Abstract
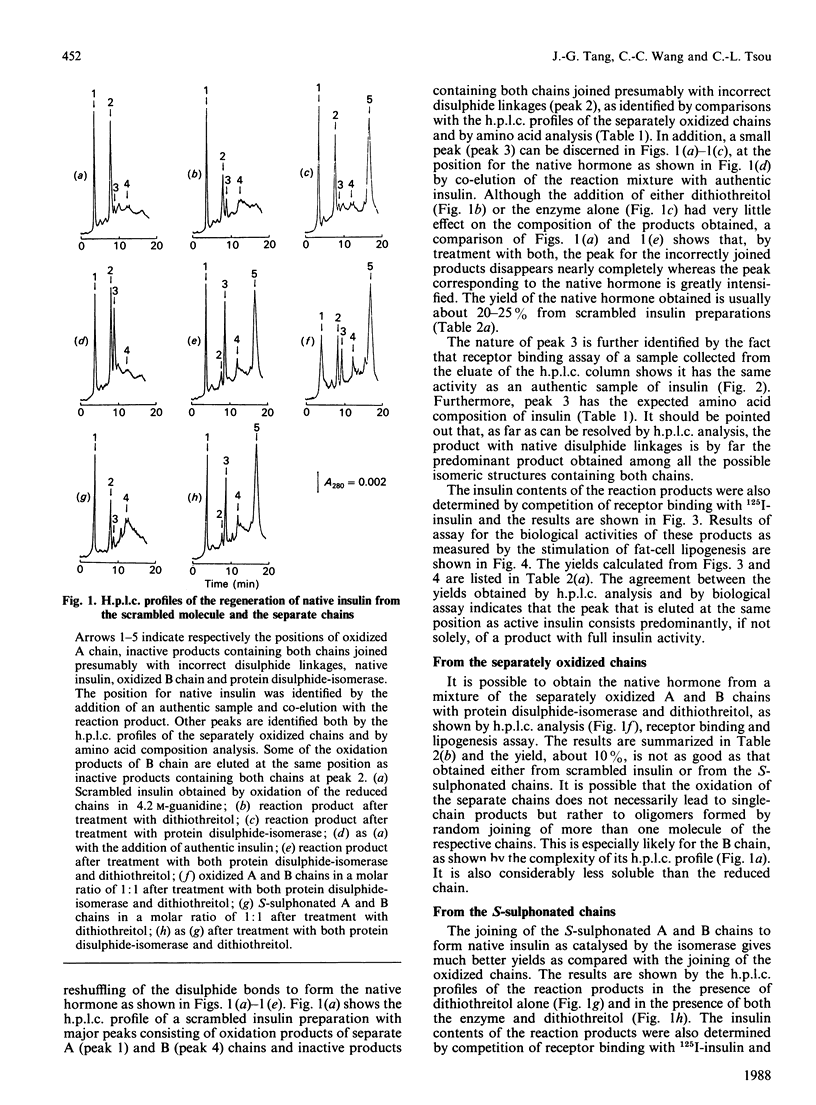
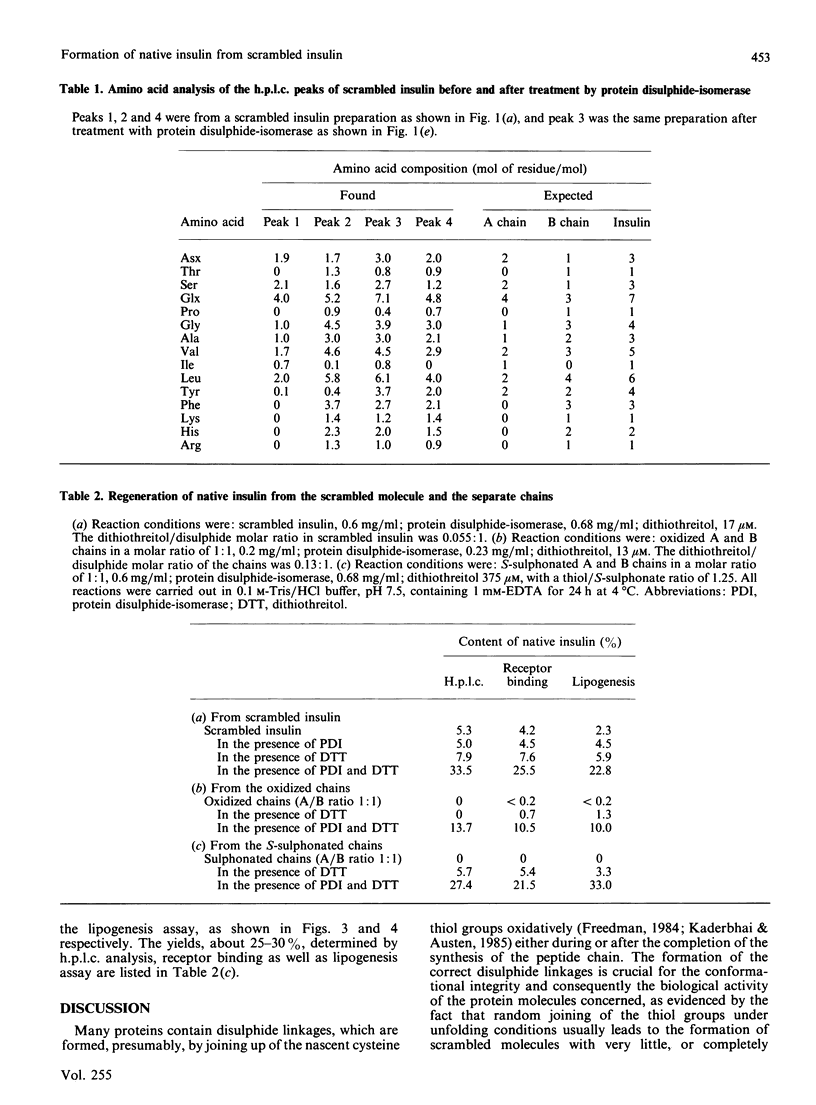
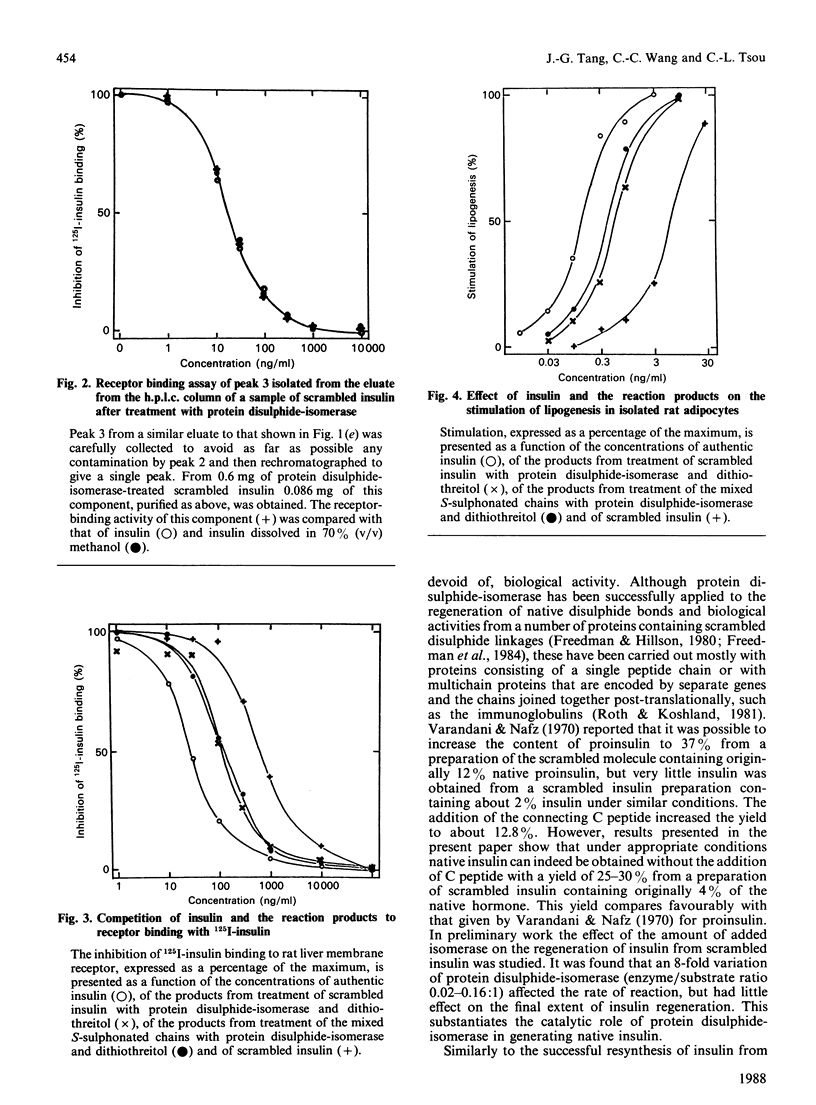
The formation of native insulin either from scrambled insulin or from the separated A chain and B chain S-sulphonates by protein disulphide-isomerase was demonstrated with yields of 20-30% as measured by h.p.l.c. analysis, receptor binding and stimulation of lipogenesis. The h.p.l.c. profile of the reaction products shows that, among all the possible isomers containing both chains, the native hormone is by far the predominating product and consequently the most stable under certain conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B., Scheraga H. A. Experimental and theoretical aspects of protein folding. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:205–300. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60413-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg D., Gattner H. G., Schermutzki W., Schüttler A., Uschkoreit J., Weimann J., Wollmer A. Crosslinked insulins: preparation, properties, and application. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;86A:261–282. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3282-4_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg D., Wollmer A. The effect of a non-peptide interchain crosslink on the reoxidation of reduced insulin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Jun;354(6):613–627. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DU Y. C., ZHANG Y. S., LU Z. X., TSOU C. L. Resynthesis of insulin from its glycyl and phenylalanyl chains. Sci Sin. 1961 May;10:84–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B., Brockway B. E., Lambert N. Protein disulphide-isomerase and the formation of native disulphide bonds. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Dec;12(6):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bst0120929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillson D. A., Lambert N., Freedman R. B. Formation and isomerization of disulfide bonds in proteins: protein disulfide-isomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:281–294. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbetson A. L., Freedman R. B. Thiol-protein disulphide oxidoreductases. Assay of microsomal membrane-bound glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase and comparison with protein disulphide-isomerase. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):377–384. doi: 10.1042/bj1590377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaderbhai M. A., Austen B. M. Studies on the formation of intrachain disulphide bonds in newly biosynthesised bovine prolactin. Role of protein-disulphide isomerase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):167–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsoyannis P. G., Trakatellis A. C., Johnson S., Zalut C., Schwartz G. Studies on the synthesis of insulin from natural and synthetic A and B chains. II. Isolation of insulin from recombination mixtures of natural A and B chains. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2642–2654. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen H. M., Tietze F. Studies on the specificity and mechanism of action of hepatic glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3561–3570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody A. J., Stan M. A., Stan M., Gliemann J. A simple free fat cell bioassay for insulin. Horm Metab Res. 1974 Jan;6(1):12–16. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K. F., Wood R. J. A radioreceptor assay method for insulin. J Biol Stand. 1984 Oct;12(4):427–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(84)80066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paynovich R. C., Carpenter F. H. Oxidation of the sulfhydryl forms of insulin A-chain and B-chain. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979 Feb;13(2):113–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Koshland M. E. Role of disulfide interchange enzyme in immunoglobulin synthesis. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6594–6599. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Nafz M. A. Enzymatic destruction of immunoreactivity in proinsulin and insulin and activation of their scrambled forms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Tsou C. L. Interaction and reconstitution of carboxyl-terminal-shortened B chains with the intact A chain of insulin. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5336–5340. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. X., Ju M., Tsou C. L. Number of ways of joining SH groups to form multi-peptide chain proteins. J Theor Biol. 1987 Feb 7;124(3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(87)80117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn H., Gutte B., Pfeiffer E. F., Ammon J. Resynthese von Insulin aus präoxydierter A-Kette und reduzierter B-Kette. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1966 Feb;691:225–231. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19666910132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


