Abstract
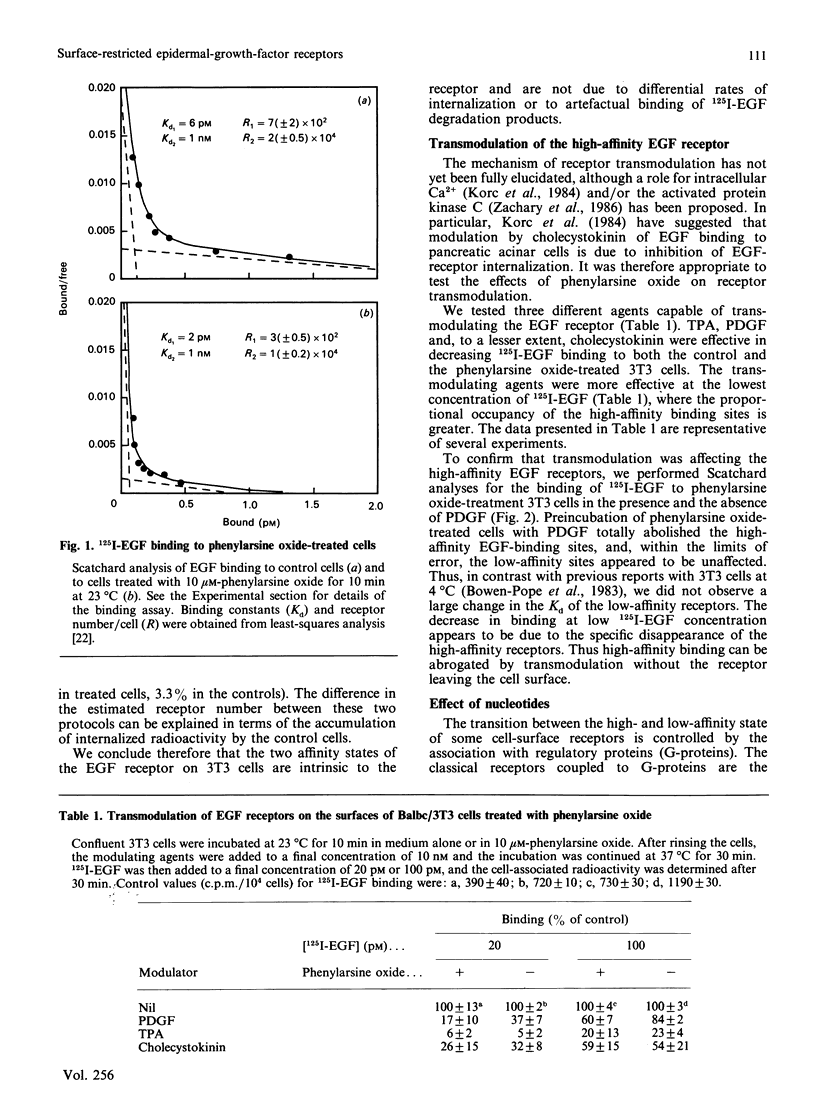
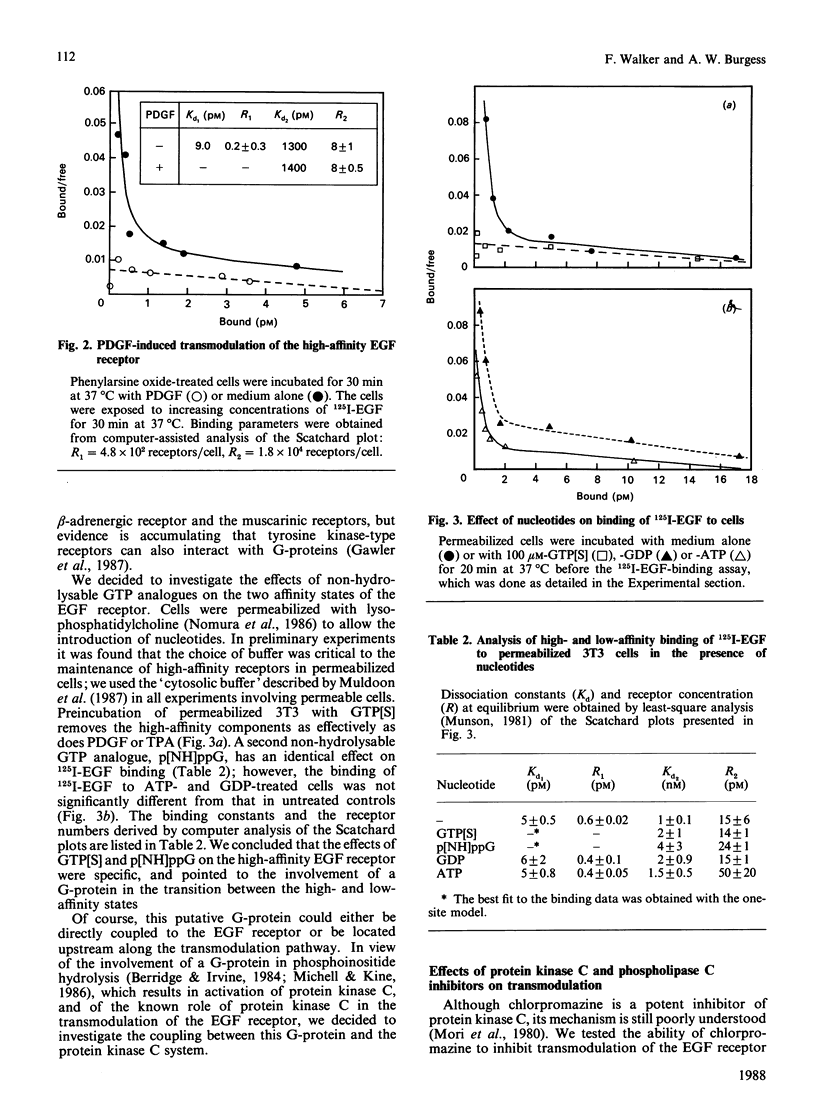
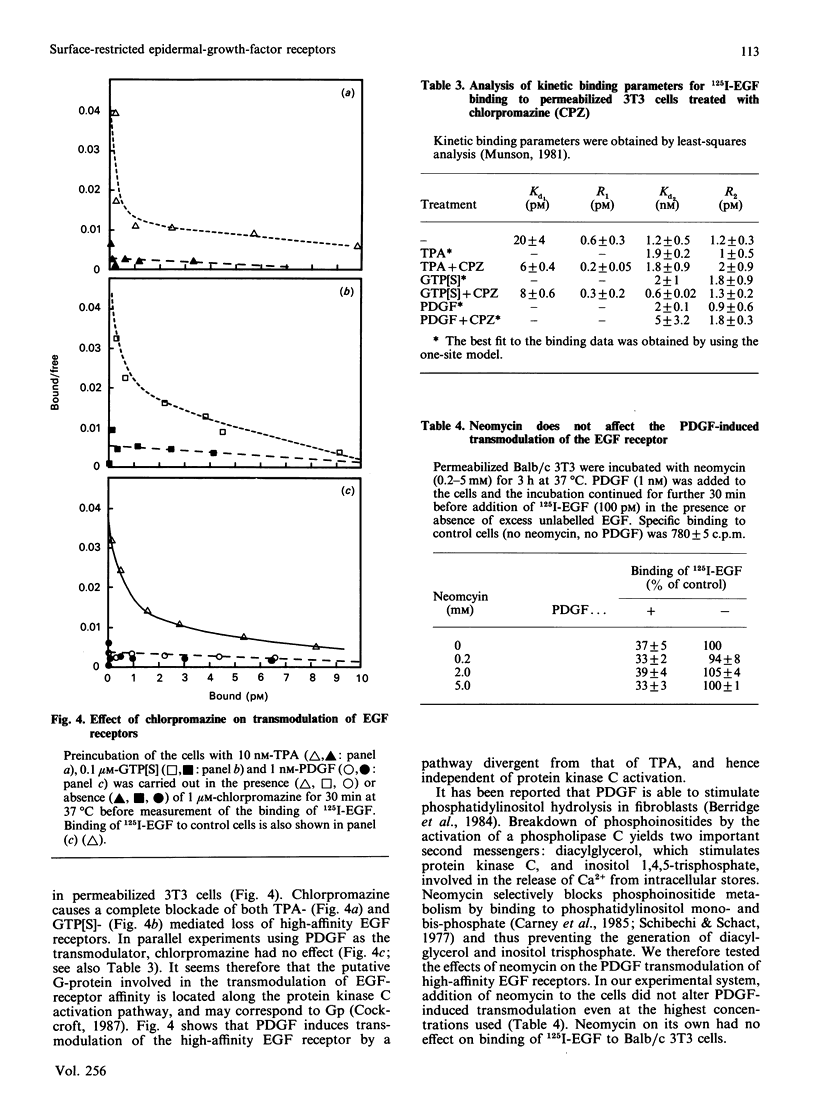
Binding of murine epidermal growth factor (EGF) to its high-affinity receptor can be modulated by a variety of structurally unrelated mitogens. The transmodulation, however, is temperature-dependent and has not been observed in isolated membranes. We report here the transmodulation of high-affinity EGF receptors by platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF) and tumour-promoting phorbol esters in 3T3 cells even when they are rendered incapable of fluid-phase endocytosis by treatment with phenylarsine oxide or by permeabilization with lysophosphatidylcholine. The relative affinity of the EGF receptors in the absence of modulating agents is not significantly altered by phenylarsine oxide treatment. Thus the difference in affinity between the two classes of EGF receptors seems to be unrelated to dynamic membrane changes or to differential rates of internalization. In permeabilized cells, non-hydrolysable GTP analogues transmodulate the high-affinity EGF receptor; however, the effects of these analogues are blocked by the protein kinase C inhibitor chlorpromazine. In contrast, transmodulation by PDGF is not blocked by chloropromazine. Thus the high-affinity EGF receptor can be transmodulated by both protein kinase C-dependent or -independent pathways, and the transmodulation processes do not require fluid-phase endocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Brown K. D. Inositol trisphosphate formation and calcium mobilization in Swiss 3T3 cells in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):195–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2220195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Dicorleto P. E., Ross R. Interactions between the receptors for platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):679–683. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Lloyd C. J., Nice E. C. Murine epidermal growth factor: heterogeneity on high resolution ion-exchange chromatography. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2065–2069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Scott D. L., Gordon E. A., LaBelle E. F. Phosphoinositides in mitogenesis: neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover and initiation of cell proliferation. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Properties of the receptor for epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):357–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Platelet-derived growth factor treatment decreases the affinity of the epidermal growth factor receptors of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11689–11693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Dansylcadaverine inhibits internalization of 125I-epidermal growth factor in BALB 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1239–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Resolution of high and low affinity epidermal growth factor receptors. Inhibition of high affinity component by low temperature, cycloheximide, and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3053–3060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Matrisian L. M., Magun B. E. Cytosolic calcium regulates epidermal growth factor endocytosis in rat pancreas and cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):461–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Carpenter C. D., Gill G. N., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Protein kinase C phosphorylation at Thr 654 of the unoccupied EGF receptor and EGF binding regulate functional receptor loss by independent mechanisms. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):839–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta modulates the high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1508–1514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell B., Kirk C. G-protein control of inositol phosphate hydrolysis. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):112–113. doi: 10.1038/323112b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldoon L. L., Jamieson G. A., Jr, Villereal M. L. Calcium mobilization in permeabilized fibroblasts: effects of inositol trisphosphate, orthovanadate, mitogens, phorbol ester, and guanosine triphosphate. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jan;130(1):29–36. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Kamiya T., Oishi M. A procedure to introduce protein molecules into living mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):434–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Livneh E., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of EGF receptor affect EGF binding and receptor internalization. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2179–2190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibeci A., Schacht J. Action of neomycin on the metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in the guinea pig kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 1;26(19):1769–1774. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Cohen S. Transformation by murine and feline sarcoma viruses specifically blocks binding of epidermal growth factor to cells. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):26–31. doi: 10.1038/264026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Ho T. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. II. A survey of inhibitors. J Exp Zool. 1972 Sep;181(3):303–317. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401810303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark B., Heldin C. H. Similar action of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor in the prereplicative phase of human fibroblasts suggests a common intracellular pathway. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jul;124(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041240108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. The endocytotic rate constant. A cellular parameter for quantitating receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., VanNostrand W., McKinley D. N., Cunningham D. D. Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor and its effect on ligand-receptor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5290–5295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. The EGF receptor kinase: evidence for allosteric activation and intramolecular self-phosphorylation. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;116:23–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470720974.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


