Abstract
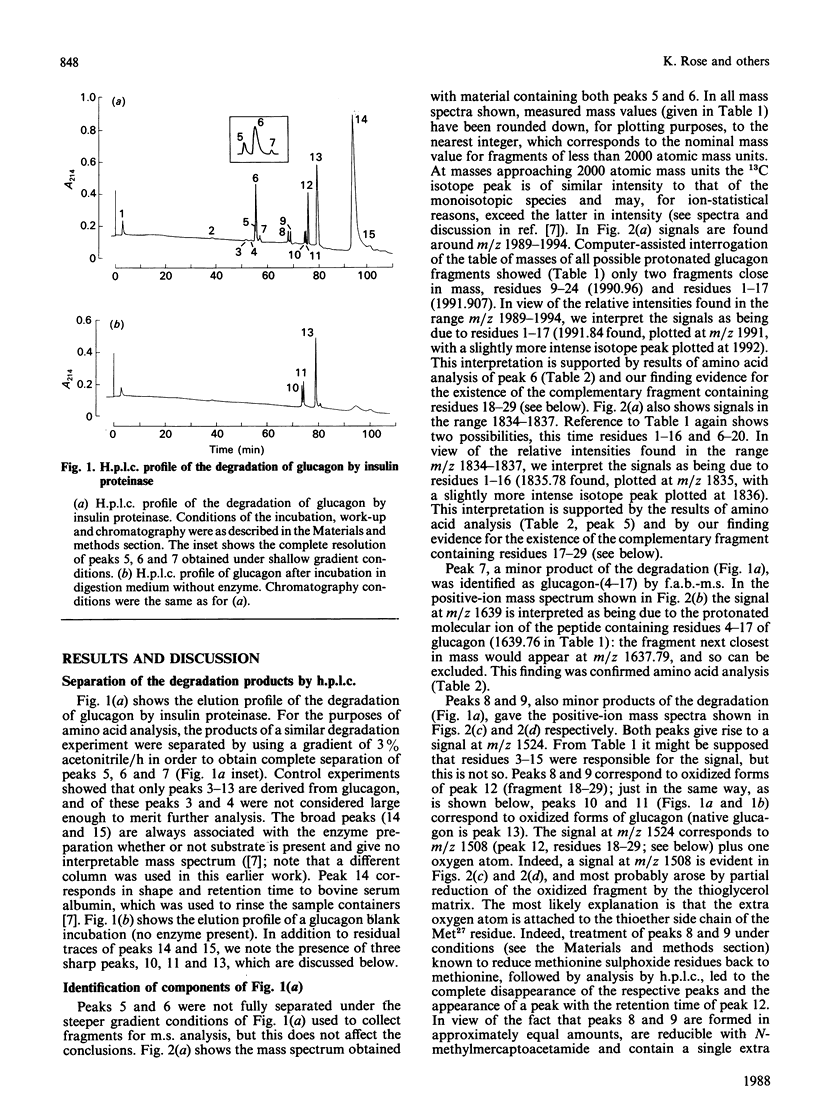
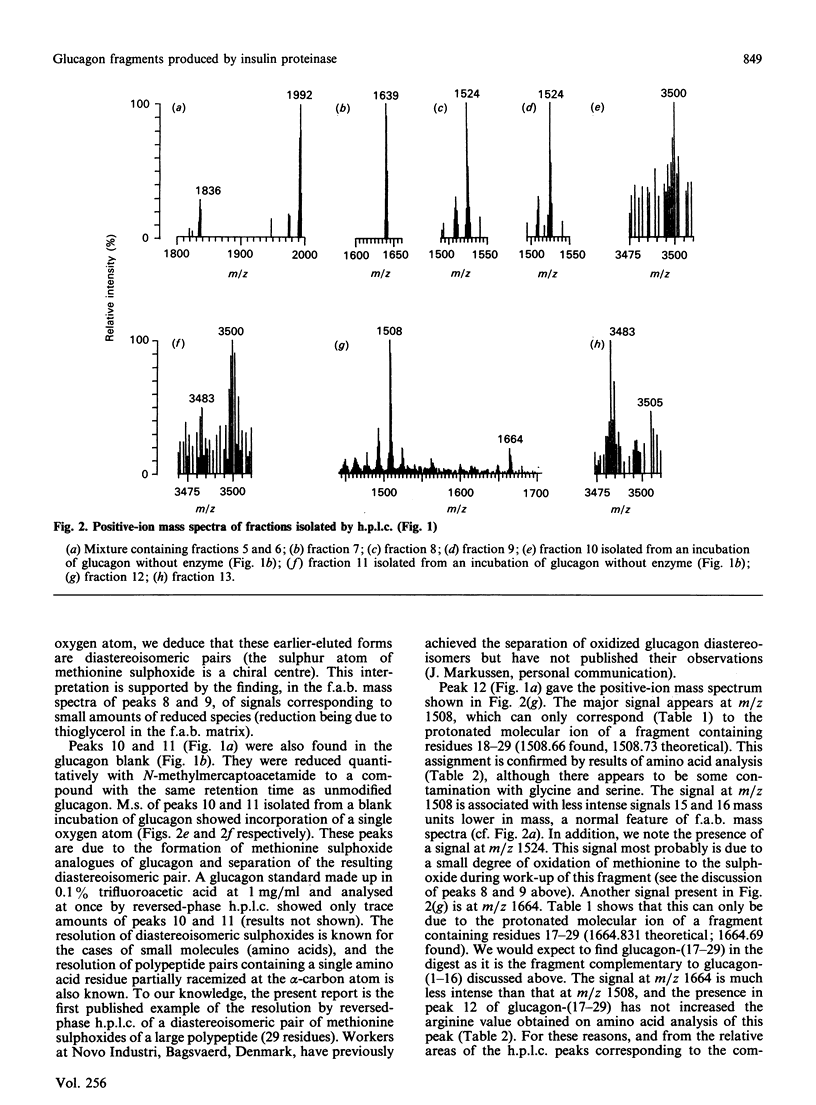
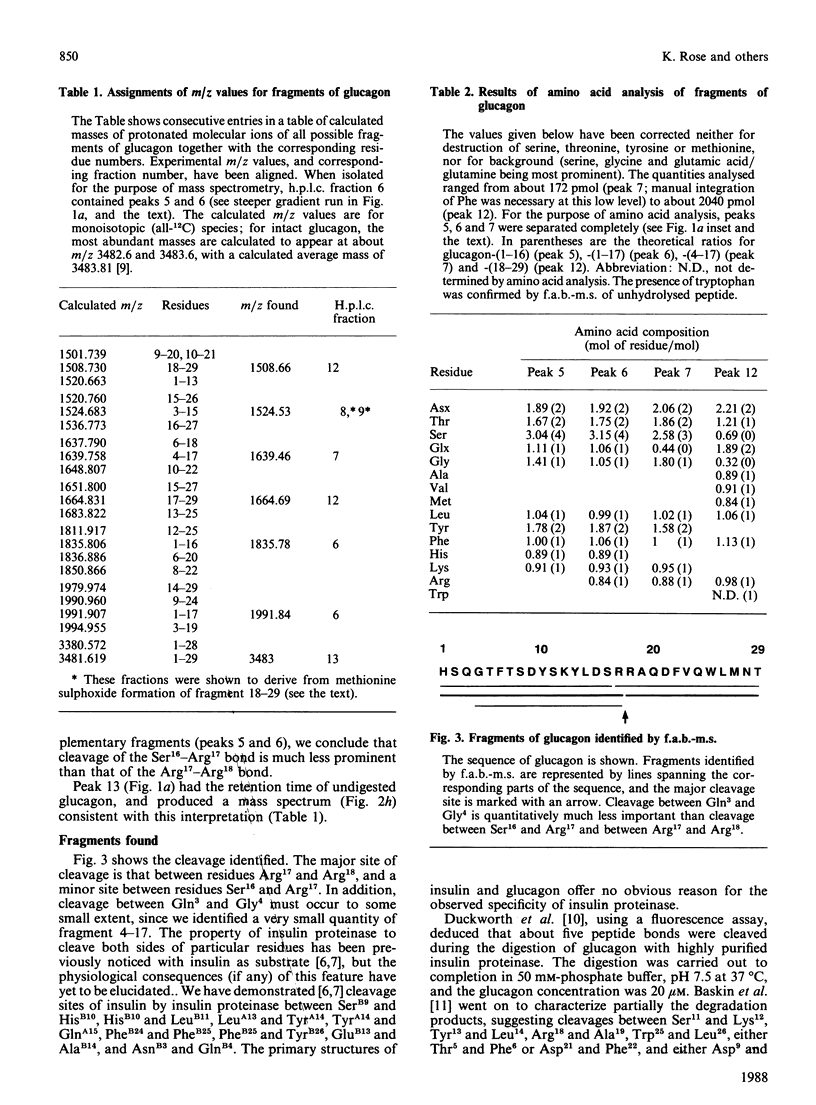
We find, contrary to previous reports, that substantial cleavage of glucagon by insulin proteinase occurs at only one region, namely the double-basic sequence -Arg17-Arg18-. Cleavage takes place almost exclusively between these two residues, liberating fragments glucagon-(1-17) and glucagon-(18-29). Others have shown that the fragment glucagon-(19-29) is 1000-fold more efficient compared with intact glucagon, at inhibiting the Ca2+-activated and Mg2+-dependent ATPase activity and the Ca2+ pump of liver plasma membranes. We show that this fragment is not liberated in detectable quantities by our insulin proteinase preparation. On the other hand, others have shown that glucagon-(18-29), though less active than glucagon-(19-29), was still 100-fold more active than glucagon itself in the above-mentioned system. Our observations represent the first demonstration of the release by insulin proteinase of a hormone fragment having enhanced activity, although it has yet to be shown that the activity of this fragment is important in vivo. Since the formation of glucagon-(19-29) from glucagon-(18-29) would involve merely removal of Arg18, a second enzyme might exist to provide the more active fragment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskin F. K., Duckworth W. C., Kitabchi A. E. Sites of cleavage of glucagon by insulin-glucagon protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90297-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Muir A. V., Offord R. E. Identification of some cleavage sites of insulin by insulin proteinase. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):609–612. doi: 10.1042/bj2400609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Muir A. V., Rose K., Offord R. E. Identification of radioactive insulin fragments liberated by insulin proteinase during the degradation of semisynthetic [3H]GlyA1]insulin and [3H]PheB1]insulin. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):209–214. doi: 10.1042/bj2490209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Heinemann M., Kitabchi A. E. Proteolytic degradation of insulin and glucagon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C., Kitabchi A. E. Insulin metabolism and degradation. Endocr Rev. 1981 Spring;2(2):210–233. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-2-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian W. A., Tager H. S. Hepatic glucagon metabolism. Correlation of hormone processing by isolated canine hepatocytes with glucagon metabolism in man and in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):409–417. doi: 10.1172/JCI112827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Shii K., Roth R. A. In vivo association of [125I]-insulin with a cytosolic insulin-degrading enzyme: detection by covalent cross-linking and immunoprecipitation with a monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):829–831. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Reduction of sulfoxides in peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:549–559. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallat A., Pavoine C., Dufour M., Lotersztajn S., Bataille D., Pecker F. A glucagon fragment is responsible for the inhibition of the liver Ca2+ pump by glucagon. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):620–622. doi: 10.1038/325620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K., Savoy L. A., Simona M. G., Offord R. E., Wingfield P. C-terminal peptide identification by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):253–259. doi: 10.1042/bj2500253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoy L. A., Jones R. M., Pochon S., Davies J. G., Muir A. V., Offord R. E., Rose K. Identification by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry of insulin fragments produced by insulin proteinase. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):215–222. doi: 10.1042/bj2490215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shroyer L. A., Varandani P. T. Purification and characterization of a rat liver cytosol neutral thiol peptidase that degrades glucagon, insulin, and isolated insulin A and B chains. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):205–219. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90620-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thein S. L., Jeffreys A. J., Gooi H. C., Cotter F., Flint J., O'Connor N. T., Weatherall D. J., Wainscoat J. S. Detection of somatic changes in human cancer DNA by DNA fingerprint analysis. Br J Cancer. 1987 Apr;55(4):353–356. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


