Abstract
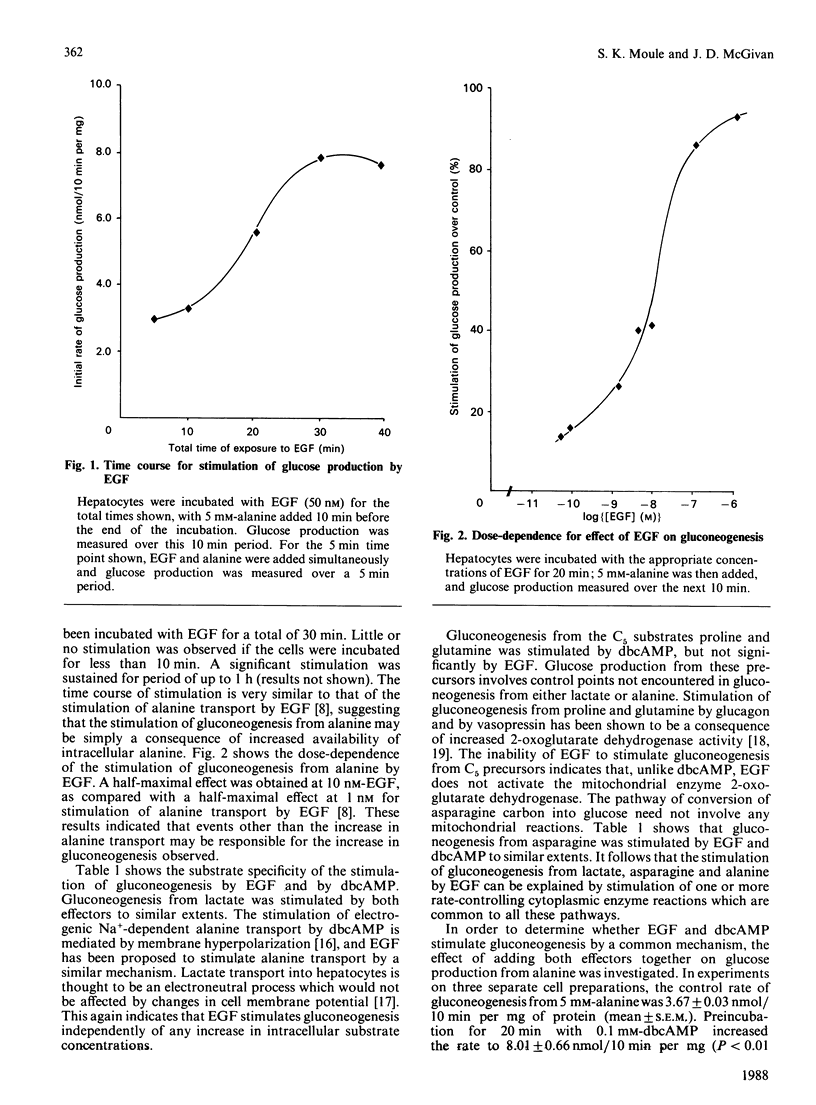
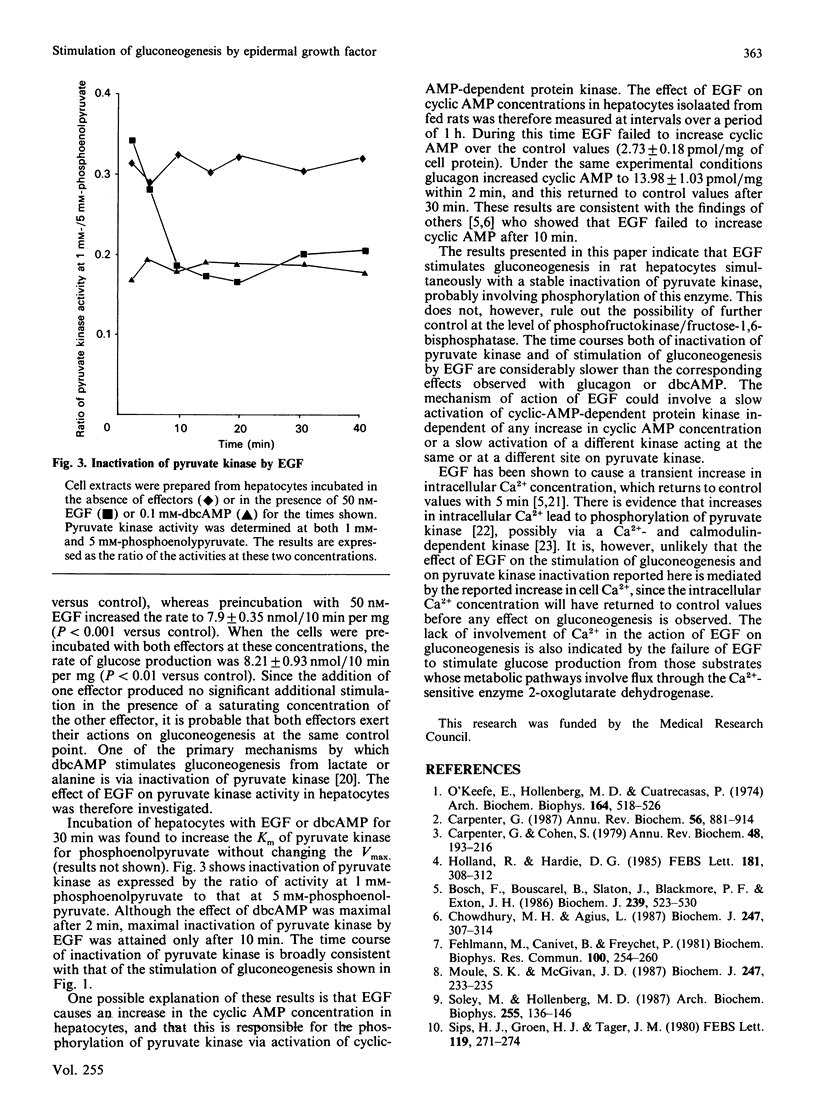
Preincubation of rat hepatocytes with EGF (epidermal growth factor) caused a stimulation of gluconeogenesis from alanine. The effect was maximal after preincubation of 20 min, and a half-maximal effect of EGF was obtained at 10 nM. EGF also stimulated gluconeogenesis from lactate and asparagine, but not from glutamine or from proline. Preincubation of hepatocytes with EGF caused a stable inactivation of pyruvate kinase, which may account, at least in part, for the observed effects of EGF on gluconeogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair J. B., Cimbala M. A., Foster J. L., Morgan R. A. Hepatic pyruvate kinase. Regulation by glucagon, cyclic adenosine 3'-5'-monophosphate, and insulin in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3756–3762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F., Bouscarel B., Slaton J., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Epidermal growth factor mimics insulin effects in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):523–530. doi: 10.1042/bj2390523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford N. M., Hayes M. R., McGivan J. D. The use of 36Cl- to measure cell plasma membrane potential in isolated hepatocytes--effects of cyclic AMP and bicarbonate ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 22;845(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. H., Agius L. Epidermal growth factor counteracts the glycogenic effect of insulin in parenchymal hepatocyte cultures. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2470307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Edgell N. J., Bridges B. J., Poole G. P. Acute regulation of pyruvate kinase activity in rat epididymal adipose tissue by insulin. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 15;180(3):523–531. doi: 10.1042/bj1800523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund G. L., Halestrap A. P. The kinetics of transport of lactate and pyruvate into rat hepatocytes. Evidence for the presence of a specific carrier similar to that in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):117–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2490117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Canivet B., Freychet P. Epidermal growth factor stimulates monovalent cation transport in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):254–260. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R., Hardie D. G. Both insulin and epidermal growth factor stimulate fatty acid synthesis and increase phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and ATP-citrate lyase in isolated hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 25;181(2):308–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Y. C., Bloxham D. P., Giles I. G. Phosphorylation of type-L pyruvate kinase in intact hepatocytes. Localisation of the phosphorylation site in response to both glucagon and the Ca2+-linked agonist phenylephrine. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 22;218(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Garrison J. C. Epidermal growth factor and angiotensin II stimulate formation of inositol 1,4,5- and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in hepatocytes. Differential inhibition by pertussis toxin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17285–17293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moule S. K., Bradford N. M., McGivan J. D. Short-term stimulation of Na+-dependent amino acid transport by dibutyryl cyclic AMP in hepatocytes. Characteristics and partial mechanism. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):737–743. doi: 10.1042/bj2410737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moule S. K., McGivan J. D. Epidermal growth factor, like glucagon, exerts a short-term stimulation of alanine transport in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):233–235. doi: 10.1042/bj2470233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E., Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor. Characteristics of specific binding in membranes from liver, placenta, and other target tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Oct;164(2):518–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Groen A. K., Tager J. M. Plasma-membrane transport of alanine is rate-limiting for its metabolism in rat-liver parenchymal cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Schworer C. M., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis S. J. Phosphorylation of liver pyruvate kinase by Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: characterization of two phosphorylation sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soley M., Hollenberg M. D. Epidermal growth factor (urogastrone)-stimulated gluconeogenesis in isolated mouse hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 May 15;255(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90303-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. M., McGivan J. D. Ca2+-dependent activation of oxoglutarate dehydrogenase by vasopressin in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):327–333. doi: 10.1042/bj2250327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. M., McGivan J. D. Distinct effects of glucagon and vasopressin on proline metabolism in isolated hepatocytes. The role of oxoglutarate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 15;217(2):477–483. doi: 10.1042/bj2170477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinder P. Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J Clin Pathol. 1969 Mar;22(2):158–161. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


