Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit R. R., Backlund P. S., Jr, Cantoni G. L. Cholera toxin inhibits chemotaxis by a cAMP-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7475–7479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Epinephrine inhibits adenylate cyclase and stimulates a GTPase in human platelet membranes via alpha-adrenoceptors. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano T., Ui M., Ogasawara N. Prevention of the agonist binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors by guanine nucleotides and islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in bovine cerebral cortex. Possible coupling of the toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins to receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12653–12658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beals C. R., Wilson C. B., Perlmutter R. M. A small multigene family encodes Gi signal-transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7886–7890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Hulme E. C., Burgen A. The character of the muscarinic receptors in different regions of the rat brain. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Feb 13;207(1166):1–12. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. Selection of a variant lymphoma cell deficient in adenylate cyclase. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):750–752. doi: 10.1126/science.163487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. GTP-binding proteins. One molecular machine can transduce diverse signals. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):814–816. doi: 10.1038/321814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A. Mammalian G proteins: structure and function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):35–38. doi: 10.1042/bst0150035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brann M. R., Collins R. M., Spiegel A. Localization of mRNAs encoding the alpha-subunits of signal-transducing G-proteins within rat brain and among peripheral tissues. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 28;222(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray P., Carter A., Simons C., Guo V., Puckett C., Kamholz J., Spiegel A., Nirenberg M. Human cDNA clones for four species of G alpha s signal transduction protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8893–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Gierschik P., Somers R., Spiegel A. M., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Specificity of the functional interactions of the beta-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. A role for Ni in the hormonal stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):293–295. doi: 10.1038/318293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Gierschik P., Codina J., Somers R. L., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Mechanism of guanine nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Studies with isolated subunits of transducin in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9514–9520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Yatani A., Grenet D., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The alpha subunit of the GTP binding protein Gk opens atrial potassium channels. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2436299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deery W. J., Rebeiro-Neto F., Field J. B. Multiple isoforms of ADP-ribosylated G-like proteins from mammalian thyroid membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):536–542. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80542-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deretic D., Hamm H. E. Topographic analysis of antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies to the photoreceptor guanyl nucleotide-binding protein, transducin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10839–10847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J. R., Ho Y. S., Snyderman R. Human Gi protein alpha-subunit: deduction of amino acid structure from a cloned cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81428-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide B., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Mullaney I., Unson C., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. GTP-binding proteins in brain and neutrophil are tethered to the plasma membrane via their amino termini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1398–1405. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falloon J., Malech H., Milligan G., Unson C., Kahn R., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. Detection of the major pertussis toxin substrate of human leukocytes with antisera raised against synthetic peptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Reconstitution of resolved muscarinic cholinergic receptors with purified GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3477–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Kinney D. M. ADP-ribosylating microbial toxins. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1985;11(4):273–298. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao B., Gilman A. G., Robishaw J. D. A second form of the beta subunit of signal-transducing G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6122–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Falloon J., Milligan G., Pines M., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. Immunochemical evidence for a novel pertussis toxin substrate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8058–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Jakobs K. H. Receptor-mediated ADP-ribosylation of a phospholipase C-stimulating G protein. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Morrow B., Milligan G., Rubin C., Spiegel A. Changes in the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, Gi and Go, during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
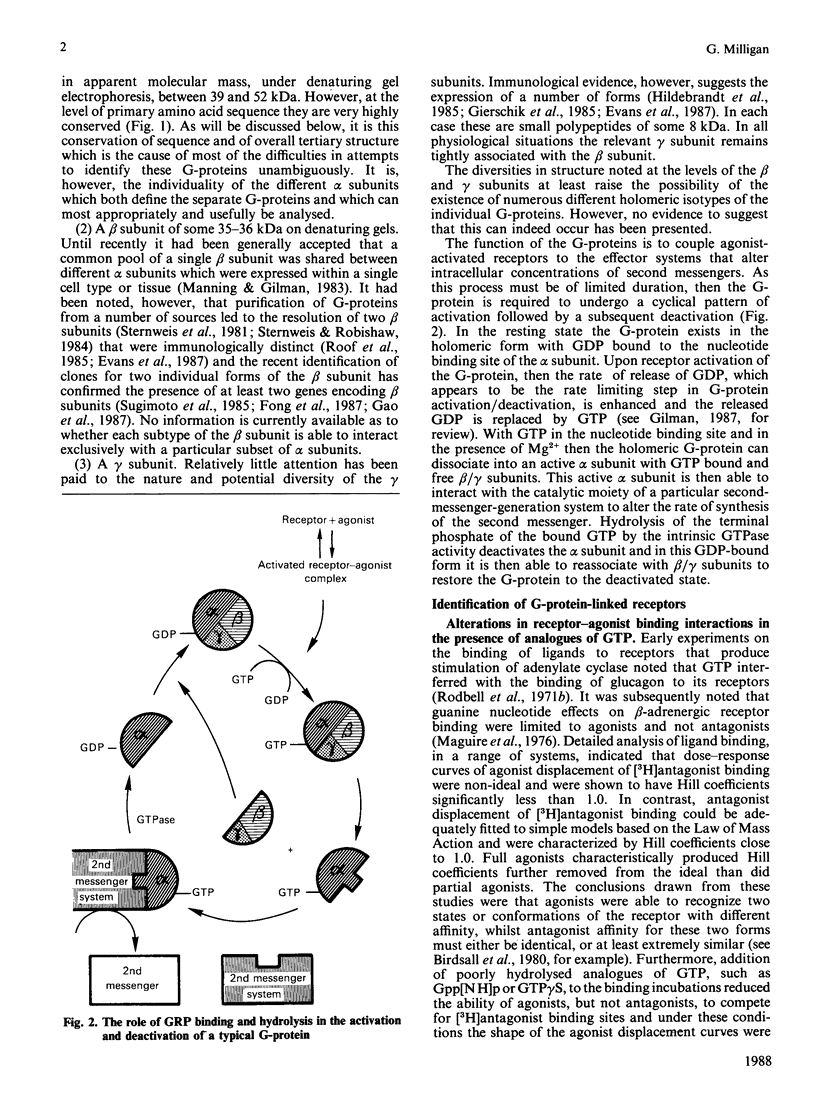
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Malech H. L., Spiegel A. M. Antibodies directed against synthetic peptides distinguish between GTP-binding proteins in neutrophil and brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14683–14688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziano M. P., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of cDNAs for G proteins in Escherichia coli. Two forms of Gs alpha stimulate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11375–11381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Ross E. M., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Adenylate cyclase permanently uncoupled from hormone receptors in a novel variant of S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Hofmann K. P., Schleicher A., Kohl B. Mechanism of action of monoclonal antibodies that block the light activation of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein, transducin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10831–10838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris B. A., Robishaw J. D., Mumby S. M., Gilman A. G. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA for the alpha subunit of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.3839937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-dependent pertussis-toxin-insensitive stimulation of inositol phosphate formation by carbachol in a membrane preparation from human astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2390141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heydorn W. E., Gierschik P., Creed G. J., Milligan G., Spiegel A., Jacobowitz D. M. The beta subunit of the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins: identification of its location on two-dimensional gels of brain tissue and its regional and subcellular distribution in brain. J Neurosci Res. 1986;16(3):541–552. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490160309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Rosenthal W., Birnbaumer L., Neer E. J., Yamazaki A., Bitensky M. W. Characterization by two-dimensional peptide mapping of the gamma subunits of Ns and Ni, the regulatory proteins of adenylyl cyclase, and of transducin, the guanine nucleotide-binding protein of rod outer segments of the eye. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14867–14872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Gawler D., O'Hagan S., Wilson A. Thrombin, unlike vasopressin, appears to stimulate two distinct guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2380109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Wilson A. Platelet activating factor and U44069 stimulate a GTPase activity in human platelets which is distinct from the guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins, Ns and Ni. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):737–740. doi: 10.1042/bj2340737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia J. A., Moss J., Hewlett E. L., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase by pertussis toxin. Effects on inhibitory agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1086–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. H., Roeber J. F., Johnson G. L. Conformational changes of adenylate cyclase regulatory proteins mediated by guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Shoback D. M., Pattison G., Stobo J. D. Cholera toxin inhibits the T-cell antigen receptor-mediated increases in inositol trisphosphate and cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Maguire M. E., Gilman A. G., Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Melmon K. L. Beta adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase: products of separate genes? Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):1062–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nagata S., Nakamura S., Katada T., Ui M., Iwai S., Ohtsuka E., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of cDNAs for alpha subunits of the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins Gs, Gi, and Go from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Aktories K., Schultz G. A nucleotide regulatory site for somatostatin inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cells. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):177–178. doi: 10.1038/303177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., Kaslow H. R., Bourne H. R. Genetic evidence that cholera toxin substrates are regulatory components of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7120–7123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Islet-activating protein. A modifier of receptor-mediated regulation of rat islet adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8310–8317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Islet-activating protein. Enhanced insulin secretion and cyclic AMP accumulation in pancreatic islets due to activation of native calcium ionophores. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):469–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kozawa O., Kaibuchi K., Katada T., Ui M., Takai Y. Direct evidence for involvement of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein in chemotactic peptide-stimulated formation of inositol bisphosphate and trisphosphate in differentiated human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Reconstitution with Gi or Go of the plasma membranes ADP-ribosylated by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11558–11562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Klee W. A. Opiates inhibit adenylate cyclase by stimulating GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. Specific uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, of negative signal transduction via alpha-adrenergic, cholinergic, and opiate receptors in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4870–4875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Katada T., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Ui M. Functional interaction of purified muscarinic receptors with purified inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6423–6428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad R. P., Simons C., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Woodard C., Griffo M., Goldsmith P., Ornberg R., Gerfen C. R., Spiegel A. Differential distribution of signal-transducing G-proteins in retina. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 13;423(1-2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea C. L., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B., Klock I. B., Bunt-Milam A. H. Identification of specific transducin alpha subunits in retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3529395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo W. W., Hughes J. A novel cholera toxin-sensitive G-protein (Gc) regulating receptor-mediated phosphoinositide signalling in human pituitary clonal cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80840-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lochrie M. A., Hurley J. B., Simon M. I. Sequence of the alpha subunit of photoreceptor G protein: homologies between transducin, ras, and elongation factors. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.3856323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetje C. W., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Unson C., Spiegel A., Nathanson N. M. Tissue-specific regulation of GTP-binding protein and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor levels during cardiac development. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4876–4884. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the beta adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. The regulatory components of adenylate cyclase and transducin. A family of structurally homologous guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7059–7063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattera R., Codina J., Sekura R. D., Birnbaumer L. The interaction of nucleotides with pertussis toxin. Direct evidence for a nucleotide binding site on the toxin regulating the rate of ADP-ribosylation of Ni, the inhibitory regulatory component of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11173–11179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Kelly E. C., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Antibodies which recognize the C-terminus of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) demonstrate that opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulate the high-affinity GTPase activity of two separate pertussis-toxin substrates. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):653–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2490653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. The GTP-binding regulatory proteins of neuroblastoma x glioma, NG108-15, and glioma, C6, cells. Immunochemical evidence of a pertussis toxin substrate that is neither Ni nor No. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. The use of specific antibodies to identify and quantify guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):42–45. doi: 10.1042/bst0150042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Guanine nucleotide regulation of the pertussis and cholera toxin substrates of rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 6;929(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Klee W. A. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Ni) purified from bovine brain is a high affinity GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2057–2063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Mullaney I., Unson C. G., Marshall L., Spiegel A. M., McArdle H. GTP analogues promote release of the alpha subunit of the guanine nucleotide binding protein, Gi2, from membranes of rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):391–396. doi: 10.1042/bj2540391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Simonds W. F., Streaty R. A., Tocque B., Klee W. A. Functional control of the delta-opiate receptor by the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Dec;13(6):1110–1113. doi: 10.1042/bst0131110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Streaty R. A., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. Development of opiate receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in neonatal rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8626–8630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kahn R. A., Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. Antisera of designed specificity for subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M., Eide B., Goldsmith P., Brann M., Gierschik P., Spiegel A., Malech H. L. Detection of multiple forms of Gi alpha in HL60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S. E., Fung B. K. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. Participation of the amino-terminal region of T alpha in subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15746–15751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukada T., Mishina M., Numa S. Functional expression of cloned cDNA encoding the alpha-subunit of adenylate cyclase-stimulating G-protein. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 19;211(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta H., Okajima F., Ui M. Inhibition by islet-activating protein of a chemotactic peptide-induced early breakdown of inositol phospholipids and Ca2+ mobilization in guinea pig neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15771–15780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. R., Frame L. T., Ui M., Cooper D. M. Cholera toxin ADP-ribosylates the islet-activating protein substrate in adipocyte membranes and alters its function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15946–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines M., Gierschik P., Milligan G., Klee W., Spiegel A. Antibodies against the carboxyl-terminal 5-kDa peptide of the alpha subunit of transducin crossreact with the 40-kDa but not the 39-kDa guanine nucleotide binding protein from brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4095–4099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall T., Harris B. A. Identification of the lesion in the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of the uncoupled S49 lymphoma. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 30;224(2):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robishaw J. D., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. Molecular basis for two forms of the G protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9587–9590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Krans H. M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. V. An obligatory role of guanylnucleotides in glucagon action. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1877–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer L. S., Garrison J. C., Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase from uncoupled S49 lymphoma cells differs in charge from the wild type protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2641–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Tsai S. C., Kung H. F., Oroszlan S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Hydroxylamine-stable covalent linkage of myristic acid in G0 alpha, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein of bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1234–1239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90780-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Dolphin A. C. Activation of a G protein promotes agonist responses to calcium channel ligands. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):760–762. doi: 10.1038/330760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad C. F., Carchman R. A. Human T lymphocyte mitogenesis in response to the B oligomer of pertussis toxin is associated with an early elevation in cytosolic calcium concentrations. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Nukada T., Tanabe T., Takahashi H., Noda M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Inayama S. Primary structure of the beta-subunit of bovine transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suki W. N., Abramowitz J., Mattera R., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. The human genome encodes at least three non-allellic G proteins with alpha i-type subunits. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80900-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. A., Miller R. T., Masters S. B., Beiderman B., Heideman W., Bourne H. R. Identification of receptor contact site involved in receptor-G protein coupling. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):758–760. doi: 10.1038/330758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashima T., Katada T., Oinuma M., Inoue Y., Ui M. Immunohistochemical localization of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in rat retina. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 28;410(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(87)80026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Aunis D., Bockaert J., Homburger V., Rouot B. Presence of three pertussis toxin substrates and Go alpha immunoreactivity in both plasma and granule membranes of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M., Uhing R. J., Snyderman R. A pertussis/choleratoxin-sensitive N protein may mediate chemoattractant receptor signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):887–894. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Regulation of G-proteins in differentiation. Altered ratio of alpha- to beta-subunits in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatsunami K., Pandya B. V., Oprian D. D., Khorana H. G. cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of the gamma subunit of GTPase from bovine rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]