable enzyme-substrate intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1993–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A., Jordan P. M., Seehra J. S. The isolation and characterization of catalytically competent porphobilinogen deaminase-intermediate complexes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 6;129(2):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80169-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloxham D. P., Parmelee D. C., Kumar S., Wade R. D., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Primary structure of porcine heart citrate synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5381–5385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell D. R., McLachlan A. D. Sequence comparison by exponentially-damped alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):457–464. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesareni G., Muesing M. A., Polisky B. Control of ColE1 DNA replication: the rop gene product negatively affects transcription from the replication primer promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6313–6317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. C., Neuberger A. Polypyrroles formed from porphobilinogen and amines by uroporphyrinogen synthetase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):471–492. doi: 10.1042/bj1330471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandchamp B., Romeo P. H., Dubart A., Raich N., Rosa J., Nordmann Y., Goossens M. Molecular cloning of a cDNA sequence complementary to porphobilinogen deaminase mRNA from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5036–5040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Abell C., Battersby A. R. Purification, N-terminal amino acid sequence and properties of hydroxymethylbilane synthase (porphobilinogen deaminase) from Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2400273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Bogorad L. The purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthases and uroporphyrinogen III cosynthase. Interactions between the enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 15;244:401–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb41545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Berry A. Mechanism of action of porphobilinogen deaminase. The participation of stable enzyme substrate covalent intermediates between porphobilinogen and the porphobilinogen deaminase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1950177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Shemin D. Purification and properties of uroporphyrinogen I synthetase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1019–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Warren M. J. Evidence for a dipyrromethane cofactor at the catalytic site of E. coli porphobilinogen deaminase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeper F. J. The biosynthesis of porphyrins, chlorophylls, and vitamin B12. Nat Prod Rep. 1985 Feb;2(1):19–47. doi: 10.52054/FVVO.16.2.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmer R., Bogorad L. A tetrapyrrylmethane intermediate in the enzymatic synthesis of uroporphyrinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):904–910. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. D., Jordan P. M. Nucleotide sequence of the hemC locus encoding porphobilinogen deaminase of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6215–6226. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. C., Morgan G. S., McDonald E., Battersby A. R. Purification of porphobilinogen deaminase from Euglena gracilis and studies of its kinetics. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):301–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1930301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]