Abstract
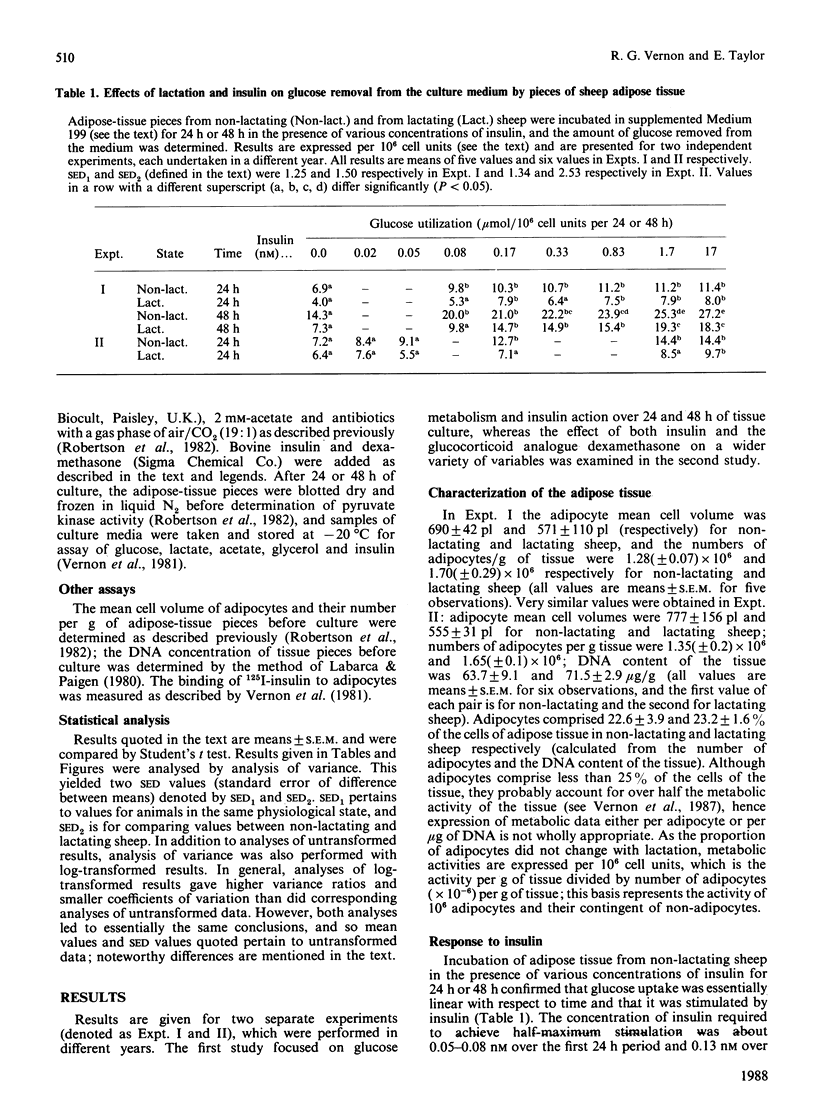
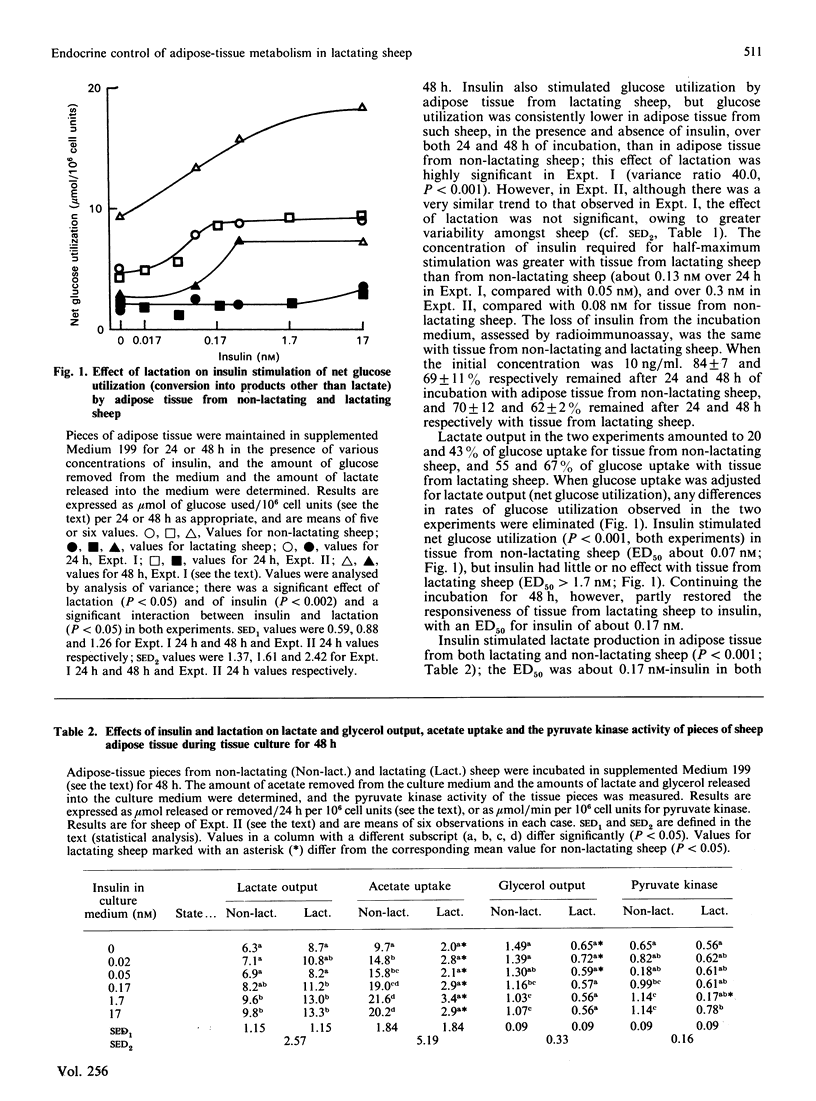
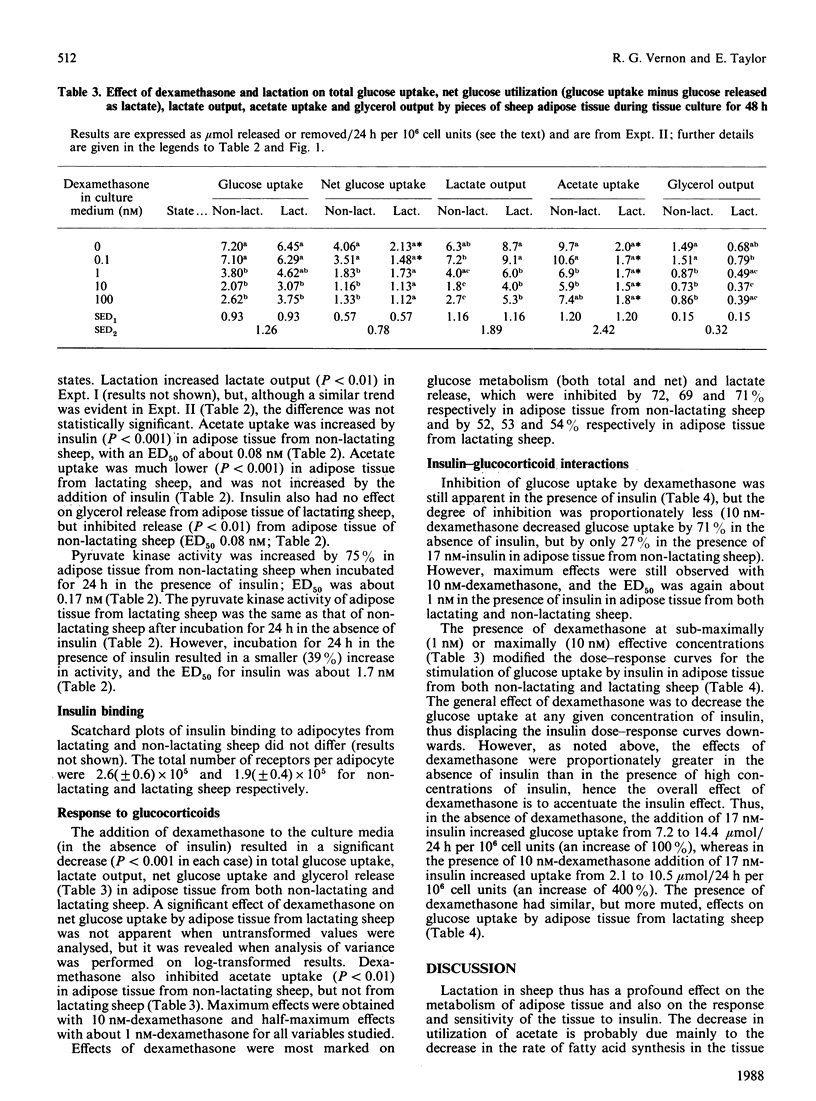
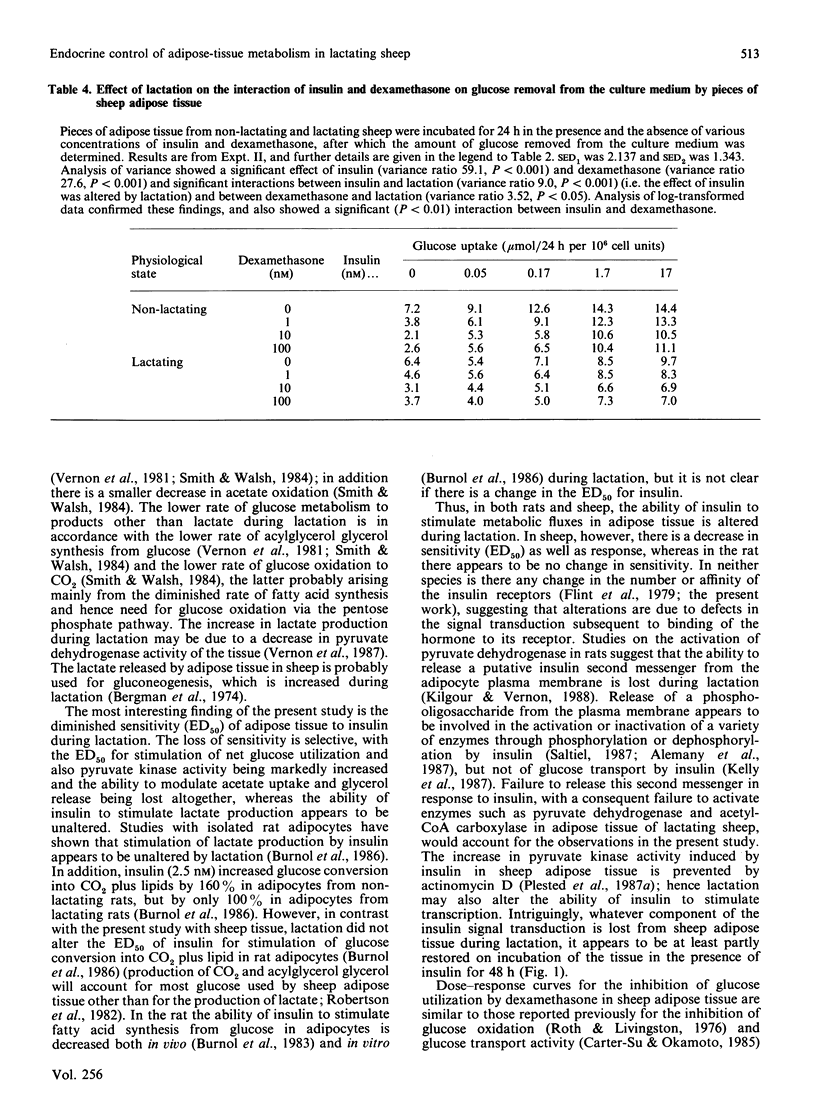
1. Lactation results in decreased glucose and acetate utilization and increased lactate output by sheep adipose tissue. 2. The ability of insulin to stimulate acetate uptake was lost in adipose tissue from lactating sheep, whereas both the response and the sensitivity (ED50) for insulin for stimulation of glucose conversion into products other than lactate were decreased. These impairments were partly restored by prolonged incubation of adipose tissue for 48 h. 3. The ability of insulin to stimulate lactate output was not altered by lactation. 4. Dexamethasone inhibited glucose uptake, lactate output and glycerol output in adipose tissue from both non-lactating and lactating sheep, with an ED50 of about 1 nM. Dexamethasone inhibited acetate uptake by adipose tissue from non-lactating sheep, but this effect was not observed with adipose tissue from lactating sheep. 5. Dexamethasone inhibited the stimulation of glucose uptake at all concentrations of insulin used; the effect varied with insulin concentration and resulted in an accentuation of the insulin dose-response curve. The insulin dose-response curve in the presence of dexamethasone was muted during lactation. 6. The overall effect of these adaptations is to ensure that glucose and acetate utilization by adipose tissue after an insulin surge is diminished during lactation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemany S., Mato J. M., Strålfors P. Phospho-dephospho-control by insulin is mimicked by a phospho-oligosaccharide in adipocytes. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):77–79. doi: 10.1038/330077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W., Kronfeld D. S. Gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis in tissue from ruminant and nonruminant animals. Fed Proc. 1969 Jan-Feb;28(1):218–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A. W. Lipid metabolism in liver and selected tissues and in the whole body of ruminant animals. Prog Lipid Res. 1979;18(3):117–164. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(79)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman E. N., Brockman R. P., Kaufman C. F. Glucose metabolism in ruminants: comparison of whole-body turnover with production by gut, liver, and kidneys. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1849–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman E. N., Hogue D. E. Glucose turnover and oxidation rates in lactating sheep. Am J Physiol. 1967 Dec;213(6):1378–1384. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.6.1378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Guerre-Millo M., Lavau M., Girard J. Effect of lactation on insulin sensitivity of glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Leturque A., Ferré P., Girard J. Glucose metabolism during lactation in the rat: quantitative and regulatory aspects. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):E351–E358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.4.E351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Okamoto K. Inhibition of hexose transport in adipocytes by dexamethasone: role of protein synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 1):E215–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.2.E215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Fain J. N. Antagonism of insulin action on glucose metabolism in white fat cells by dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1972 Aug;91(2):518–522. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-2-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherton T. D., Evock C. M. Stimulation of lipogenesis in bovine adipose tissue by insulin and insulin-like growth factor. J Anim Sci. 1986 Feb;62(2):357–362. doi: 10.2527/jas1986.622357x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint D. J., Sinnett-Smith P. A., Clegg R. A., Vernon R. G. Role of insulin receptors in the changing metabolism of adipose tissue during pregnancy and lactation in the rat. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 15;182(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1820421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Baird K., Van Obberghen E., Kahn C. R. Glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance in vitro: evidence for both receptor and postreceptor defects. Endocrinology. 1981 Nov;109(5):1723–1730. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-5-1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Mato J. M., Merida I., Jarett L. Glucose transport and antilipolysis are differentially regulated by the polar head group of an insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6404–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachadurian A. K., Adrouni B., Yacoubian H. Metabolism of adipose tissue in the fat tail of the sheep in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1966 May;7(3):427–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgour E., Vernon R. G. Defect in signal transduction at the level of the plasma membrane accounts for inability of insulin to activate pyruvate dehydrogenase in white adipocytes of lactating rats. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):667–672. doi: 10.1042/bj2520667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plested C. P., Taylor E., Brindley D. N., Vernon R. G. Interactions of insulin and dexamethasone in the control of pyruvate kinase activity and glucose metabolism in sheep adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):459–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2470459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. P., Faulkner A., Vernon R. G. Regulation of glycolysis and fatty acid synthesis from glucose in sheep adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):577–586. doi: 10.1042/bj2060577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. S., Livingston J. N. Reductions in glucocorticoid inhibition of glucose oxidation and presumptive glucocorticoid receptor content in rat adipocytes during aging. Endocrinology. 1976 Sep;99(3):831–839. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-3-831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R. Insulin generates an enzyme modulator from hepatic plasma membranes: regulation of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1987 Mar;120(3):967–972. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-3-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe P. M., Buttery P. J., Haynes N. B. The effect of manipulating growth in sheep by diet or anabolic agents on plasma cortisol and muscle glucocorticoid receptors. Br J Nutr. 1986 Jul;56(1):289–304. doi: 10.1079/bjn19860108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Walsh A. Effect of lactation on the metabolism of sheep adipose tissue. Res Vet Sci. 1984 Nov;37(3):320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Clegg R. A., Flint D. J. Metabolism of sheep adipose tissue during pregnancy and lactation. Adaptation and regulation. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 15;200(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2000307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Effects of growth hormone on fatty acid synthesis in sheep adipose tissue. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(4):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Faulkner A., Finley E., Pollock H., Taylor E. Enzymes of glucose and fatty acid metabolism of liver, kidney, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue and mammary gland of lactating and non-lactating sheep. J Anim Sci. 1987 May;64(5):1395–1411. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6451395x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Flint D. J. Control of fatty acid synthesis in lactation. Proc Nutr Soc. 1983 Jun;42(2):315–331. doi: 10.1079/pns19830035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Lipid metabolism in the adipose tissue of ruminant animals. Prog Lipid Res. 1980;19(1-2):23–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(80)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G. Metabolism of ovine adipose tissue in tissue culture. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorke R. E. The influence of dexamethasone on adipose tissue metabolism in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1967 Nov;39(3):329–343. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


