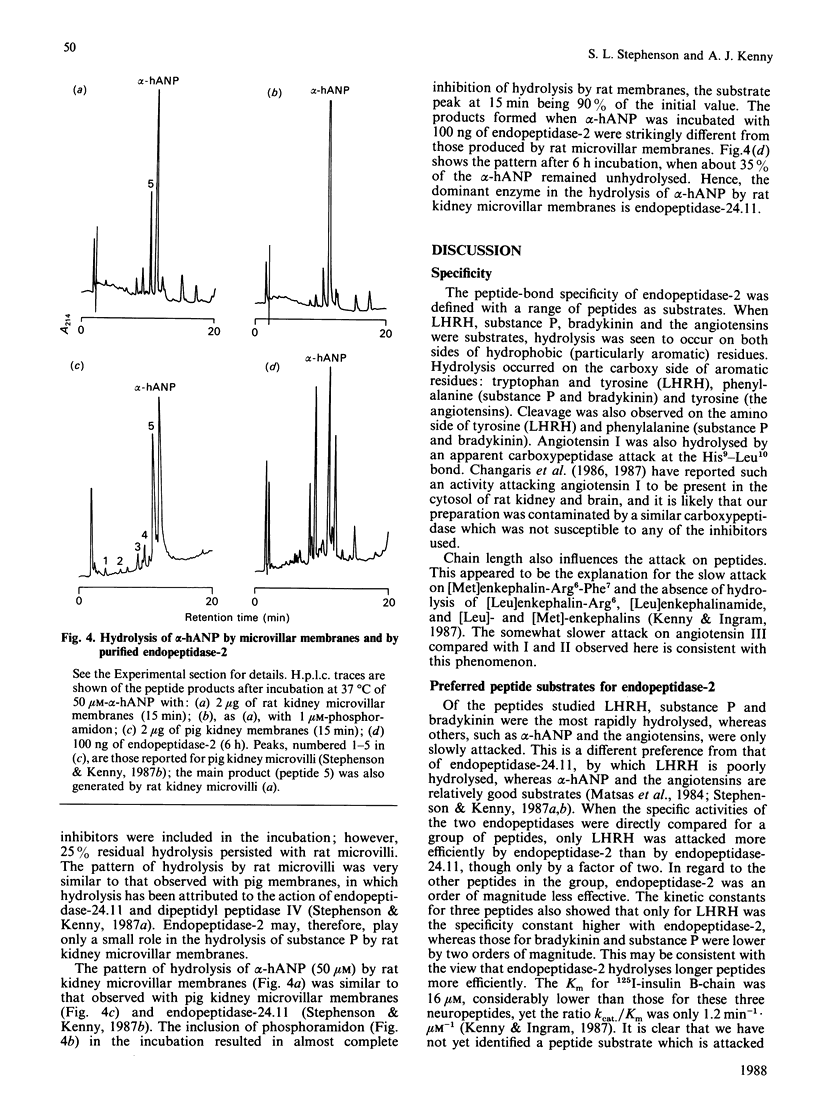
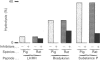Abstract
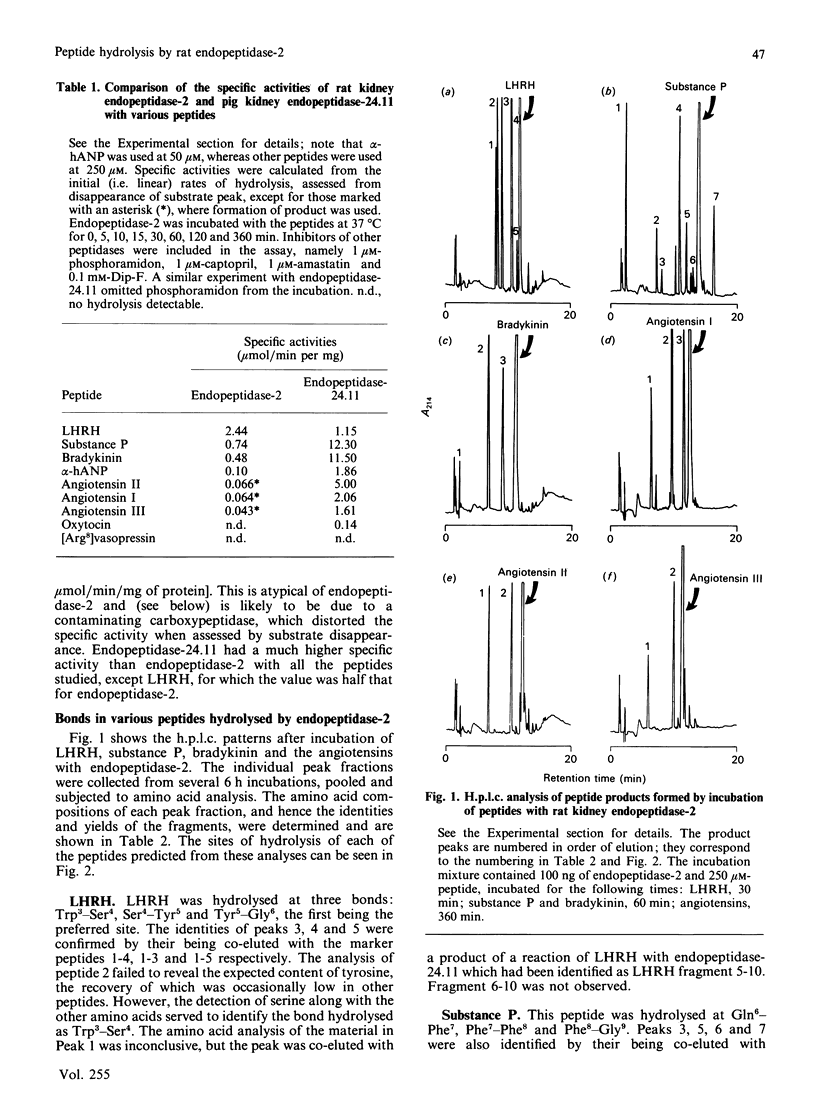
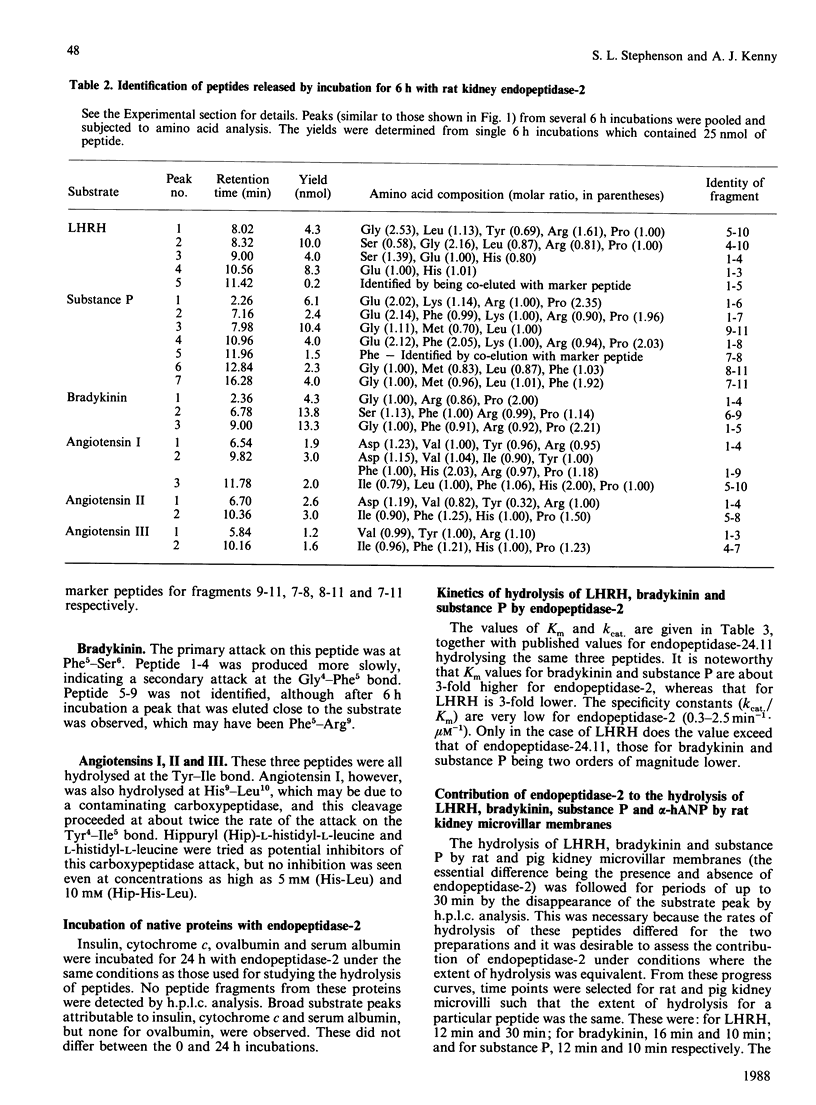
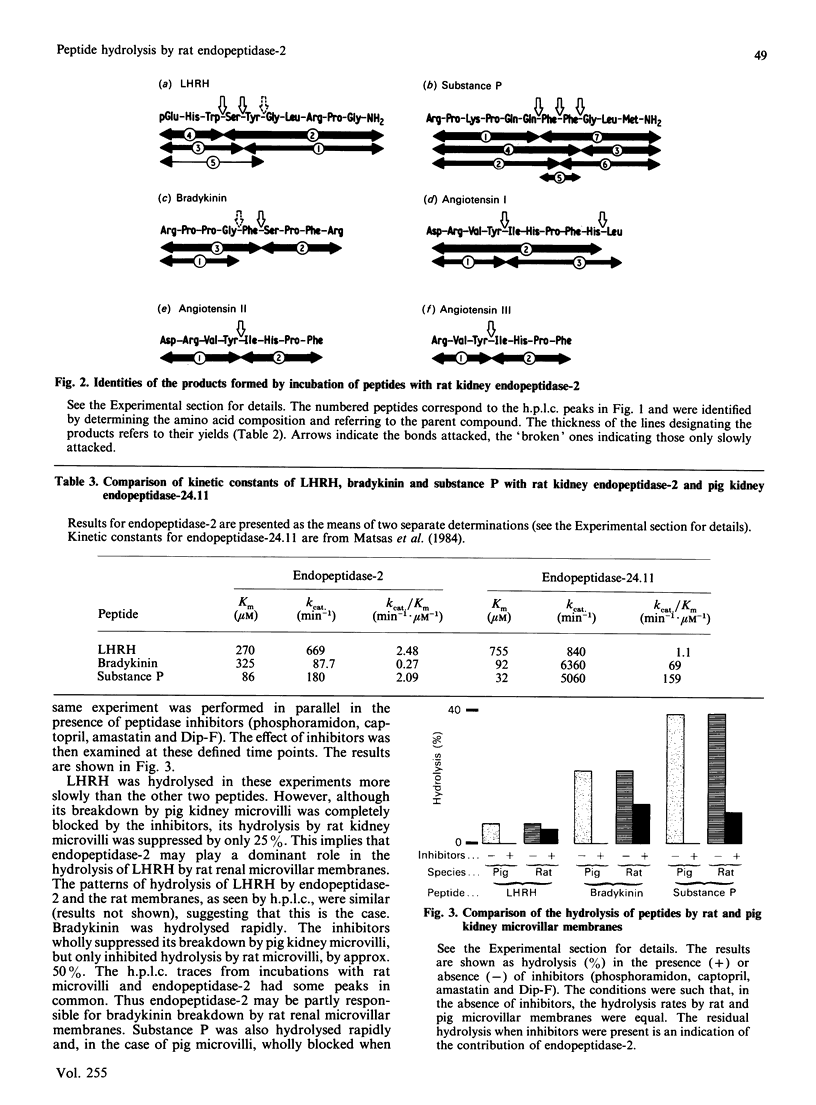
Endopeptidase-2, the second endopeptidase in rat kidney brush border [Kenny & Ingram (1987) Biochem. J. 245, 515-524] has been further characterized in regard to its specificity and its contribution to the hydrolysis of peptides by microvillar membrane preparations. The peptide products were identified, after incubating luliberin, substance P, bradykinin and angiotensins I, II and III with the purified enzyme. The bonds hydrolysed were those involving a hydrophobic amino acid residue, but this residue could be located at either the P1 or P1' site. Luliberin was hydrolysed faster than other peptides tested, followed by substance P and bradykinin. Human alpha-atrial natriuretic peptide and the angiotensins were only slowly attacked. Oxytocin and [Arg8]vasopressin were not hydrolysed. No peptide fragments were detected on prolonged incubation with insulin, cytochrome c, ovalbumin and serum albumin. In comparison with pig endopeptidase-24.11 the rates for the susceptible peptides were, with the exception of luliberin, much lower for endopeptidase-2. Indeed, for bradykinin and substance P the ratio kcat./Km was two orders of magnitude lower. Since both endopeptidases are present in rat kidney microvilli, an assessment was made of the relative contributions to the hydrolysis of luliberin, bradykinin and substance P. Only for the first named was endopeptidase-2 the dominant enzyme; for bradykinin it made an equal, and for substance P a minor, contribution.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbs M. T., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane; analysis by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Nov;65(5):551–559. doi: 10.1042/cs0650551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon R. J., Shannon J. D., Bond J. S. Purification and characterization of a metallo-endoproteinase from mouse kidney. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1990591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S., Butler P. E., Beynon R. J. Metalloendopeptidases of the mouse kidney brush border: meprin and endopeptidase-24.11. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1986;45(11-12):1515–1521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S., Shannon J. D., Beynon R. J. Certain mouse strains are deficient in a kidney brush-border metallo-endopeptidase activity. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):251–255. doi: 10.1042/bj2090251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. E., McKay M. J., Bond J. S. Characterization of meprin, a membrane-bound metalloendopeptidase from mouse kidney. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):229–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2410229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changaris D. G., Miller J. J., Levy R. S. Angiotensin II generated by a human renal carboxypeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):573–579. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80535-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The amphipathic forms of endopeptidase purified from pig kidneys. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):743–753. doi: 10.1042/bj2110743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Matsas R., Kenny A. J. A monoclonal antibody to kidney endopeptidase-24.11. Its application in immunoadsorbent purification of the enzyme and immunofluorescent microscopy of kidney and intestine. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):377–386. doi: 10.1042/bj2140377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Fulcher I. S., Ridgwell K., Ingram J. Microvillar membrane neutral endopeptidases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1465–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Ingram J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. Purification and properties of the phosphoramidon-insensitive endopeptidase ('endopeptidase-2') from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):515–524. doi: 10.1042/bj2450515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Stephenson S. L. Role of endopeptidase-24.11 in the inactivation of atrial natriuretic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. Metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of the angiotensins, bradykinin, substance P and oxytocin by pig kidney microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2410237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide by pig kidney microvillar membranes is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2430183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Green J. R., Lentze M. J. Non-pancreatic hydrolysis of N-benzoyl-l-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA-peptide) in the human small intestine. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 May;62(5):557–560. doi: 10.1042/cs0620557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterchi E. E., Green J. R., Lentze M. J. Nonpancreatic hydrolysis of N-benzoyl-L-tyrosyl-p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA peptide) in the rat small intestine. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1983;2(3):539–547. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198302030-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]