Abstract
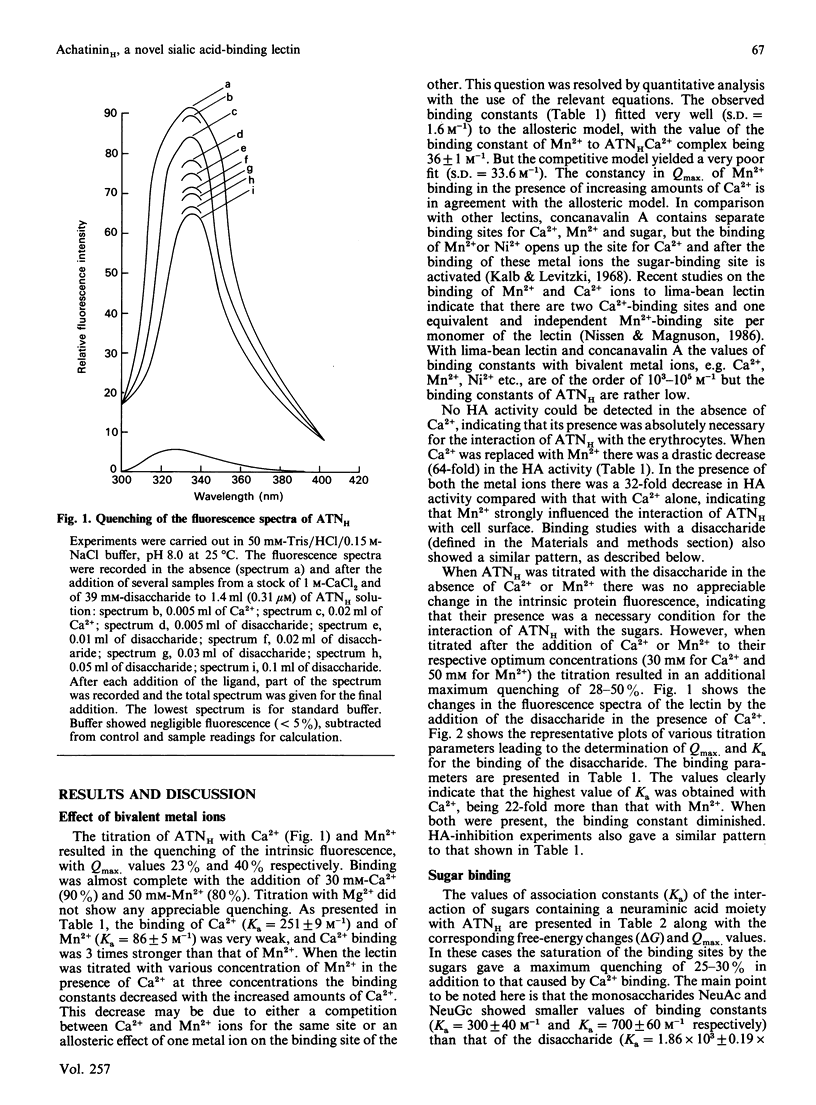
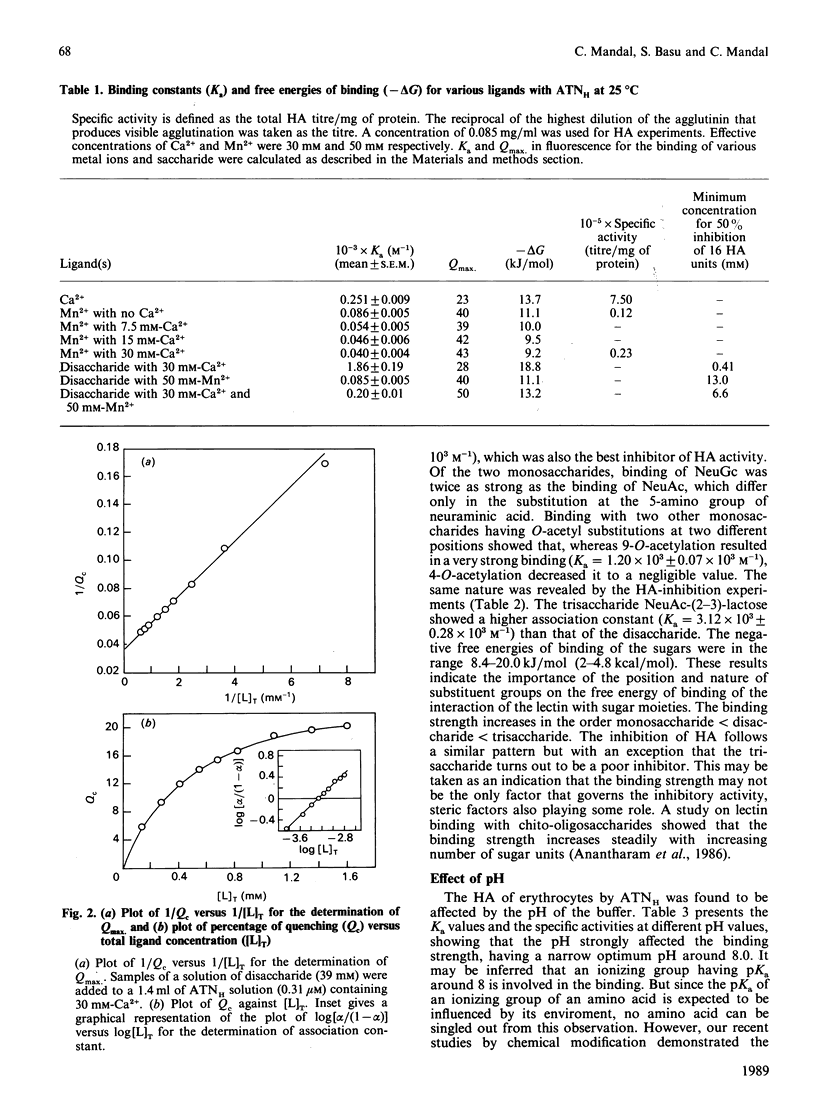
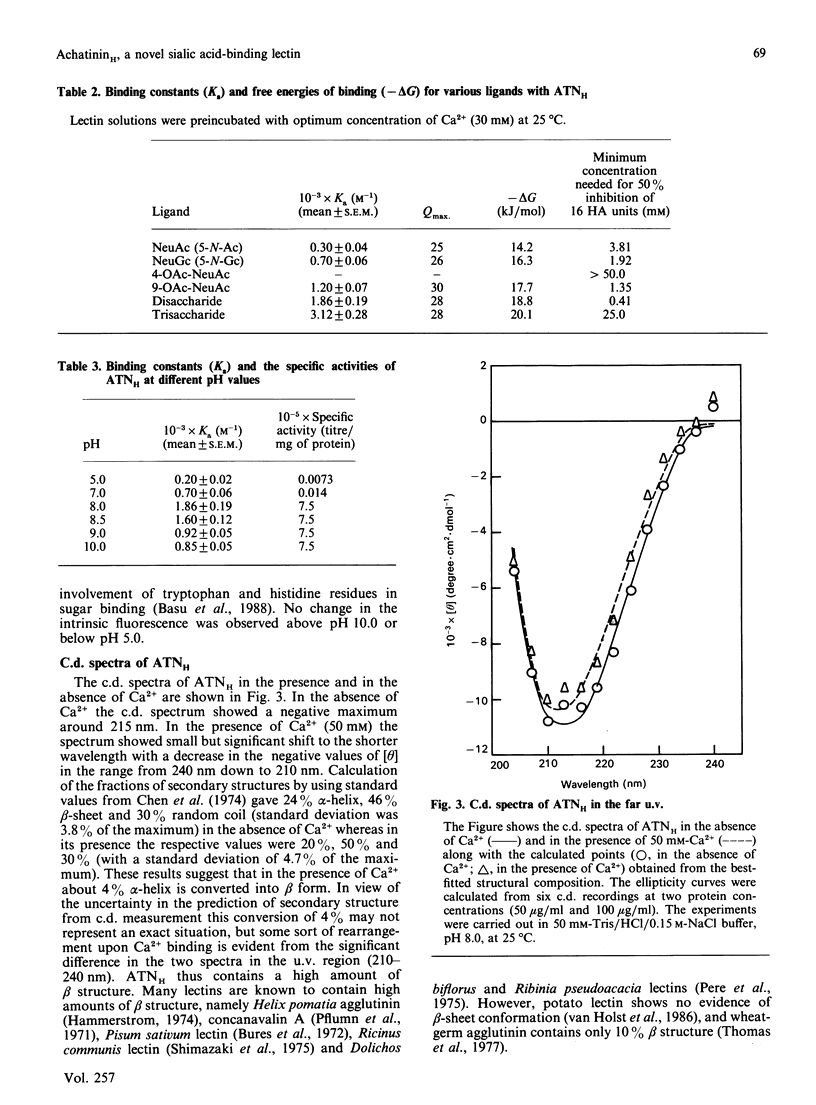
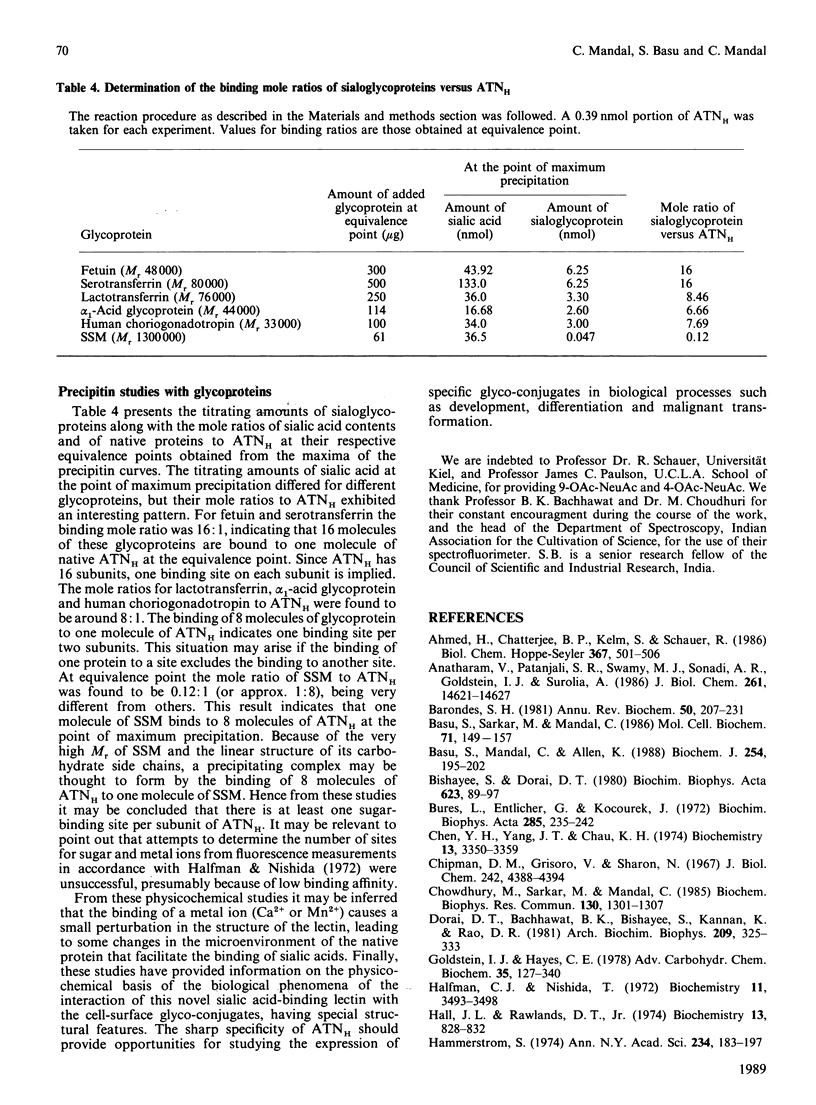
We have purified a sialic acid-binding lectin, achatininH, in a single step by affinity chromatography, having high affinity for 9-O-acetylneuraminic acid. The physicochemical characterization of the interaction of achatininH with bivalent metal ions and sialic acid derivatives by the use of spectrofluorimetry, spectropolarimetry and precipitin reaction is reported. From fluorescence quenching studies the binding of Ca2+ (Ka = 251 +/- 9 M-1) and of Mn2+ (Ka = 86 +/- 5 M-1) was found to be weak, but their presence is absolutely necessary for sugar binding as well as biological activity. The nature and position of the substituent group play a very important role in the binding affinity. AchatininH shows a high affinity for 9-O-acetylneuraminic acid (Ka = 1.20 x 10(3) +/- 0.07 x 10(3) M-1) compared with that for the 4-O-acetyl derivative. In oligomers the binding strength increases in the order monosaccharide less than disaccharide less than trisaccharide. The binding affinity of achatininH for the disaccharide was found to reach a peak around pH 8. From c.d. spectral studies achatininH was found to have a high beta-sheet content (46%) and a low alpha-helix content (24%). From precipitin analysis at least one sugar-binding site on each of the 16 monomer subunits of the protein is indicated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed H., Chatterjee B. P., Kelm S., Schauer R. Purification of a sialic acid-specific lectin from the Indian scorpion Heterometrus granulomanus. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jun;367(6):501–506. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.1.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharam V., Patanjali S. R., Swamy M. J., Sanadi A. R., Goldstein I. J., Surolia A. Isolation, macromolecular properties, and combining site of a chito-oligosaccharide-specific lectin from the exudate of ridge gourd (Luffa acutangula). J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14621–14627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H. Lectins: their multiple endogenous cellular functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:207–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S., Mandal C., Allen A. K. Chemical-modification studies of a unique sialic acid-binding lectin from the snail Achatina fulica. Involvement of tryptophan and histidine residues in biological activity. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):195–202. doi: 10.1042/bj2540195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S., Sarkar M., Mandal C. A single step purification of a sialic acid binding lectin (AchatininH) from Achatina fulica snail. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 Aug;71(2):149–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00214774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishayee S., Dorai D. T. Isolation and characterisation of a sialic acid-binding lectin (carcinoscorpin) from Indian horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotunda cauda. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 29;623(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bures L., Entlicher G., Kocourek J. Studies on phytohemagglutinins. XL. Importance of tryptophan residues for the activity of pea phytohemagglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):235–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipman D. M., Grisaro V., Sharon N. The binding of oligosaccharides containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid to lysozyme. The specificity of binding subsites. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4388–4394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M., Sarkar M., Mandal C. Identification and isolation of an agglutinin from uterus of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1301–1307. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91756-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorai D. T., Bachhawat B. K., Bishayee S., Kannan K., Rao D. R. Further characterization of the sialic acid-binding lectin from the horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotunda cauda. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jun;209(1):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. J., Hayes C. E. The lectins: carbohydrate-binding proteins of plants and animals. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1978;35:127–340. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfman C. J., Nishida T. Method for measuring the binding of small molecules to proteins from binding-induced alterations of physical-chemical properties. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3493–3498. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. L., Rowlands D. T., Jr Heterogeneity of lobster agglutinins. II. Specificity of agglutinin-erythrocyte binding. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):828–832. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S. Structure, specificity, binding properties, and some biological activities of a blood group A-reactive hemagglutinin from the snail Helix pomatia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;234(0):183–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb53031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkamp J., Veh R. W., Sander M., Schauer R., Kamerling J. P., Vliegenthart J. G. Demonstration of 9-O-acetyl-N-acetylneuraminic acid in brain gangliosides from various vertebrates including man. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Dec;358(12):1609–1612. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.2.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. Metal-binding sites of concanavalin A and their role in the binding of alpha-methyl d-glucopyranoside. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1090669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis H., Sharon N. Lectins as molecules and as tools. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:35–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY W. H., GOTTSCHALK A. Studies on mucoproteins. VII. The linkage of the prosthetic group to aspartic and glutamic acid residues in bovine submaxillary gland mucoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:349–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal C., Basu S. An unique specificity of a sialic acid binding lectin AchatininH, from the hemolymph of Achatina fulica snail. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):795–801. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90946-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal C., Karush F. Restriction in IgM expression. III. Affinity analysis of monoclonal anti-lactose antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1240–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchialonis J. J., Edelman G. M. Isolation and characterization of a hemagglutinin from Limulus polyphemus. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):453–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Collawn J. F., Jr, Fish W. W. Purification and macromolecular properties of a sialic acid-specific lectin from the slug Limax flavus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7574–7580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Magnuson J. A. Metal ion binding to tetrameric lima bean lectin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2514–2519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Katchalski E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by concanavalin A and its reversion by methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pflumm M. N., Wang J. L., Edelman G. M. Conformational changes in concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4369–4370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Père M., Bourrillon R., Jirgensons B. Circular dichroism and conformational transition of Dolichos biflorus and Robinia pseudoacacia lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravindranath M. H., Higa H. H., Cooper E. L., Paulson J. C. Purification and characterization of an O-acetylsialic acid-specific lectin from a marine crab Cancer antennarius. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8850–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar M., Bachhawat B. K., Mandal C. A new cold agglutinin from Achatina fulica snails. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 15;233(1):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90627-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Chemistry, metabolism, and biological functions of sialic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1982;40:131–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki K., Walborg E. F., Jr, Neri G., Jirgensons B. Circular dichroism and saccharide-induced conformational transitions of lectins from Ricinus communis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90218-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. W., Walborg E. F., Jr, Jirgensons B. Circular dichroism and saccharide-induced conformational transitions of wheat germ agglutinin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Kornfeld S. An autosomal dominant gene regulates the extent of 9-O-acetylation of murine erythrocyte sialic acids. A probable explanation for the variation in capacity to activate the human alternate complement pathway. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):532–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Holst G. J., Martin S. R., Allen A. K., Ashford D., Desai N. N., Neuberger A. Protein conformation of potato (Solanum tuberosum) lectin determined by circular dichroism. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2330731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


