Abstract
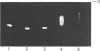
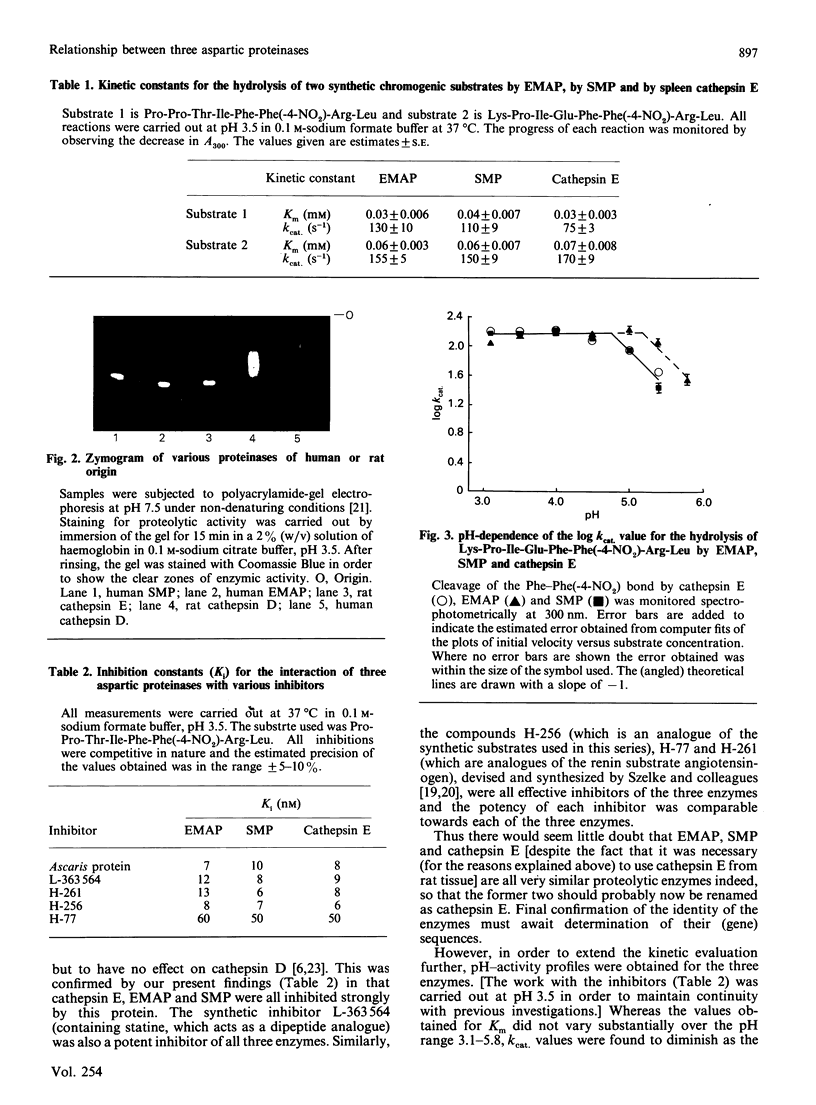
Three aspartic proteinases with similar Mr values (approx. 80,000) but from distinct sources (human gastric mucosa, human erythrocyte membranes and rat spleen) were shown to have immunological cross-reactivity and comparable mobilities when subjected to polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis under non-denaturing conditions. Kinetic parameters (kcat, Km and Ki) were determined for the interactions of the three enzymes with two synthetic chromogenic substrates and five inhibitors (naturally occurring and synthetic). On this basis it would appear that all of the enzymes should be considered equivalent to cathepsin E. pH-activity measurements indicated that the aspartic proteinase that originated from the erythrocyte membranes retained activity at a higher pH value than either of its readily soluble counterparts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Erreish G. M., Peanasky R. J. Pepsin inhibitors from Ascaris lumbricoides. Pepsin-inhibitor complex: stoichiometry of formation, dissociation, and stability of the complex. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1566–1571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Cooper J., Foundling S. I., Jones D. M., Atrash B., Szelke M. On the rational design of renin inhibitors: X-ray studies of aspartic proteinases complexed with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5585–5590. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J., Foundling S., Hemmings A., Blundell T., Jones D. M., Hallett A., Szelke M. The structure of a synthetic pepsin inhibitor complexed with endothiapepsin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 16;169(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Jimenez M., Parten B. F., Valler M. J., Rolph C. E., Kay J. A systematic series of synthetic chromophoric substrates for aspartic proteinases. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj2370899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. M., Valler M. J., Rolph C. E., Foundling S. I., Jimenez M., Kay J. The pH dependence of the hydrolysis of chromogenic substrates of the type, Lys-Pro-Xaa-Yaa-Phe-(NO2)Phe-Arg-Leu, by selected aspartic proteinases: evidence for specific interactions in subsites S3 and S2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 17;913(2):122–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Haass C., Kloetzel P. M., Niedel B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Drosophila small cytoplasmic 19S ribonucleoprotein is homologous to the rat multicatalytic proteinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):190–192. doi: 10.1038/331190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foundling S. I., Cooper J., Watson F. E., Cleasby A., Pearl L. H., Sibanda B. L., Hemmings A., Wood S. P., Blundell T. L., Valler M. J. High resolution X-ray analyses of renin inhibitor-aspartic proteinase complexes. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):349–352. doi: 10.1038/327349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilová H., Tomásek V. Effect of pepsin inhibitor from Ascaris lumbricoides on cathepsin D and E. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 12;284(2):461–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapresle C., Puizdar V., Porchon-Bertolotto C., Joukoff E., Turk V. Structural differences between rabbit cathepsin E and cathepsin D. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jun;367(6):523–526. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.1.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto N., Yamamoto M., Tani S. Comparative studies of two types of acid proteases from rat gastric mucosa and spleen. J Biochem. 1987 May;101(5):1069–1075. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFANOVIC J., WEBB T., LAPRESLE C. [Study of cathepsins D and E in the preparation of polynuclear cells, macrophages and rabbit lymphocytes]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1962 Aug;103:276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Taggart R. T., Shiraishi T., Branch T., Reid W. A., Heath R., Lewis R. W., Valler M. J., Kay J. Slow moving proteinase. Isolation, characterization, and immunohistochemical localization in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarasova N. I., Szecsi P. B., Foltmann B. An aspartic proteinase from human erythrocytes is immunochemically indistinguishable from a non-pepsin, electrophoretically slow moving proteinase from gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 15;880(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk V., Kregar I., Gubensek F., Lebez D. In vitro transition of beef spleen cathepsin E into cathepsin D. Enzymologia. 1969;36(3):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valler M. J., Kay J., Aoyagi T., Dunn B. M. The interaction of aspartic proteinases with naturally-occurring inhibitors from actinomycetes and Ascaris lumbricoides. J Enzyme Inhib. 1985;1(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/14756368509031284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Katsuda N., Kato K. Affinity purification and properties of cathepsin-E-like acid proteinase from rat spleen. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Marchesi V. T. Purification and characterization of acid proteinase from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 9;790(3):208–218. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ueno E., Uemura H., Kato Y. Biochemical and immunochemical similarity between erythrocyte membrane aspartic proteinase and cathepsin E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa S., Tanaka T., Miyauchi T. Cathepsin E from rat neutrophils: its properties and possible relations to cathepsin D-like and cathepsin E-like acid proteinases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 1;256(2):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90607-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa S., Tanaka T., Muto N., Tani S. Immunochemical similarity between a gastric mucosa non-pepsin acid proteinase and neutrophil cathepsin E of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 14;144(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91445-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]