Abstract
To examine whether or not the activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase is coupled to the exocytosis of amylase from rat parotid cells, the effect of protein kinase inhibitors on amylase release and protein phosphorylation was studied. A membrane-permeable inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulphonamide (H-8), and peptide fragments of the heat-stable protein kinase inhibitor [PKI-(5-24)-peptide and PKI-(14-24)-amide] strongly inhibited cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity in the cell homogenate. However, H-8 had no inhibitory effect on amylase release from either intact or saponin-permeabilized parotid cells stimulated by isoproterenol or cyclic AMP. Moreover, PKI-(5-24)-peptide and PKI-(14-24)-amide did not inhibit cyclic AMP-evoked amylase release from saponin-permeabilized cells, whereas cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylations of 21 and 26 kDa proteins in intact or permeabilized cells were markedly inhibited by these inhibitors. These results suggest that cyclic AMP-dependent protein phosphorylation is not directly involved in the exocytosis of amylase regulated by cyclic AMP.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum B. J., Freiberg J. M., Ito H., Roth G. S., Filburn C. R. beta-Adrenergic regulation of protein phosphorylation and its relationship to exocrine secretion in dispersed rat parotid gland acinar cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9731–9736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher F. R., Putney J. W., Jr Regulation of parotid gland function by cyclic nucleotides and calcium. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;13:215–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. C., Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Smith A. J., Misconi L., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):989–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowd F. J., Watson E. L., Horio B., Lau Y. S., Park K. Phosphorylation of rabbit parotid microsomal protein occurs only with beta-adrenergic stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):281–288. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. D., Jamieson J. D. Hormone-induced protein phosphorylation. I. Relationship between secretagogue action and endogenous protein phosphorylation in intact cells from the exocrine pancreas and parotid. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):903–908. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gergely P., Bot G. The control of phosphorylase phosphatase by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. B., Masaracchia R. A., Feramisco J. R., Kemp B. E. Isolation of phosphorylated peptides and proteins on ion exchange papers. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):566–575. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90707-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Phosphorylated proteins as physiological effectors. Science. 1978 Jan 13;199(4325):146–152. doi: 10.1126/science.22932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Interaction of calmodulin with myosin light chain kinase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. Serotonin secretion from human platelets may be modified by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent myosin phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14321–14323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
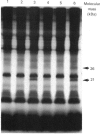
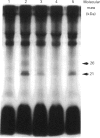
- Jahn R., Unger C., Söling H. D. Specific protein phosphorylation during stimulation of amylase secretion by beta-agonists or dibutyryl adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the rat parotid gland. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):345–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgensen S. R., Chock P. B., Taylor S., Vandenheede J. R., Merlevede W. Inhibition of the Mg(II).ATP-dependent phosphoprotein phosphatase by the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7565–7569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasuntheram P., Teo T. S. Does calmodulin mediate stimulus-secretion coupling in the parotid gland? Studies using trifluoperazine. Biochem Int. 1983 Oct;7(4):511–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatra B. S., Printz R., Cobb C. E., Corbin J. D. Regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits phosphoprotein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):567–573. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90454-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., DeCamilli P., Einig I., Walter U. High-affinity binding of the regulatory subunit (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase to microtubule-associated and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6723–6727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandol S. J., Schoeffield M. S. 1,2-Diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and pancreatic enzyme secretion. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4438–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quissell D. O., Deisher L. M., Barzen K. A. The rate-determining step in cAMP-mediated exocytosis in the rat parotid and submandibular glands appears to involve analogous 26-kDa integral membrane phosphoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3237–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata A., Ida E., Tominaga M., Onoue K. Calmodulin inhibitors, W-7 and TFP, block the calmodulin-independent activation of NADPH-oxidase by arachidonate in a cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. D., Fischer E. H., Takio K., Demaille J. G., Krebs E. G. Amino acid sequence of the heat-stable inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5732–5736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spearman T. N., Hurley K. P., Olivas R., Ulrich R. G., Butcher F. R. Subcellular location of stimulus-affected endogenous phosphoproteins in the rat parotid gland. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1354–1363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuma T., Ichida T. Amylase secretion from saponin-permeabilized parotid cells evoked by cyclic AMP. J Biochem. 1988 Jan;103(1):95–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuma T., Ichida T. Does cyclic AMP mobilize Ca2+ for amylase secretion from rat parotid cells? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 16;887(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojyo Y., Uchida M., Matsumoto Y. Inhibitory effects of calmodulin antagonists on isoproterenol- and dibutyryl cyclic AMP-stimulated amylase release from rat parotid acinar cells. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;45(4):487–491. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Takio K., Titani K., Steitz T. A. The cAMP-binding domains of the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the catabolite gene activator protein are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7679–7683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]