Abstract
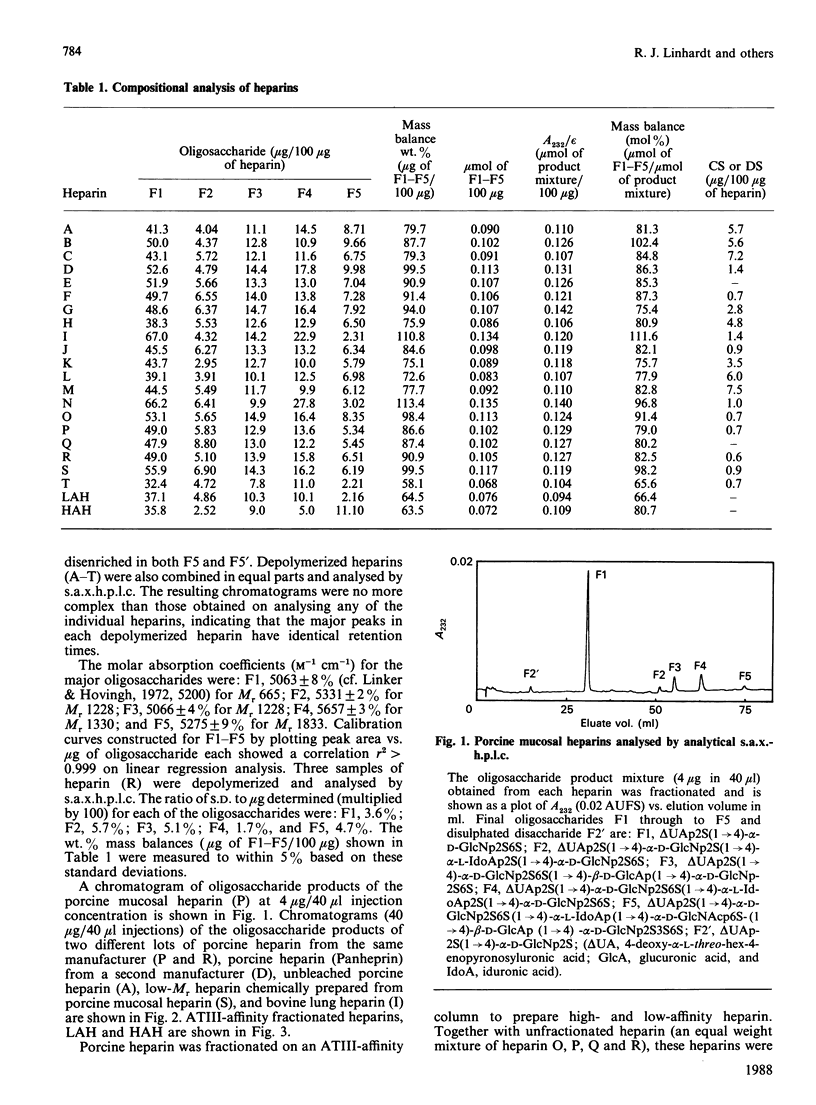
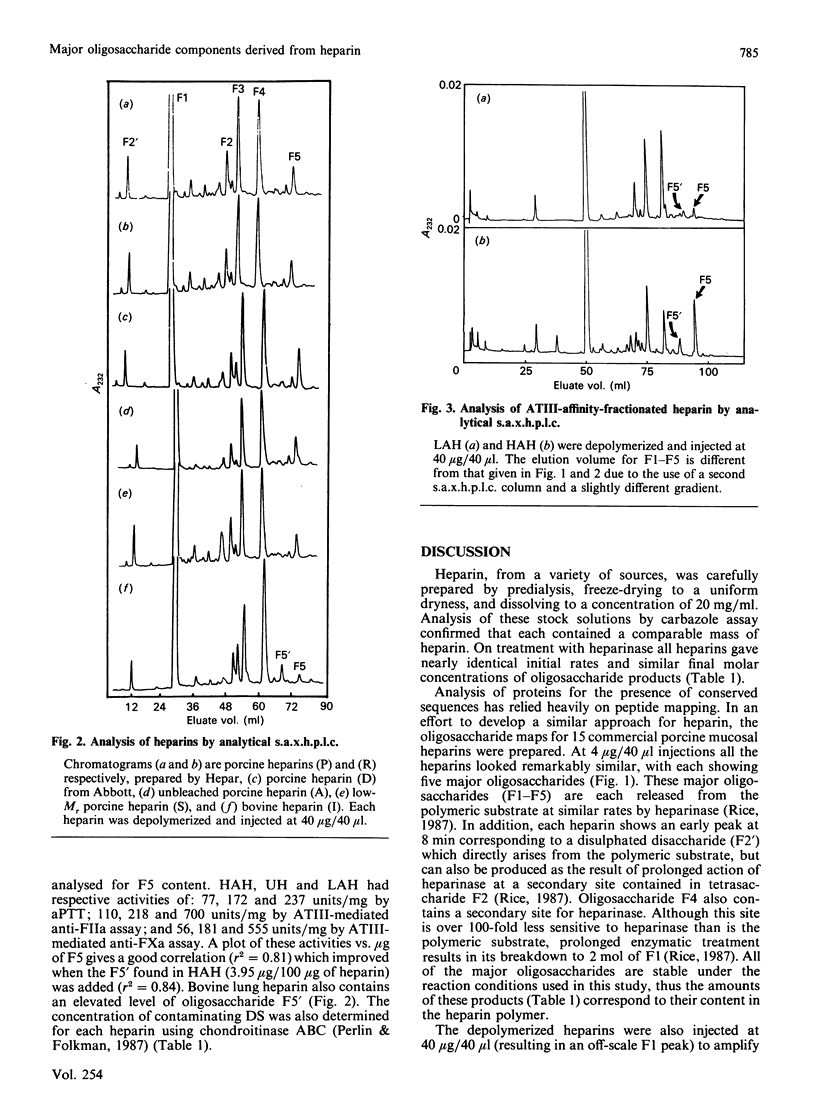
A new method of determining the oligosaccharide composition of commercial glycosaminoglycan heparin is described in which heparin was first depolymerized using heparin lyase (EC 4.2.2.7), and then analysed by a single h.p.l.c. step. All 20 of the porcine and bovine heparins examined were found to contain a small number of major oligosaccharide components, which on average comprised 86% of their mass. The five most abundant oligosaccharides have defined chemical structures. Although the relative abundance of oligosaccharides varied, the heparins examined were surprisingly similar. Porcine, bovine, low-Mr, and high and low antithrombin III (ATIII)-affinity heparins, however, each had distinctly different proportions of these major oligosaccharide components. The concentrations of one of these five oligosaccharides, containing a portion of the ATIII binding site, correlated with the anticoagulant activity of the ATIII-affinity-fractionated porcine-mucosal heparins from which it was derived. An additional oligosaccharide of undetermined structure was found in significant quantities in both bovine heparin and high ATIII-affinity porcine-mucosal heparin. The correlation between oligosaccharide concentration and anticoagulant activity suggests that the oligosaccharide is derived from a structural variant of the ATIII-binding site. Finally, for the heparins examined chondroitin/dermatan sulphate formed 0.6-7.4% of their mass.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atha D. H., Stephens A. W., Rosenberg R. D. Evaluation of critical groups required for the binding of heparin to antithrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski M. J., Conrad H. E. Structural characterization of the oligosaccharides formed by depolymerization of heparin with nitrous acid. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):356–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton J., Lewis W. E., Nieduszynski I. A., Phelps C. F. Fractionation of heparin using antithrombin III reversibly bound to concanavalin A-sepharose. Anal Biochem. 1981 Dec;118(2):388–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90598-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J., Noyes C. M., Church F. C. Reactive site peptide structural similarity between heparin cofactor II and antithrombin III. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2218–2225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovingh P., Piepkorn M., Linker A. Biological implications of the structural, antithrombin affinity and anticoagulant activity relationships among vertebrate heparins and heparan sulphates. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):573–581. doi: 10.1042/bj2370573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsson I., Lindahl U., Jensen J. W., Rodén L., Prihar H., Feingold D. S. Biosynthesis of heparin. Substrate specificity of heparosan N-sulfate D-glucuronosyl 5-epimerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1056–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques L. B. Heparin: an old drug with a new paradigm. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):528–533. doi: 10.1126/science.386509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L. The antithrombin-binding sequence in heparin. Identification of an essential 6-O-sulfate group. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9826–9830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt R. J., Grant A., Cooney C. L., Langer R. Differential anticoagulant activity of heparin fragments prepared using microbial heparinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7310–7313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt R. J., Merchant Z. M., Rice K. G., Kim Y. S., Fitzgerald G. L., Grant A. C., Langer R. Evidence of random structural features in the heparin polymer. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7805–7810. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhardt R. J., Rice K. G., Merchant Z. M., Kim Y. S., Lohse D. L. Structure and activity of a unique heparin-derived hexasaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14448–14454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker A., Hovingh P. Isolation and characterization of oligosaccharides obtained from heparin by the action of heparinase. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):563–568. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linker A., Hovingh P. Structural studies on heparin. Tetrasaccharides obtained by heparinase degradation. Carbohydr Res. 1984 Apr 2;127(1):75–94. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant Z. M., Kim Y. S., Rice K. G., Linhardt R. J. Structure of heparin-derived tetrasaccharides. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):369–377. doi: 10.1042/bj2290369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pejler G., Danielsson A., Björk I., Lindahl U., Nader H. B., Dietrich C. P. Structure and antithrombin-binding properties of heparin isolated from the clams Anomalocardia brasiliana and Tivela mactroides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11413–11421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin A. S., Sauriol F., Cooper B., Folkman J. Dermatan sulfate in pharmaceutical heparins. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Aug 4;58(2):792–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynertson R., Campbell P., Ford J. D., Jacobsson I., Rodén L., Thompson J. N. New oligosaccharides from heparin and heparan sulfate and their use as substrates for heparin-degrading enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7449–7459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice K. G., Rottink M. K., Linhardt R. J. Fractionation of heparin-derived oligosaccharides by gradient polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2440515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang V. C., Linhardt R. J., Bernstein H., Cooney C. L., Langer R. Purification and characterization of heparinase from Flavobacterium heparinum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1849–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


