Abstract
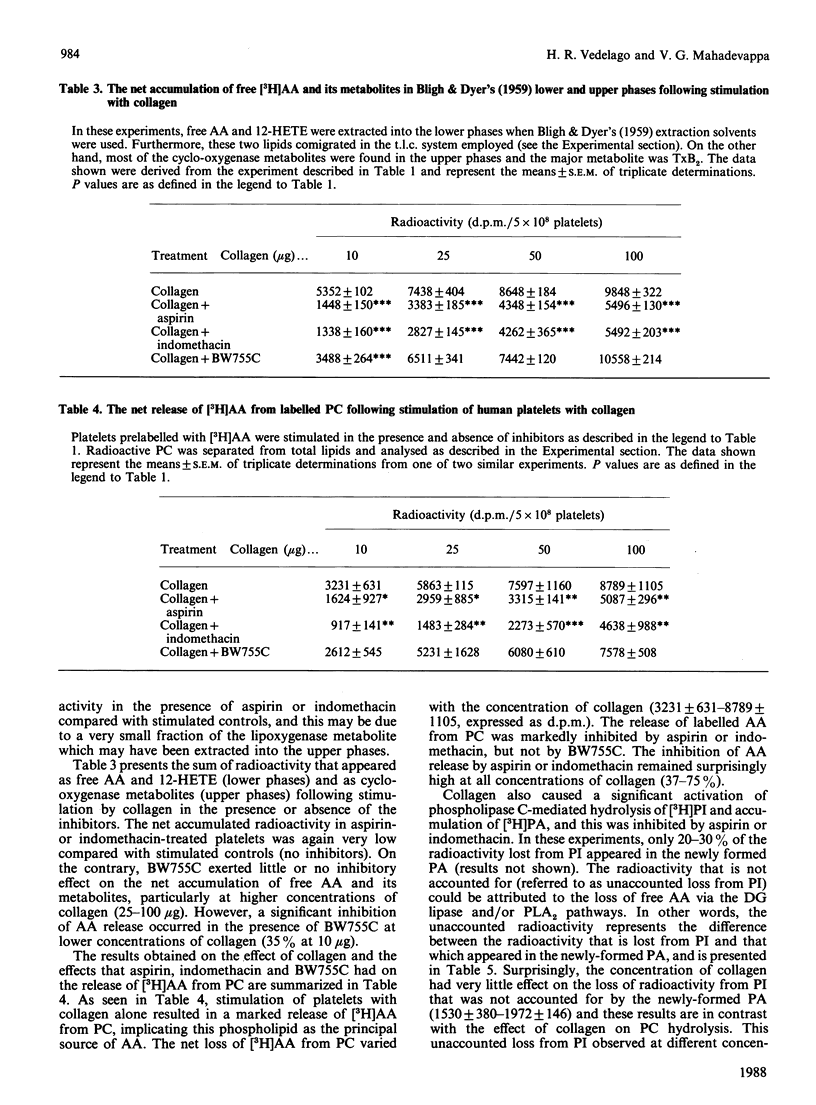
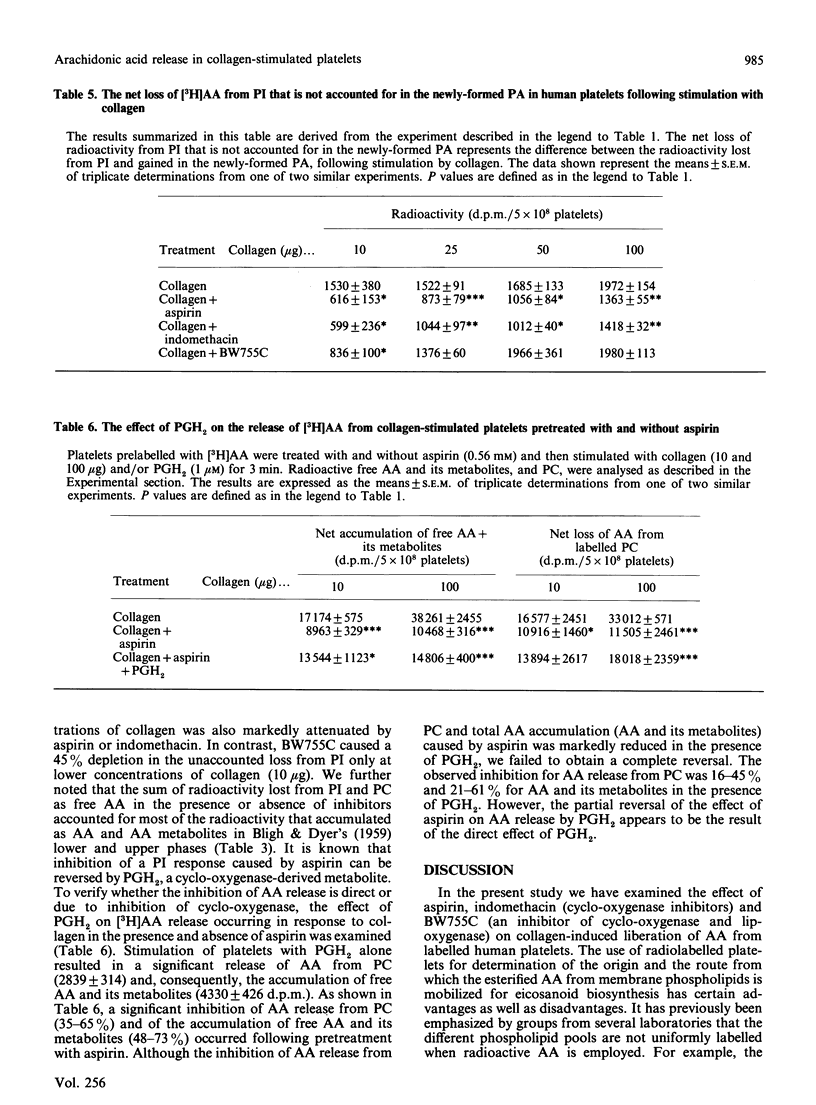
Stimulation of platelets with collagen results in the mobilization of arachidonic acid (AA) from phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylinositol (PI). In this study the effect of aspirin, indomethacin, BW755C and prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) on labelled AA release in response to varied concentrations of collagen was investigated. Our results indicate that aspirin (0.56 mM) and indomethacin (5.6 microM) not only inhibited the collagen-mediated formation of cyclo-oxygenase metabolites, but also caused a significant reduction in the accumulation of free labelled AA and 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) (21-64%). Aspirin and indomethacin also inhibited the release of [3H]AA from PC (37-75%) and PI (33-63%). The inhibition of AA release caused by aspirin was reversed partially by PGH2 (1 microM). In contrast, a smaller/no inhibition of collagen-stimulated labelled AA and 12-HETE accumulation (0-11%) and of collagen-stimulated AA loss from PC and PI was observed in the presence of BW755C. The results obtained in the presence of aspirin, indomethacin and BW755C at lower concentrations of collagen further demonstrate that AA release from PI (45-61% inhibition at 10 micrograms of collagen), but not from PC, was affected by the inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase. The results obtained on the effect of PGH2 further support that deacylation of phospholipids occurs independently of cyclo-oxygenase metabolites, particularly at higher concentrations of collagen. These results also demonstrate that aspirin and indomethacin, but not BW755C, cause a direct inhibition of collagen-induced [3H]AA liberation from PC as well as from PI. We also conclude that the diacylglycerol lipase pathway is a minor, but important, route for AA release from PI in collagen-stimulated human platelets. The mechanisms underlying the regulation of AA release by collagen in the absence of cyclo-oxygenase metabolites are not clear.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. R., Cheung W. Y. Inhibition of human platelet phospholipase A2 activity by unsaturated fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. R., DeWitt L. M., Cheung W. Y. Substrate-specific forms of human platelet phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3107–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 activity specific for phosphatidic acid. A possible mechanism for the production of arachidonic acid in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5399–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bills T. K., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Selective release of archidonic acid from the phospholipids of human platelets in response to thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Duncombe W. G., Flower R. J., Parsons M. F., Vane J. R. The distribution and metabolism of arachidonic acid in rabbit platelets during aggregation and its modification by drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):353–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Fruteau de Laclos B., Maclouf J. New concepts in the modulation of leukotriene synthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 1;32(3):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Blazek E., Kreft A. F., Lewis A. J. Inhibition of platelet and neutrophil phospholipase A2 by hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETES). A novel pharmacological mechanism for regulating free fatty acid release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 1;34(9):1571–1575. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guichardant M., Lagarde M. Effects of low doses of thrombin on human platelet phospholipids. Thromb Res. 1980 Apr 1;18(1-2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F. How is the level of free arachidonic acid controlled in mammalian cells? Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):3–16. doi: 10.1042/bj2040003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesse R. L., Franson R. C. Modulation of purified phospholipase A2 activity from human platelets by calcium and indomethacin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 18;575(3):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Low concentrations of indomethacin inhibit phospholipase A2 of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2955–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G., Holub B. J. Diacylglycerol lipase pathway is a minor source of released arachidonic acid in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1327–1333. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90395-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevappa V. G. Thrombin-induced transfer of arachidonic acid in human platelets is not inhibited by trifluoperazine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):821–828. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean M. L., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Formation of lysophosphatidylcholine by human platelets in response to thrombin. Support for the phospholipase A2 pathway for the liberation of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1522–1524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Perry D. W., Ardlie N. G., Packham M. A. Preparation of suspensions of washed platelets from humans. Br J Haematol. 1972 Feb;22(2):193–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb08800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Terawaki A., Arita H. Signal transduction in collagen-stimulated rat platelets is composed of three stages. J Biochem. 1987 May;101(5):1169–1180. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Armstrong R. A., Brydon L. J., Jones R. L., MacIntyre D. E. Thromboxane-induced phosphatidate formation in human platelets. Relationship to receptor occupancy and to changes in cytosolic free calcium. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):833–842. doi: 10.1042/bj2190833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Irvine R. F., Rink T. J. Free Ca2+ requirements of agonist-induced thromboxane A2 synthesis in human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 16;132(2-3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90622-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdon A. D., Smith J. B. Turnover of arachidonic acid in the major diacyl and ether phospholipids of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12700–12704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Russell R. A., Deykin D. Transfer of arachidonic acid to human platelet plasmalogen in response to thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Allen C. L. Synergistic activation by collagen and 15-hydroxy-9 alpha,11 alpha-peroxidoprosta-5,13-dienoic acid (PGH2) of phosphatidylinositol metabolism and arachidonic acid release in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1216–1224. doi: 10.1172/JCI110720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Flower R. J. Extraction and thin-layer chromatography of arachidonic acid metabolites. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:477–493. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sautebin L., Caruso D., Galli G., Paoletti R. Preferential utilization of endogenous arachidonate by cyclo-oxygenase in incubations of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamura H., Narita H., Park H. J., Tanaka K., Matsuura T., Kito M. Differential hydrolysis of phospholipid molecular species during activation of human platelets with thrombin and collagen. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2262–2269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedelago H. R., Mahadevappa V. G. Differential effects of 15-HPETE on arachidonic acid metabolism in collagen-stimulated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 15;150(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90502-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withnall M. T., Brown T. J., Diocee B. K. Calcium regulation of phospholipase A2 is independent of calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin stimulates human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


