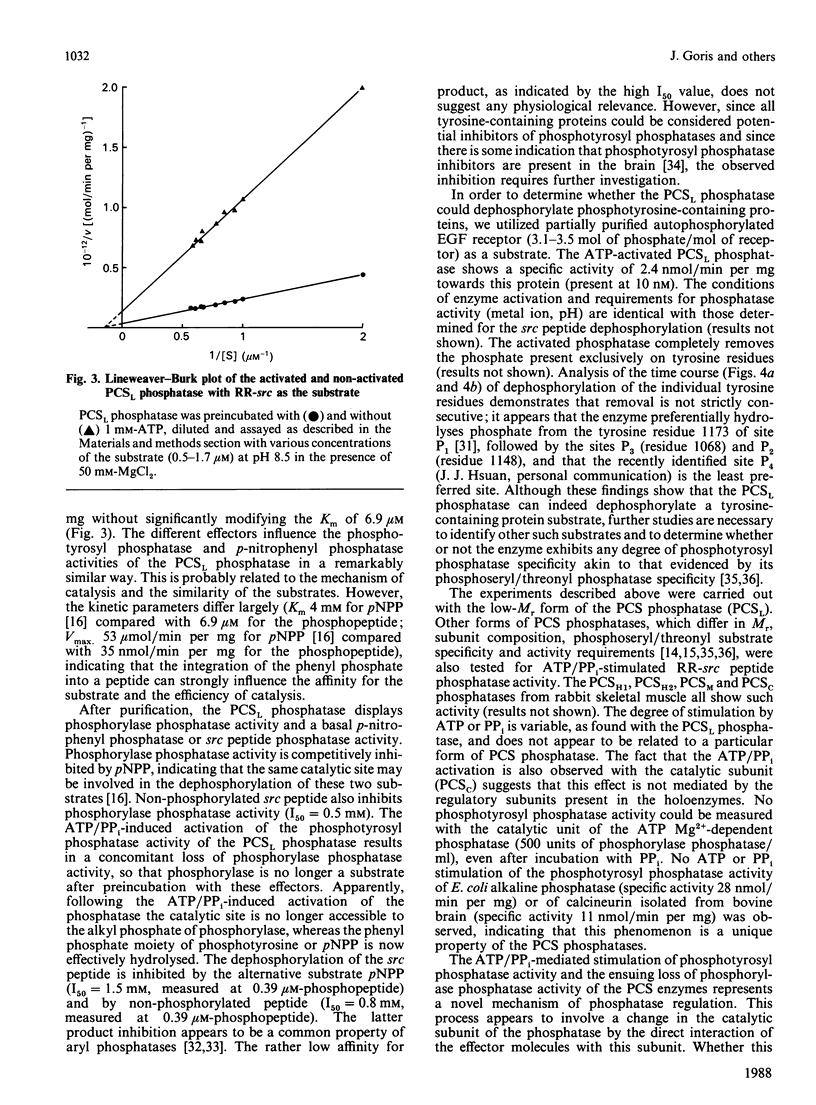
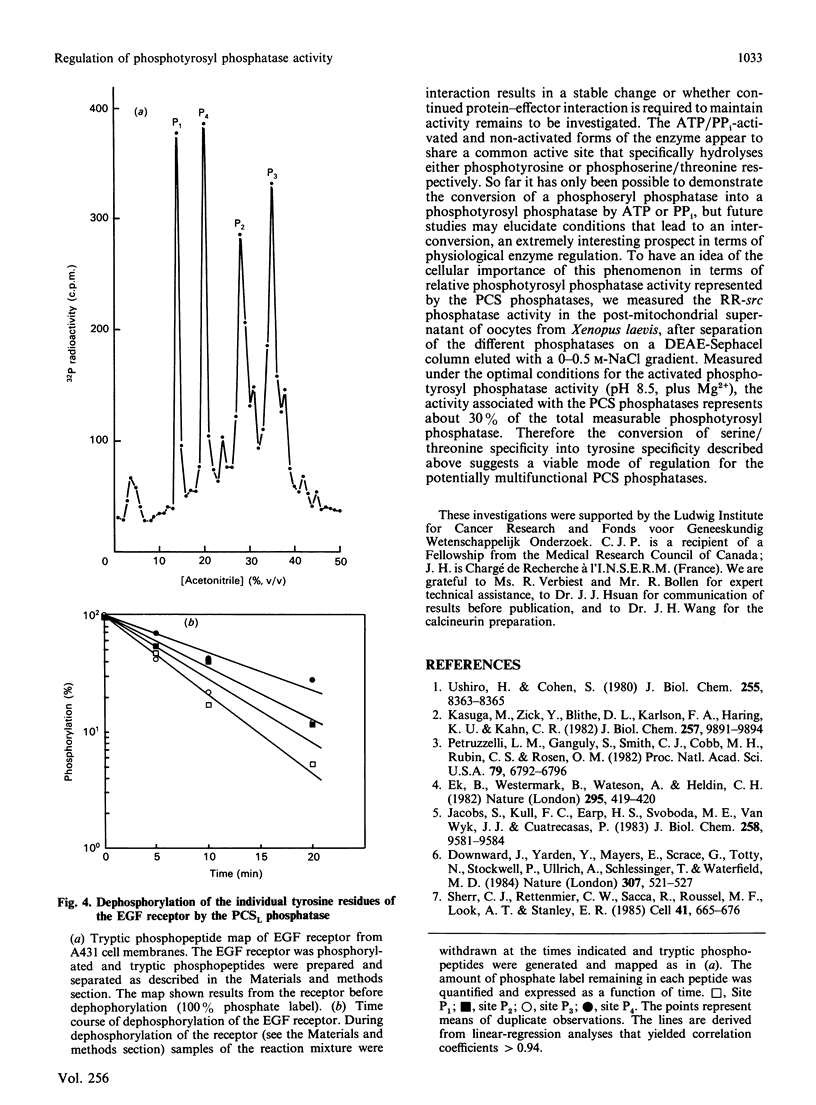
Abstract
By use of the autophosphorylated epidermal-growth-factor receptor and the synthetic peptide RRLIE-DAEY(P)AARG, representing an autophosphorylation site of the transforming protein of Rous-sarcoma virus, it is demonstrated that the phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity of the polycation-stimulated phosphatases is substantially increased by an enzyme-directed effect of ATP or PPi. Concomitant with this increase in phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity, the phosphorylase phosphatase activity is decreased, thus dramatically changing the substrate specificity of these enzymes. The dephosphorylation of four different phosphotyrosyl sites of the epidermal-growth-factor receptor is neither consecutive nor at random, but a preferred dephosphorylation of the P1 site over the P3 greater than P2 greater than P4 sites is observed. This phosphatase activity represents a substantial fraction of the total phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity in the post-mitochondrial supernatant of Xenopus laevis oocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agostinis P., Goris J., Waelkens E., Pinna L. A., Marchiori F., Merlevede W. Dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins and synthetic phosphopeptides. Study of the specificity of the polycation-stimulated and MgATP-dependent phosphorylase phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1060–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Li H. C., Cheng Y. S., Chen L. B. Characterization of a phosphotyrosyl protein phosphatase activity associated with a phosphoseryl protein phosphatase of Mr = 95,000 from bovine heart. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7852–7857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Separation of multiple phosphotyrosyl-and phosphoseryl-protein phosphatases from chicken brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Camps T., Merlevede W. Regulation of protein phosphatase activity by the deinhibitor protein. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:467–484. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W. Identification of the phosphatase deinhibitor protein phosphatases in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2390109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann J., Cayla X., Dumortier K., Goris J., Ozon R., Merlevede W. Modulation of the substrate specificity of the polycation-stimulated protein phosphatase from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):17–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., KENT A. B., FISCHER E. H. The muscle phosphorylase b kinase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blith D. L., Karlsson F. A., Häring H. U., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. Formation of both phosphoserine and phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9891–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C., Chan W. W. Co-purification of type I alkaline phosphatase and type I phosphoprotein phosphatase from various animal tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):270–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C., Hsiao K. J., Sampathkumar S. Characterization of a novel alkaline phosphatase activity which co-purifies with a phosphorylase (phosphoprotein) phosphatase of Mr = 35,000 cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3368–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C. Purification and properties of a phosphorylase (phosphoprotein) phosphatase associated with an alkaline phosphatase of Mr 35000 from bovine adrenal cortex. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec 17;102(2):363–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Activation of calcineurin by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4291–4295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. L., Graves D. J. Mechanistic aspects of the low-molecular-weight phosphatase activity of the calmodulin-activated phosphatase, calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14545–14550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Vandenheede J. R., Goris J., Yang S. D. Regulation of ATP-Mg-dependent protein phosphatase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:177–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L. M., Ganguly S., Smith C. J., Cobb M. H., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin activates a tyrosine-specific protein kinase in extracts of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6792–6796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran C., Goris J., Waelkens E., Merlevede W., Walsh D. A. The interrelationship between cAMP-dependent alpha and beta subunit phosphorylation in the regulation of phosphorylase kinase activity. Studies using subunit specific phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3210–3218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Taylor W. A., Wang J. H. Use of calmodulin affinity chromatography for purification of specific calmodulin-dependent enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:210–219. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberman S. R., Speth M., Nemani R., Ganapathi M. K., Dombradi V., Paris H., Lee E. Y. Isolation and characterization of rabbit skeletal muscle protein phosphatases C-I and C-II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):2913–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Heffernan P. A., Weinberg R. A. p185, a product of the neu proto-oncogene, is a receptorlike protein associated with tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1729–1740. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Lloyd C. W., Rees D. A. Rapid isolation of plasma membranes in high yield from cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):187–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Agostinis P., Goris J., Merlevede W. The polycation-stimulated protein phosphatases: regulation and specificity. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1987;26:241–270. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(87)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Goris J., Merlevede W. Purification and properties of polycation-stimulated phosphorylase phosphatases from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


